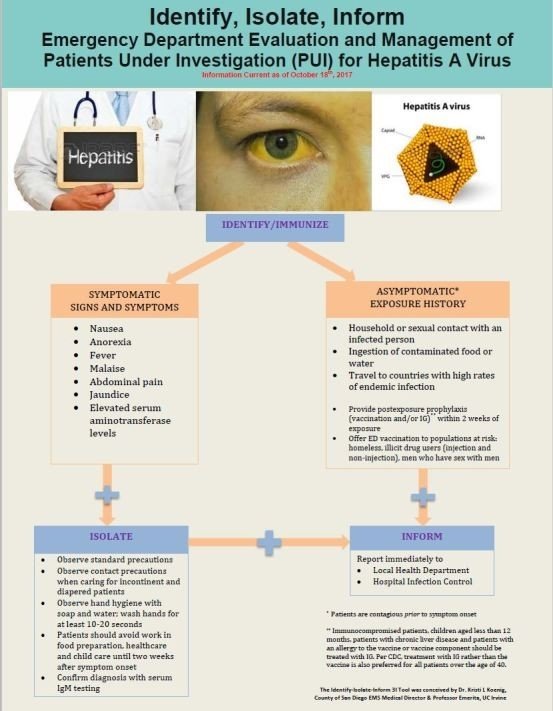
What are symptoms of chronic hepatitis?
They include:
- fatigue
- flu-like symptoms
- dark urine
- pale stool
- abdominal pain
- loss of appetite
- unexplained weight loss
- yellow skin and eyes, which may be signs of jaundice
Which hepatitis is highly contagious?
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, it’s not spread through sharing utensils or kissing.
Is there a definitive treatment for chronic hepatitis?
There is no specific therapy for acute hepatitis, and current treatment is supportive. Choosing ribavirin as the first-line therapy for chronic HEV is advisable, especially in solid organ transplant patients. Pegylated interferon-α has been used successfully for treatment of hepatitis E but is associated with major side effects.
Can HCV be cured?
Though there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C, treatments can reduce the viral load to undetectable levels which is considered cured or in remission. The virus is considered cured when it is not detected in your blood 12 weeks after treatment is completed. This is otherwise known as a sustained virologic response (SVR).

Can chronic hepatitis be cured?
Currently there is no complete cure for chronic hepatitis B. However, several effective treatment options can reduce the risk of liver damage and slow down or stop the virus from spreading.
What is the most common cause of chronic hepatitis?
Usually, chronic hepatitis is caused by infection with the hepatitis B or C virus. These viruses primarily are passed from person to person through sexual contact or through contact with blood or other bodily fluids when needles are shared or during blood transfusions.
How serious is chronic hepatitis?
Hepatitis C can be a short-term illness, but for most people, acute infection leads to chronic infection. Chronic hepatitis C can be a lifelong infection if left untreated. Chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), liver cancer, and even death.
How long can you live with chronic hepatitis?
The estimated carrier life expectancy is 71.8 years, as compared to 76.2 years among noncarriers (Figure 5). These results are consistent with other estimates, which indicate that 15% to 40% of HBV carriers die of liver complications.
What are signs of chronic hepatitis?
Symptoms of chronic viral hepatitis can take decades to develop. Symptoms of hepatitis can include: fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, light-colored stools, joint pain, and jaundice.
How do you know if you have chronic hepatitis?
People who test positive for the hepatitis B virus for more than six months (after their first blood test result) are diagnosed as having a chronic infection.
What can you do for chronic hepatitis?
See your GP if you have any persistent or troublesome symptoms that you think could be caused by hepatitis. Long-term (chronic) hepatitis also may not have any obvious symptoms until the liver stops working properly (liver failure) and may only be picked up during blood tests.
How can hepatitis become chronic?
Rarely, hepatitis E virus causes chronic hepatitis in people with a weakened immune system, such as those who are taking drugs to suppress the immune system after an organ transplant, who are taking drugs to treat cancer, or who have HIV infection. Hepatitis A virus does not cause chronic hepatitis.
