What are the three processes of cellular respiration?
- stage 1. glycolysis.
- stage 2. citric acid cycle/krebs cycle.
- stage 3. oxidative phosphorylation.
- oxidative phosphorylation consists of.. ETC and chemiosmosis to produce ATP.
- occurs in cytoplasm. glycolysis.
- anaerobic portion.
- breaks down glucose to 2 molecules pyruvate.
- occurs in mitochondrial matrix.
What are the 3 steps in order of cellular respiration?
what are the three steps of aerobic cellular respiration
- Cellular Respiration (UPDATED)
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis, Prep Steps
- Stages of cellular respiration
- Cellular Respiration Steps and Pathways
What is the first step in cellular respiration?
What stages of cellular respiration occur in the mitochondria quizlet?
- st- Glycolosis. Splitting sugars in cytoplasm, energy investment phase -> 2 ATP molecules combine with glucose molecule.
- nd- Oxidation. Pyruvates moving into mitochondria, through oxidation pyruvates broken into water.
- rd- Krebs Cycle/Citric Acid Cycle. …
- th- Electron Transport Chain.
What is cellular respiration and why is it important?
In its most basic sense, cellular respiration is a number of different metabolic processes and reactions that happen in cells. Cellular respiration is essential in creating biochemical energy by converting different kinds of nutrients into adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, all the while flushing out waste products.

What does cellular respiration start with and end with?
Products of Cellular Respiration The biochemical processes of cellular respiration can be reviewed to summarise the final products at each stage. During glycolysis, the initial reactants are glucose and 2 molecules of ATP, resulting in the end products of pyruvate, ATP, and NADH.
What is cellular respiration in order?
The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What are the 3 steps of cellular respiration?
Summary: the three stages of Aerobic Respiration Carbohydrates are broken down using all three stages of respiration (glycolysis, citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain).
What are the 4 steps of respiration?
There are four stages: glycolysis, the link reaction, the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. During glycolysis, glucose molecules (six-carbon molecules) are split into two pyruvates (three-carbon molecules) during a sequence of enzyme-controlled reactions. This occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
What is the correct sequence of steps in cellular respiration starting with glucose?
What is the correct sequence of steps in cellular respiration, starting with glucose? Glycolysis, pyruvate processing, citric acid cycle, electron transport, oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the correct order of the stages of cellular respiration quizlet?
The reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, and electron transport.
What is the starting material of the second stage of cellular respiration?
The second stage of cellular respiration is the transfer of the energy in pyruvate, which is the energy initially in glucose, into two energy carriers, NADH and FADH2. A small amount of ATP is also made during this process.
What are the 3 steps of cellular respiration and where does each occur?
Cellular respiration is the process in which cells break down glucose, release the stored energy, and use it to make ATP. The process begins in the cytoplasm and is completed in a mitochondrion. Cellular respiration occurs in three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport.
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an organic compound the body can use for ene...
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for...
What are the main steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where o...
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA...
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage, but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide deriv...
What are the products of cellular respiration?
The final end products of cellular respiration are ATP and H2O. Glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, four ATPs (a net of two ATP), two NADH,...
What are the rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration?
There are three primary rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration. These enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting steps, which are the slowest rea...
What diseases can affect cellular respiration?
Several diseases can affect cellular respiration. Since cellular respiration is so vital to bodily functions, many of these diseases severely affec...
What are the most important facts to know about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions...
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Where does cellular respiration happen?
Cellular Respiration happens in your cells and you entire body is made up of cells, it goes on all throughout your body including your lungs and brain. Comment on DonaShae's post “Cellular Respiration happ...”. Button opens signup modal.
What is the cycle of carbon dioxide and NADH?
Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Citric acid cycle. The acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule. ATP (or, in some cases, GTP), NADH, and FADH_2 are made, and carbon dioxide is released.
How do protons flow back into the matrix?
The protons flow back into the matrix through an enzyme called ATP synthase, making ATP. At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water.
How is ATP produced?
Oxidative phosphorylation is powered by the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain , a series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
What is the process of converting glucose into pyruvate?
Glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose—a six-carbon sugar—undergoes a series of chemical transformations. In the end, it gets converted into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon organic molecule. In these reactions, ATP is made, and is converted to . Pyruvate oxidation.
Which three stages of cellular respiration require oxygen?
The other three stages of cellular respiration—pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation— require oxygen in order to occur. Only oxidative phosphorylation uses oxygen directly, but the other two stages can't run without oxidative phosphorylation. Each stage of cellular respiration is covered in more detail in other ...
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process by which our bodies harvest the energy stored in food. It is how we get energy at the cellular level that allows our organs and tissues to function. Glycolysis is the first pathway in cellular respiration.
