
Full Answer
What does cold hardiness zone mean for plants?
Cold Hardiness. The USDA plant cold hardiness zone designation is an approximate guide of where a plant is cold hardy in the U.S. Determination of cold hardiness is not an exact science. Many factors influence whether a plant is cold hardy in a particular area including micro climates that exist within zones.
What is plant hardiness and why does it matter?
A basic definition of hardiness is a plant’s ability to withstand cold winter temperatures. The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s plant hardiness zone map breaks geographical regions into zones based on the average low winter temperatures. These zones give gardeners a starting point when determining what plants will fare well in their gardens.
How do you determine whether a plant is cold hardy or not?
Many factors influence whether a plant is cold hardy in a particular area including micro climates that exist within zones. Therefore an excepted + or - one zone accuracy is accepted. For example: If a plant is listed as zone 7 it may be hardy farther north in zone 6.
How do you use the cold hardiness map?
How to Use the Cold Hardiness Map. Cold Hardiness zones are based on the average annual minimum temperature in a given area of the country, with USDA Zone 1 being the coldest at minus 50 degrees F and USDA Zone 13 the warmest at above 60 degrees F. Each of the map's colored zones is separated by 10 degrees.
What does hardiness mean for plants?
Hardiness of plants describes their ability to survive adverse growing conditions. It is usually limited to discussions of climatic adversity. Thus a plant's ability to tolerate cold, heat, drought, flooding, or wind are typically considered measurements of hardiness.
What is a cold hardy?
Cold hardiness is the ability to resist injury during exposure to low temperature. Cold tenderness is the opposite of cold hardiness.
What does hardy to 20 degrees mean?
A Zone 9 plant is hardy only to 20 degrees F. Some references provide a range of zones in which the plant will grow. A plant listed as hardy in Zones 4-9 means it will grow in all of those zones.
What makes plants cold hardy?
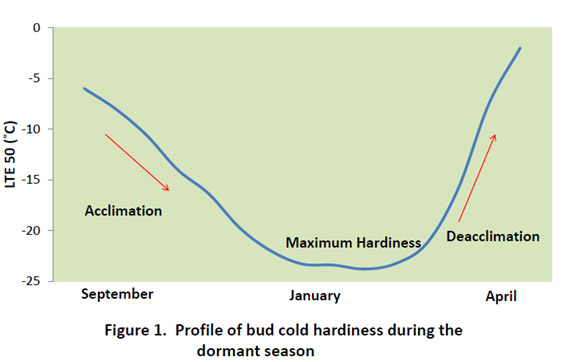
The degree of cold hardiness generally increases from early fall until mid-winter so that a temperature of -20° might kill a plant in November, it might not cause any damage in January. Plants are generally able to withstand these colder temperatures by regulating the water content inside and around the plant's cells.
What is the coldest hardiness zone?
USDA Zone 1Cold Hardiness zones are based on the average annual minimum temperature in a given area of the country, with USDA Zone 1 being the coldest at minus 50 degrees F and USDA Zone 13 the warmest at above 60 degrees F. Each of the map's colored zones is separated by 10 degrees.
When should you plant cold hardy plants?
We typically plant cold hardy plants in our garden anywhere from two weeks before last frost all the way up to last frost. For cold hardy root vegetables, these can be direct sowed up to two weeks before the last frost date. In general, we look at the 10 day weather outlook when we get to two weeks before last frost.
What is the lowest temperature a plant can survive?
Light freeze - 29° to 32° Fahrenheit will kill tender plants. Moderate freeze - 25° to 28° Fahrenheit is widely destructive to most vegetation. Severe or hard freeze - 25° Fahrenheit and colder causes heavy damage to most plants.
Will 50 degrees hurt plants?
You have to remember that most common houseplants are tropical, and a lot of them are extremely sensitive to temperatures under 50 degrees Fahrenheit. Some will start dying the second the temps dip, but others can regenerate from healthy roots below the soil even if the top part of the plant is completely frozen.
What is the coldest zone number?
Zone 1The USDA plant hardiness map divides North America into 11 hardiness zones. Zone 1 is the coldest; zone 11 is the warmest.
What plants are sensitive to cold?