Which hepatitis is not curable?
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by a virus (called the hepatitis B virus, or HBV). It can be serious and there's no cure, but the good news is it's easy to prevent.
Can you recover from chronic hepatitis B?
Most adults with hepatitis B recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic (long-lasting) hepatitis B infection. A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but there's no cure if you have the condition.
How do you treat chronic hepatitis B?
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B may include: Antiviral medications. Several antiviral medications — including entecavir (Baraclude), tenofovir (Viread), lamivudine (Epivir), adefovir (Hepsera) and telbivudine (Tyzeka) — can help fight the virus and slow its ability to damage your liver.
Can you recover from hepatitis?
About 85 percent of people with hepatitis A recover within three months, and almost all recover within six months. The disease does not become chronic, and there are no long-term health implications.
How does hepatitis become chronic?
Age plays a role in whether hepatitis B will become chronic. The younger a person is when infected with the hepatitis B virus, the greater the chance of developing chronic infection. About 9 in 10 infants who become infected go on to develop life-long, chronic infection. The risk goes down as a child gets older.
How do you get chronic viral hepatitis?
Hepatitis A and hepatitis E typically spread through contact with food or water that has been contaminated by an infected person's stool. People may also get hepatitis E by eating undercooked pork, deer, or shellfish. Hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and hepatitis D spread through contact with an infected person's blood.
What is the cause of chronic hepatitis C?
Chronic hepatitis C infection is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). As the virus enters the body, it causes an infection in the liver. Over time, the infection can scar the liver and prevent it from working normally.
How many people with hepatitis C are chronic?
According to the CDC, over half of people with acute hepatitis C develop chronic hepatitis C.
What is the leading diagnosis for people seeking liver transplants?
This made hepatocellular carcinoma the leading diagnosis for people seeking liver transplants. Hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with conditions including hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
How can hepatitis C be passed from person to person?
Hepatitis C can be passed from person to person. Most people with HCV get it through direct contact with blood containing the virus. People with hepatitis C can pass on the virus to others by sharing needles and syringes. Hepatitis C is easily transmitted among people who use intravenous drugs.
How to confirm hepatitis C?
A positive result means you’ve been exposed to the virus, but you may not have an infection. To confirm an HCV infection, you must undergo an HCV viral load test to check for genetic material (RNA).
How long does it take for hepatitis C to go away?
of people with acute hepatitis C spontaneously clear the virus within 6 months. This means that the virus goes away even though it hasn’t been treated. The 55 to 85 percent of people who don’t clear the virus will develop a chronic HCV infection.
What are the most common complications of hepatitis C?
Cirrhosis is the most common complication of hepatitis C. Less common complications of hepatitis C include liver failure and cancer.
How long does hepatitis last?
any of several types of hepatitis persisting for longer than 6 months, often progressing to cirrhosis.
How much greater risk of being hospitalized with hepatitis C?
Patients with chronic hepatitisC had a nearly 25-fold greater risk of being hospitalized with liver-related conditions, compared with other health system patients.
What is the hepatitis B program?
The program aims to improve the capacity of health care providers and stakeholder groups to reduce the burden of chronic hepatitisB in Asian American and other at-risk communities through increased hepatitis B education, screening, vaccination, and linkage to care.
How long does hepatitis B stay in the blood?
Chronic hepatitis B is usually defined by the presence of hepatitis B surface antigen in the blood or serum for longer than 6 months. Chronic viral hepatitis--costs of diagnosis and treatment.
Where is hepatitis B most common?
Chronic hepatitisB remains the most common serious health problem in the world, especially in the Asia Pacific region.
What is the term for a person who has hepatitis B?
When a person is first infected with the hepatitis B virus, it is called an " acute infection " (or a new infection).
How long does hepatitis B last?