How many ATPs does cellular respiration produce?
Each pathway in cellular respiration produces ATP. Glycolysis specifically generates 4 ATP, but has a net gain of 2 ATP. There is another energy metabolite, NADH, that is also generated but to a lesser extent. For this lesson we will focus more on ATP.
What are the steps of glycolysis?
The first four steps in glycolysis involve the preparation of glucose into a molecule that's easily split in half: glucose 1,6-bisphosphate. Glucose 1,6-bisphosphate is split into two molecules of glucose 3 phosphate or G3P. G3P continues to change and winds up as pyruvate. Remember, glycolysis generates two pyruvate molecules.
How many steps are involved in glycolysis?
Glycolysis is a 10-step process, but it begins with one molecule of glucose, a 6-carbon molecule and results in two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules. The conversion creates energy in the form of ATP, or adenosine triphosphate.
How many steps does glycolysis take?
Glycolysis occurs in a series of ten unique and distinct steps, each step being catalyzed by a specific enzyme, a protein that speeds up a chemical reaction and essentially allows it to occur. More generally, glycolysis can be broken down into three stages:
How many ATPs are generated during glycolysis?
During glycolysis, 4 ATP and 2 NADPH are generated, and since 2 ATP are used during the process the net gain is 2 ATP. Glycolysis is unique in that it does not need oxygen in order to occur. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
What is the chemical composition of glucose?
The chemical composition of glucose is C6H12O6. While you don't need to go and study chemistry and understand the chemical bonds involved in glucose, you do need to understand (and know!) that glucose is a 6-carbon molecule. It has six carbons, or six Cs, for all intents and purposes. So, sugar=glucose. Let's move on.
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
While most aerobic respiration (with oxygen) takes place in the cell's mitochondria, and anaerobic respiration (without oxygen) takes place within the cell's cytoplasm. Loading PDF ... (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy.
What is the process by which food, in the form of sugar (glucose), is transformed into energy within
Cellular Respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which food, in the form of sugar (glucose), is transformed into energy within cells. Grades.
What are the organelles of plants?
Some of the major organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus. Plant cells also include chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis. Use these classroom resources to examine how cells function with your students. View Collection.
What is the definition of ATP?
Adjective. living, active, or occurring in the presence of free oxygen. anaerobic. Adjective. living, active, or occurring in the absence of free oxygen. ATP. Noun. (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy. cellular respiration.
Where is the mitochondria located?
mitochondria. Plural Noun. (singular: mitochondrion) structure (organelle) in the cytoplasm of most cells in which nutrients (sugars, fatty acids, and amino acids) are broken down in the presence of oxygen and converted to energy in the form of ATP. molecule.
What is the definition of fermentation?
Adjective. relating to organisms whose cells have a nuceleus. fermentation. Noun. natural or artificial process of changing a food's sugars into alcohols. glycolysis. Noun. breakdown of a carbohydrate (such as glucose) using enzymes, resulting in the release of energy. habitat.
What happens during cellular respiration?
During cellular respiration, catabolic reactions occur, which is the process wherein large molecules are broken down. As nutrients like fatty acids, aminos, and sugars are broken down into ATP, their molecules release a large amount of biochemical energy.
Why is cellular respiration important?
Cellular respiration is essential in creating biochemical energy by converting different kinds of nutrients into adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, ...
What are the metabolic pathways of cellular respiration?
Other metabolic pathways of cellular respiration include oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate (which is when pyruvates are oxidized to acetyl-CoA and CO2) , Citric Acid Cycle (also known as the Kreb Cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation, with the latter producing water as a was te product.
What are the two types of respiration?
There are 2 kinds of reactions in Cellular Respiration: Aerobic Respiration. Anaerobic respiration. Aerobic Respiration is when the biological fuels (i.e., nutrients) are oxidized. In this case, it happens in the presence of an inorganic electron receptor (i.e. oxygen).
What is the process of ATP?
Instead, it ferments. Fermentation is another biochemical process wherein energy is extracted from carbohydrates. Fermentation is the primary way for microorganisms like eukaryotes and bacteria to produce ATP. In higher organisms like mammals, fermentation usually occurs during strenuous activities like exercise.
Is cellular respiration a combustion reaction?
Although cellular respiration can be classified as a combustion reaction (thanks to its release of energy in the form of heat), because it occurs inside of cells, the energy is released in slow bursts, and only after a series of reactions and processes. As cellular respiration occurs, it produces CO2, carbon dioxide, as a waste product.
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
The purpose of cellular respiration is simple: it provides cells with the energy they need to function. If living things could not get the energy they need out of food, it would be absolutely worthless. All living things would eventually die, no matter the quality and amount of food. Cellular respiration is used to create usable energy from ...