Some plants tolerate frost and cold temperatures better than others. Plants always killed by frost include summer annual flowers and summer vegetables like impatiens, marigolds, coleus, tomatoes and peppers. Subtropical and Tropical plants are the most sensitive to frost (citrus, hibiscus and bougainvillea).
What is the most hardy plant?
Purple Saxifrage, the Hardiest Plant in the World With its pretty purple flowers carpeting the tundra in spring, purple saxifrage looks a bit delicate. It certainly doesn't look like it could take much of a beating. Yet it's common throughout the Arctic and grows further north than any other flowering plant.
What plants can tolerate cold weather?
Plants that survive winterConeflower (Echinacea) ... Lily of the Valley. ... Blue Spruce. ... Wintergreen Boxwood. ... Catmint. ... Coral Bells (Heuchera) ... Pansies. ... Hostas.More items...•
What are some cold hardy plants?
Freeze-Proof PlantsLily-of-the-Valley. Don't let its dainty blooms fool you — lily-of-the-valley (Convallaria majalis) is a tough plant. ... Siberian Iris. ... American Mountain Ash. ... Coral Bells (Heuchera) ... Pansies. ... Hosta. ... Siberian Cypress. ... 'Fastigiata' Spruce (Picea pungens var.More items...
What is the most cold hardy plant?
Purple Saxifrage, the Hardiest Plant in the World Yet it's common throughout the Arctic and grows further north than any other flowering plant.
What vegetables are cold hardy?
According to Myers, the hardiest vegetables that can withstand heavy frost of air temperatures below 28 include spinach, Walla Walla sweet onion, garlic, leeks, rhubarb, rutabaga, broccoli, kohlrabi, kale, cabbage, chicory, Brussels sprouts, corn salad, arugula, fava beans, radish, mustard, Austrian winter pea and ...
How cold hardy are carrots?
The carrot tops are cold-hardy down to at least 18°F but the roots can take even colder temps, especially if you pile on a thick layer of straw mulch to insulate them.
Cold Hardiness
The USDA plant cold hardiness zone designation is an approximate guide of where a plant is cold hardy in the U.S.
How to Use the Cold Hardiness Map
Cold Hardiness zones are based on the average annual minimum temperature in a given area of the country, with USDA Zone 1 being the coldest at minus 50 degrees F and USDA Zone 13 the warmest at above 60 degrees F.
How do palms survive in cold climates?
Then, finally, of course, genetics plays the biggest role, with some palms innately able to handle temperatures down to -10F while others succumb to temps in the 50s. Why some palms are able to survive climates far harsher than their origins would suggest is not totally understood. But many anatomical and physiologic adaptations that allow a palm to survive certain climate extremes other that cold sometimes also influence their ability to deal with cold, too. Palms that live in arid but tropical climates sometimes have a natural ability to handle cold temperatures thanks to their evolutionary adaptations to deal with drought, winds, flooding, etc. How to predict which palms will survive in a cold climate is not that easy however- trial and error is mostly how it's done.
How do hills and valleys protect against frost?
Hills and valleys are very different than flat surfaces when it comes to very cold weather. High elevations can have a protective advantage as long as they are not so high that they push the zone down a notch. I am not talking about mountains versus deserts, but just hills versus valleys. Cold air flows off hillsides, so palms planted near the tops of hills will often have much less cold damage during a frost than those planted near the bottom, or in a valley, where cold air tends to collect and sit for long periods. Hills also get much more sunlight and more ground warmth from being heated all day long, further protecting plants on its surface. Hillsides may experience more wind, too, which can be protective, or damaging depending on the circumstances. I have seen several magnificent palm collections in marginal climates that show little or no damage year after year thanks to being grown on steep slopes or hills, while surrounding gardens suffer from damaging frosts yearly.
Is palm a cold hardy plant?
The term cold hardy is not an unfamiliar one to most people growing plants. For palms, any palm that can grow outside a tropical environment is considered to be at least somewhat cold hardy. Obviously any palm that can grow in a temperate climate is very cold hardy (there are very few of these unfortunately). But there is more to this designation than just a label and these more subtle distinctions are relevant to those who live in marginal climates and want to grow palms.