An acute hepatitis B infection may last up to six months (with or without symptoms) and infected persons are able to pass the virus to others during this time. A simple blood test can let a person know if the hepatitis B virus is in their blood or if they have successfully gotten rid of the virus. Until your health care provider confirms that the blood test shows that there is no more hepatitis B virus in your blood, it is important to protect others from a possible infection.
How many people have hepatitis B?
90% of infected newborns and babies will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection. Up to 50% of infected children (1-5 years) will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection. 5-10% of infected adults will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection (that is, 90% will recover) Learning that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection can be very upsetting.
How long does it take for a person to get rid of hepatitis B?
Some adults are unable to get rid of the virus after six months and they are diagnosed as having a " chronic infection .". A simple blood test can diagnose an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection. The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is directly related to the age at which a person is first exposed to the hepatitis B virus.
How to take care of liver after infection?
Simple tips for taking care of your liver during a new infection is to avoid alcohol, stop or limit smoking, eat healthy foods, avoid greasy or fatty foods, and talk to your health care provider about your prescriptions, over-the-counter medications and ask any other questions you may have during this time.
How to help liver function?
Eat a healthy diet with lots of vegetables since fried, greasy foods are hard on your liver
Why is it important to have your blood tested for hepatitis B?
Until your health care provider confirms that the blood test shows that there is no more hepatitis B virus in your blood, it is important to protect others from a possible infection. It is also important to have your sexual partner (s) and family members (or those you live in close household contact) get tested for hepatitis B.
Chronic inactive hepatitis B: what it means
The condition of asymptomatic hepatitis B virus infection is now more correctly defined as ‘inactive carrier status’.
Screening in case of chronic inactive hepatitis virus
Although most inactive carriers remain permanently in this state, there is a small percentage of individuals who may change their status to active infection.
Treatment of chronic inactive hepatitis in case of cancer
It is also important to bear in mind that in the case of chronic intake of therapies such as those for oncohaematological diseases, cortisone or other immunosuppressive drugs, the viral infection can reactivate, in some cases even with pictures of real acute hepatitis.
What does hepatitis mean?
minus. Related Pages. Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected.
How long does hepatitis A last?
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
How does hepatitis C spread?
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus – even in microscopic amounts – enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
How long does it take for hepatitis to show symptoms?
Many people with hepatitis do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected. If symptoms occur with an acute infection, they can appear anytime from 2 weeks to 6 months after exposure. Symptoms of chronic viral hepatitis can take decades to develop. Symptoms of hepatitis can include: fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, light-colored stools, joint pain, and jaundice.
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
Chronic: There are several medications available to treat chronic hepatitis C. Current treatments usually involve 8-12 weeks of oral therapy (pills) and cure over 90% of people with few side effects
What percentage of people with hepatitis B are Asian?
About 50% of people with hepatitis B in the U.S are Asian. Hepatitis B is a leading cause of liver cancer. About 50% of people with hepatitis C do not know they are infected. Hepatitis C is a leading cause of liver transplants and liver cancer.
What causes hepatitis A?
Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. What causes it? Hepatitis A.
How long does hepatitis B last?
Chronic hepatitis B infection lasts six months or longer. It lingers because your immune system can't fight off the infection. Chronic hepatitis B infection may last a lifetime, possibly leading to serious illnesses such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
How long does hepatitis B go undetected?
Chronic infection may go undetected for decades until a person becomes seriously ill from liver disease.
What are the complications of HBV?
Complications. Having a chronic HBV infection can lead to serious complications, such as: Scarring of the liver (cirrho sis). The inflammation associated with a hepatitis B infection can lead to extensive liver scarring (cirrhosis), which may impair the liver's ability to function. Liver cancer.
What to do if you think you have hepatitis B?
If you think you have signs or symptoms of hepatitis B, contact your doctor.
Can hepatitis B be recovered?
Most adults with hepatitis B recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic (long-lasting) hepatitis B infection.
Can hepatitis B cause kidney disease?
Other conditions. People with chronic hepatitis B may develop kidney disease or inflammation of blood vessels.