What is the process of respiration?
It involves the processes by which energy (at the cellular level) is provided to the bodies of living things. Cellular respiration involves catabolic reaction in order to break down food into usable energy so that cells, and the living organisms that contain them, can survive and thrive.
What is anabolic reaction?
Anabolic reactions are characterized by the release of energy and breakdown of molecules. True | False. 2. Cellular respiration is a process that converts chemical energy from oxygen molecules to ADP. True | False. 3. In the Krebs cycle, pyruvate transforms into metabolites that generate ATP. True | False.
What is the role of cellular respiration in the catabolic reaction?
Key point: Cellular respiration involves catabolic reaction in order to break down food into usable energy so that cells , and the living organisms that contain them, can survive and thrive. 3:42. You must c C reate an account to continue watching. Register to view this lesson.
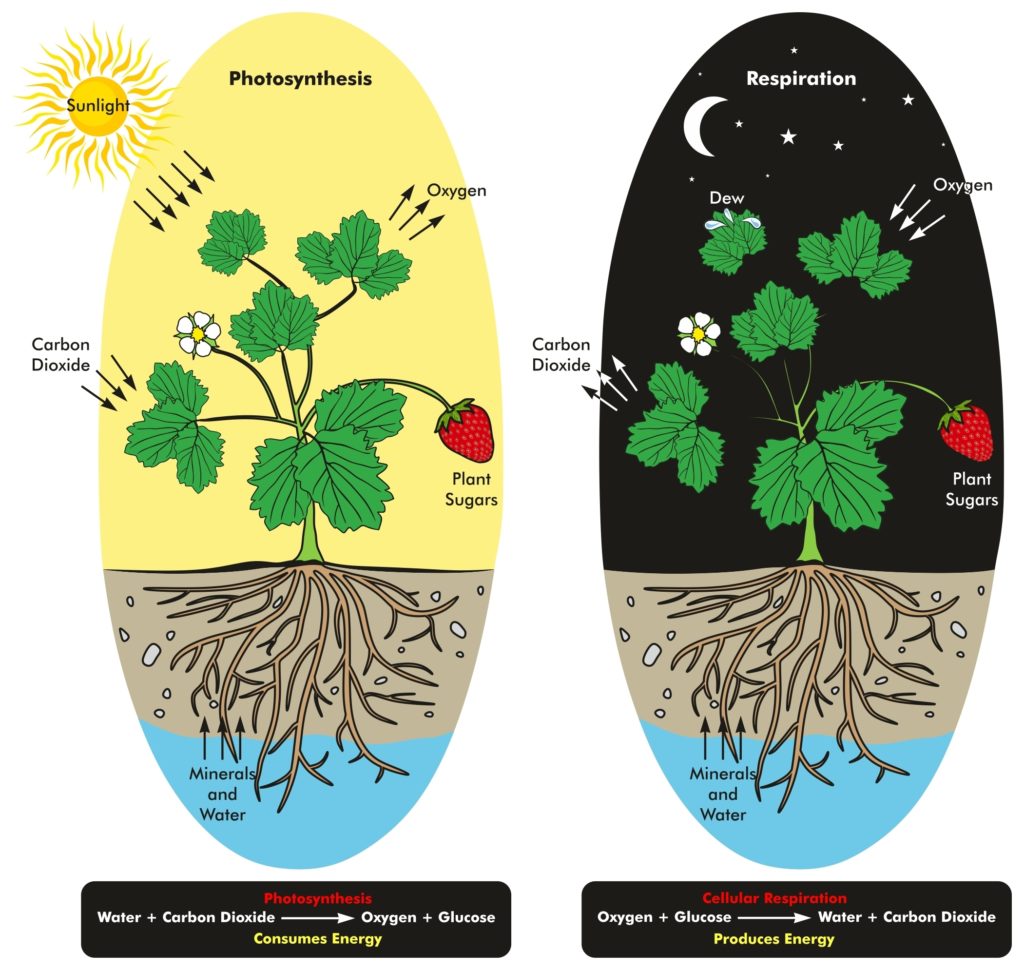
How do cellular respiration and photosynthesis work?
Both cellular respiration and photosynthesis work with the same intermediates and each uses the other's end result as starting points for their own processes, thereby creating a cycle. The cycle of cellular respiration and photosnthesis.
Why is cellular respiration important?
Cellular respiration is used to create usable energy from the foods that living things eat. It's important to know that the reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic, meaning they break down molecules into smaller ones.
What is the name of the molecule that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic molecule that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells. True | False. 10. Gluconeogenesis is the cellular degradation of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvate.