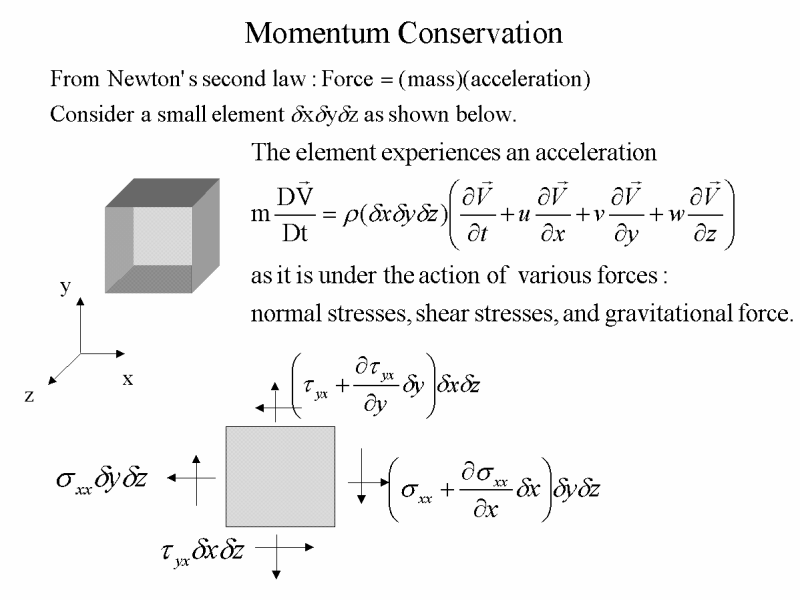
What is the formula of Conservation of momentum?
- Work out the total momentum before the event (before the collision): p = m × v.
- Work out the total momentum after the event (after the collision): Because momentum is conserved, total momentum afterwards = 60,000 kg m/s.
- Work out the total mass after the event (after the collision):
- Work out the new velocity:
What is the theory of Conservation of momentum?
The principle of conservation of momentum states that if two objects collide, then the total momentum before and after the collision will be the same if there is no external force acting on the colliding objects.
What does it mean to say that momentum is conserved?
When it is said that momentum is conserved, it means that momentum is conserved within a defined system in which the mass of the system of interest remains constant and when no net external force acts on the system during an interaction that occurs within the system among parts of the system.
How to tell if momentum is conserved?
Key Points
- Angular momentum is defined, mathematically, as L=Iω, or L=rxp. ...
- In a closed system, angular momentum is conserved in all directions after a collision.
- Since momentum is conserved, part of the momentum in a collision may become angular momentum as an object starts to spin after a collision.

What is conservation of momentum in physics?
The conservation of momentum states that, within some problem domain, the amount of momentum remains constant; momentum is neither created nor destroyed, but only changed through the action of forces as described by Newton's laws of motion.
What is conservation of momentum short answer?
The law of conservation of momentum states that in an isolated system the total momentum of two or more bodies acting upon each other remains constant unless an external force is applied. Therefore, momentum can neither be created nor destroyed.
What is an example of conservation of momentum?
Example of Conservation of Momentum Balloon: The small particles of gas move quickly crashing into one another and the walls of the balloon. Despite the fact that the particles themselves move quicker and slower when they lose or pick-up momentum when they collide. The total momentum of the system stays as before.
Why is the conservation of momentum important in physics?
The importance of this law of conservation of momentum is that as long as no external force acts on a body the velocity vector can be deduced after some period of time of a body if we knew its initial velocity.
How do you prove conservation of momentum?
Formula used: p = mv, FAB=−FBA and F=dpdt. Complete answer: Law of conservation of momentum states that unless an external force is applied, the two or more objects acting upon each other in an isolated system, the total momentum of the system remains constant.
Which equation best describes the law of conservation of momentum?
What best explains the results of the experiment? This experiment did not occur in a closed system. This proves the conservation of momentum since pi = pf .