Are we missing a good definition for cold hardy? Don't keep it to yourself..
The ASL fingerspelling provided here is most commonly used for proper names of people and places; it is also used in some languages for concepts for which no sign is available at that moment.
Definitions & Translations
Get instant definitions for any word that hits you anywhere on the web!
What is hardiness in plants?
Hardiness refers to how well a plant will survive cold temperatures. Where the USDA zones fall short, however, is that they don’t account for other factors. These include freeze dates, freeze-thaw cycles, the effects of snow cover, precipitation, and elevation.
What Do Hardiness Zones Mean?
Department of Agriculture. It divides North America into eleven zones by minimum average annual temperatures. The lower the number is , the lower the temperatures in that zone.
What is a USDA zone?
If you are new to gardening, you may be confused by some of the terminology associated with plants. For instance, a USDA zone explanation may be necessary. This is a useful system for determining what plants will survive and grow in certain areas of North America.
How many degrees of temperature difference are there in each zone?
The lower the number is, the lower the temperatures in that zone. Each zone represents ten degrees of temperature difference. Each zone is also divided into “a” and “b” segments. These represent five degrees of temperature difference.
What is hardiness zone?
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined to encompass a certain range of climatic conditions relevant to plant growth and survival. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by annual extreme minimum temperature.
What is the temperature scale used to define USDA hardiness zones?
Temperature scale used to define USDA hardiness zones. These are annual extreme minima (an area is assigned to a zone by taking the lowest temperature recorded there in a given year). As shown, the USDA uses a GIS dataset averaged over 1976 to 2005 for its United States maps.
What is the minimum temperature a plant can withstand?
For example, a plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of 30 °F (−1.1 °C) to 40 °F (4.4 °C).
When did Arbor Day update hardiness zones?
In 2006, the Arbor Day Foundation released an update of U.S. hardiness zones, using mostly the same data as the AHS. It revised hardiness zones, reflecting generally warmer recent temperatures in many parts of the country, and appeared similar to the AHS 2003 draft.
Who created the first hardiness zone?
The first attempts to create a geographical hardiness zone system were undertaken by two researchers at the Arnold Arboretum in Boston: the first was published in 1927 by Alfred Rehder, and the second by Donald Wyman in 1938.
Which states have the coldest weather?
The warmest zone in the 48 contiguous states is the Florida Keys (11b) and the coldest is in north-central Minnesota (3a).
Is the USDA based on average annual temperature?
As the USDA system is based entirely on average annual extreme minimum temperature in an area, it is limited in its ability to describe the climatic conditions a gardener may have to account for in a particular area: there are many other factors that determine whether or not a given plant can survive in a given zone.
What temperature do plants need to survive?
Answer: Plants have certain minimum temperatures below which they simply cannot survive. For tropical hibiscus, for example, it’s 32 degrees F. For rose of Sharon, a type of woody and hardy hibiscus, it’s -10 degrees F. Every plant has its limits. Years ago the United States Department of Agriculture cataloged all of the counties in the United States to determine their average lowest temperature of each winter, then they broke the country into 10 different zones. Four of those zones are represented in Texas. Keep in mind that the larger the zone number, the warmer the winters. The Texas Panhandle is Zone 6 (-10 F to 0), while much of the Trans-Pecos and North Central Texas fall into Zone 7 (0 to +10 F). Central Texas, the Hill Country and Big Bend are mostly in Zone 8 (10 F to 20F), while deep South Texas is in Zone 9 (20 F to 30 F). When you go shopping, you should buy only plants that are winter-hardy to your county’s zone rating or northward. In other words, if you live in Zone 7, you should choose only plants suited to Zones 7, 6, 5, 4 and perhaps 3. Many of those really cold-hardy plants, from Zone 3, as counter-examples, have trouble with our heat, so they may or may not be good for the area.
What is the zone of Texas?
The Texas Panhandle is Zone 6 (-10 F to 0), while much of the Trans-Pecos and North Central Texas fall into Zone 7 (0 to +10 F). Central Texas, the Hill Country and Big Bend are mostly in Zone 8 (10 F to 20F), while deep South Texas is in Zone 9 (20 F to 30 F).