When can conservation of momentum be used?
we use conservation of momentum when momentum is transferred by one thing to another to conserve it.
What is the conversion of momentum?
Momentum is equal to the mass of an object multiplied by its velocity and is equivalent to the force required to bring the object to a stop in a unit length of time. For any array of several objects, the total momentum is the sum of the individual momenta.
What is conservation of linear momentum Class 9?
Conservation of Linear Momentum Formula The principle of conservation of momentum states that if two objects collide, then the total momentum before and after the collision will be the same if there is no external force acting on the colliding objects.
What is linear momentum Class 9?
Linear momentum is the vector quantity and defined as the product of the mass of an object, m, and its velocity, v. The letter 'p' is applied to express it and used as momentum for short. Please note that the body's momentum is always in the same direction as its velocity vector.
What does conservation mean in physics?
In physics, the term conservation refers to something which doesn't change. This means that the variable in an equation which represents a conserved quantity is constant over time. It has the same value both before and after an event. There are many conserved quantities in physics.
What is the law of conservation of momentum?
The law of conservation of momentum states that if no net external unbalanced force acts on a system, then the total momentum of all the bodies of...
What is momentum?
Momentum of a body is the product of the mass of the body and the velocity of the body.
When is the conservation of momentum applicable?
Conservation of momentum is applicable when there is no net external unbalanced force acting on a system, and the mutual interactions of the bodies...
What is the formula of conservation of momentum?
The formula of conservation of momentum is ({m_A}{v_A} + {m_B}{v_B} = {m_A}{u_A} + {m_B}{u_B}.)
What is the best example of conservation of momentum?
The recoiling of a gun is the best example of conservation of momentum. When the bullet is shot in the forward direction, the gun recoils in the ba...
Which law is the conservation of momentum?
Conservation of momentum is actually a direct consequence of Newton's third law.
What is conservation in physics?
In physics, the term conservation refers to something which doesn't change. This means that the variable in an equation which represents a conserved quantity is constant over time. It has the same value both before and after an event.
Why are collisions interesting?
Collisions are particularly interesting to analyze using conservation of momentum. This is because collisions typically happen fast, so the time colliding objects spend interacting is short. A short interaction time means that the impulse, , due to external forces such as friction during the collision is very small.
Is momentum a vector quantity?
Momentum is a vector quantity, and therefore we need to use vector addition when summing together the momenta of the multiple bodies which make up a system. Consider a system of two similar objects moving away from each other in opposite directions with equal speed. What is interesting is that the oppositely-directed vectors cancel out, so the momentum of the system as a whole is zero, even though both objects are moving.
Is impulse the same as momentum?
If we recall that impulse is equivalent to change in momentum, it follows that the change in momenta of the objects is equal but in the opposite directions. This can be equivalently expressed as the sum of the change in momenta being zero.
What does Conservation of Momentum Mean?
Conservation of Momentum comes into the picture when bodies interact with each other without any external unbalanced force acting on them. The total momentum of the interacting bodies remains the same before and after the interaction.
How to verify conservation of momentum?
Conservation of Momentum can be verified by considering two bodies that interact with each other without any external unbalanced force acting on them.
What happens when a bullet is fired from a gun?
The recoiling of the gun. This happens when the bullet is fired from the gun, and the gun recoils in the direction opposite to the direction of the bullet. So, the shooter should hold the gun firmly to avoid hurting. This recoiling of the gun in the opposite direction is in accordance with the law of conservation of momentum.
What is the difference between m A v A and m B v B?
Here, m A u A + m B u B is the total momentum of the two bodies A and B before the collision and m A v A + m B v B is the total momentum of the two bodies A and B after the collision.
What is the product of the mass of the body and the velocity of the body?
Momentum of a body is the product of the mass of the body and the velocity of the body. It is a vector quantity, so it possesses both magnitude and direction.
Why is momentum important?
It is very important to involve the concept of momentum while discussing the impact of force. For example, the bullet thrown by our hand may not hurt a person, but when the bullet is shot using a gun, it may kill a person. Though the mass of the bullet is the same in both cases, its velocity drastically changes while using it through the gun, and thus its impact on the person gets deadly.
How to find the rate of change of momentum of body A?
So, the rate of change of the momentum of body A is given by m A v A – m A u A t
How to determine momentum of a brick?
The loaded cart (a cart with a brick on it) is in motion with considerable momentum. The actual momentum of the loaded cart can be determined using the velocity (often determined by a ticker tape analysis) and the mass. The total amount of momentum is the sum of the dropped brick's momentum (0 units) and the loaded cart's momentum . After the collision, the momenta of the two separate objects (dropped brick and loaded cart) can be determined from their measured mass and their velocity (often found from a ticker tape analysis). If momentum is conserved during the collision, then the sum of the dropped brick's and loaded cart's momentum after the collision should be the same as before the collision. The momentum lost by the loaded cart should equal (or approximately equal) the momentum gained by the dropped brick. Momentum data for the interaction between the dropped brick and the loaded cart could be depicted in a table similar to the money table above.
How many units of momentum did the cart lose in the collision?
Note that the loaded cart lost 14 units of momentum and the dropped brick gained 14 units of momentum. Note also that the total momentum of the system (45 units) was the same before the collision as it was after the collision.
What is the momentum of an object in a collision?
In a collision, the momentum change of object 1 is equal to and opposite of the momentum change of object 2. That is, the momentum lost by object 1 is equal to the momentum gained by object 2. In most collisions between two objects, one object slows down and loses momentum while the other object speeds up and gains momentum.
What is the purpose of vector diagrams?
A vector diagram can be used to represent this principle of momentum conservation; such a diagram uses an arrow to represent the magnitude and direction of the momentum vector for the individual objects before the collision and the combined momentum after the collision.
How many units of momentum does object 1 lose?
If object 1 loses 75 units of momentum, then object 2 gains 75 units of momentum. Yet, the total momentum of the two objects (object 1 plus object 2) is the same before the collision as it is after the collision. The total momentum of the system (the collection of two objects) is conserved. A useful analogy for understanding momentum conservation ...
What is the most powerful law in physics?
One of the most powerful laws in physics is the law of momentum conservation . The law of momentum conservation can be stated as follows. For a collision occurring between object 1 and object 2 in an isolated system, the total momentum of the two objects before the collision is equal to the total momentum of the two objects after the collision.
How to find the velocity of the Earth?
To find the velocity of the Earth, use the momentum equation, p = m*v. This equation rearranges to v=p/m. By substituting into this equation,
What is conservation of momentum?
Conservation of momentum means that momentum is neither created nor destroyed and that the total momentum of a closed system is constant. Work through an example experiment on conservation of momentum and analyze the resulting data to understand this concept. Updated: 11/03/2021
How to find momentum conservation?
This is the equation for conservation of momentum: (m1*v1 + m2*v2) before = (m1*v1 + m2*v2) after. So if we can make two objects collide, measure the masses, and their velocities before and after the collision, we can use this to confirm that momentum is indeed conserved. Though, this will only work if there isn't much friction, and momentum isn't transferred to the earth itself.
What is momentum in science?
Momentum is a quantity of motion equal to the product of the mass and the velocity of the object. An object with more mass has more momentum, and an object with more velocity also has more momentum. Conservation of momentum says that momentum is neither created nor destroyed; it only moves from one place to another.
Why does momentum disappear?
So, if two cars hit each other in a crash, all that momentum goes somewhere. The reason it seems like it disappears is that momentum can be absorbed into the earth.
Why is it not perfect to analyze momentum?
Clearly, it won't be perfect, because nobody is perfect at using a stopwatch and measuring distances. But we can still have a go at seeing how close we can get our data.
What happens when momentum is conserved?
If momentum is conserved(which only happens when the Hamiltonian commutes with the translation operator, which only happens when the potential is a constant), then what momentum conservation guarantees is that if you start the system in a momentum eigenstate, it will always remain in a momentum eigenstate (although the phase will change).
What is conservation law for momentum?
The conservation law for momentum states that if there is a translation symmetry in our system, the momentum will be conserved. Translation symmetry requires that the potential should be constant.
Is momentum conserved in harmonic oscillators?
Note that momentum is not conserved in the case of a Harmonic oscillator, mentioned in the OP, although the time-averaged momentum of a classical oscillator is the same as the quantum mechanical average (that is zero).
Which theorem is used to describe the equations of motion for average quantities?
The equations of motion for average quantities obey the Ehrenfest theorem- in case of linear system they are simply identical with the classical equations of motion, and the conservation of averagemomentum works in the same way as in classical mechanics.
When a measurement is performed, the system is no longer isolated for the time it is happening?
When a measurement is performed, the system is no longer isolated for the time it is happening. The agent doing the measurement is interacting therewith, so we cannot assume the system afterward is unaltered.
Is momentum independent of time?
For example in ground state of Harmonic oscillator I know that expectation value of momentum is independent of time but that is "expectation" value and not the actual momentum of particle or the momentum that we actually measure .
Does quantum measurement change things?
The subtlety with quantum measurement is not that it changes things - it's that if you try to make the disturbance smaller, there comes a point where you cannot make it any smaller still without starting to sacrifice information gain from the measurement, and this point is wholly independentof the measuring technique.
Why do current-carrying wires have multiple thin copper wires instead of a single thick copper wire?
In domestic current-carrying wires, there are many thin copper wires inside the plastic insulation. Why is that so? Why can't there be a single thick copper wire carrying the current instead of so many thin ones?
How fast do liquids flow from the stomach into the small intestine?
I was drinking water and I started to think about if the water was draining into my intestine as fast I was drinking it.
Does altitude make a difference during earthquakes?
Let's assume the source of the earthquake is perpendicular to your position and at a fixed depth based on sea level.
Conservation
Example
Properties
- The forces act between the two objects for a given amount of time. In some cases, the time is long; in other cases the time is short. Regardless of how long the time is, it can be said that the time that the force acts upon object 1 is equal to the time that the force acts upon object 2. This is merely logical. Forces result from interactions (or contact) between two objects. If object 1 cont…
Resources
- A useful means of depicting the transfer and the conservation of money between Jack and Jill is by means of a table.
Safety
- For any collision occurring in an isolated system, momentum is conserved. The total amount of momentum of the collection of objects in the system is the same before the collision as after the collision. A common physics lab involves the dropping of a brick upon a cart in motion. 1. When fighting fires, a firefighter must use great caution to hold a hose that emits large amounts of wat…
Details
- The dropped brick is at rest and begins with zero momentum. The loaded cart (a cart with a brick on it) is in motion with considerable momentum. The actual momentum of the loaded cart can be determined using the velocity (often determined by a ticker tape analysis) and the mass. The total amount of momentum is the sum of the dropped brick's momentum (0 units) and the loaded car…
Introduction
- Collisions commonly occur in contact sports (such as football) and racket and bat sports (such as baseball, golf, tennis, etc.). Consider a collision in football between a fullback and a linebacker during a goal-line stand. The fullback plunges across the goal line and collides in midair with the linebacker. The linebacker and fullback hold each other and travel together after the collision. Th…
Usage
- Momentum is conserved for any interaction between two objects occurring in an isolated system. This conservation of momentum can be observed by a total system momentum analysis or by a momentum change analysis. Useful means of representing such analyses include a momentum table and a vector diagram. Later in Lesson 2, we will use the momentum conse...
Causes
- 9. A Tomahawk cruise missile is launched from the barrel of a mobile missile launcher. Neglect friction. Express your understanding of momentum conservation by filling in the tables below.