How does convection relate to weather?
Three factors contribute to set convection currents in motion:
- heating and cooling of the fluid,
- changes in the fluid’s density, and.
- force of gravity.
- The heat source for these currents is heat from Earth’s core and from the mantle itself.
- Hot columns of mantle material rise slowly.
How is conduction and convection related to the weather?
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th Edition. Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine, Frank P. ...
- Heat and Mass Transfer. Yunus A. Cengel. McGraw-Hill Education, 2011. ...
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer. C. P. Kothandaraman. ...
- U.S. Department of Energy, Thermodynamics, Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. DOE Fundamentals Handbook, Volume 2 of 3. May 2016.
What is the difference between convection and conduction?
Nuclear and Reactor Physics:
- J. R. ...
- J. R. ...
- W. M. ...
- Glasstone, Sesonske. Nuclear Reactor Engineering: Reactor Systems Engineering, Springer; 4th edition, 1994, ISBN: 978-0412985317
- W.S.C. Williams. ...
- G.R.Keepin. Physics of Nuclear Kinetics. ...
- Robert Reed Burn, Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Operation, 1988.
- U.S. Department of Energy, Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory. ...
- Paul Reuss, Neutron Physics. ...
What does convection have to do with the wind?
One natural example of convection currents is wind. As the Sun shines down on an area of land, it heats the air above the ground. That warm air rises. As it rises, cooler air moves in to take the place at the bottom. This moving cooler air creates…wind! Wind happens all over Earth because Earth heats unevenly.
How does convection affect weather?
How does convection affect the weather? Convection within the atmosphere can often be observed in our weather. For example, as the sun heats the Earth's surface, the air above it heats up and rises. If conditions allow, this air can continue to rise, cooling as it does so, forming Cumulus clouds.
What is convection in simple words?
Definition of convection 1 : the action or process of conveying. 2a : movement in a gas or liquid in which the warmer parts move up and the cooler parts move down convection currents. b : the transfer of heat by convection foods cooked by convection — compare conduction, radiation.
What does convection mean in storms?
Convective Storms Convection is upward atmospheric motion that transports whatever is in the air along with it – especially any moisture available in the air. A thunderstorm is a result of convection. 1. Squall line and supercell systems are examples of convective storms.
What are 4 examples of convection?
Listed below are 10 common examples of convection in everyday life.Boiling Water.Land and Sea Breeze.Air Conditioner.Body blood circulation.Melting of chilled drinks.Convection Oven.Hot-air Baloon.Refrigerator.More items...•
How do you explain convection to a child?
When water is heated, convection causes the water at the bottom to expand and become lighter. The heated molecules then rise to the top, which causes the cooler molecules to sink to the bottom. These cooler molecules then become heated. This process is repeated until all the water is the same temperature.
Does convection cause lightning?
Convection is often associated with lightning production! As these air particles rise they create winds moving upward. Those winds lift the tiny frozen droplets of water as gravity tries to bring them crashing down to the earth's surface.
Is tornado a convective storm?
In the insurance and risk management industries, hail, straight-line winds and tornadoes are “sub-perils” of convective storms— dangerous off-shoots of the weather system that can rack up serious property damage costs in a short period of time.
What are the 4 types of storms?
Types of stormsBlizzards.Hail.Heavy rain.Ice storms.Lightning.Thunderstorms.Wind.
What is a simple definition of conduction?
Conduction is the process by which heat energy is transmitted through collisions between neighboring atoms or molecules. Conduction occurs more readily in solids and liquids, where the particles are closer together than in gases, where particles are further apart.
What is convection class 7th?
Convection: The process of heat transfer from one part of a fluid to another part by the actual movement of the particles of the fluid is called convection. Liquid and gases are heated by the process of convection. For example: In winter, the air over the ocean is hot as compared to that on the landmass.
What is convection process?
Convection is the process by which heat is transferred from a solid surface to a nonsolid, such as air or water. The convection process involves the motion of the fluid relative to the solid surface and the processes by which heat is transferred across the interface.
What is a sentence for convection?
The buildings typically see a 30 percent saving in energy as air circulates by natural convection to the upper floors. Heat transfer by convection occurs as a result of the movement of fluid in the form of eddies or circulating currents.
What is dry convection?
Convection which occurs without cloud formation is called dry convection, while the visible convection processes referred to above are forms of moist convection. You can either type in the word you are looking for in the box below or browse by letter.
What is the term for the movement of heat and moisture in the atmosphere?
Convection. Generally, transport of heat and moisture by the movement of a fluid. In meteorology, the term is used specifically to describe vertical transport of heat and moisture in the atmosphere, especially by updrafts and downdrafts in an unstable atmosphere. The terms "convection" and "thunderstorms" often are used interchangeably, ...
Is a thunderstorm a convection?
The terms "convection" and "thunderstorms" often are used interchangeably, although thunderstorms are only one form of convection. Cbs, towering cumulus clouds, and ACCAS clouds all are visible forms of convection. However, convection is not always made visible by clouds.
How does convection produce electricity?
Convection is often associated with lightning production! As these air particles rise they create winds moving upward. Those winds lift the tiny frozen droplets of water as gravity tries to bring them crashing down to the earth’s surface. The particles moving past each other generate electricity and when the charge gets strong enough– a bolt of lightning!
What type of convection is not associated with storms?
Dry Convection – The type of convection not associated with storms is called dry convection. This occurs when warm air at the surface rises to be above the cooler air overhead. Because there is no moisture, this typically doesn’t have cloud cover associated with it.
What is the process of heat transfer?
Convection – Heat transfer through the movement of a liquid or gas. That is, the liquid or gas of a certain temperature moves to a new area, thus changing the temperature of the new area. This is the heat transfer we are most interested in.
Why does a storm happen horizontally?
This happens horizontally due to heating differentials at the surface as well. But lets just focus on those storms.
Why does the sun heat us from so far away?
Radiation – (Not like the nuclear stuff we are all afraid of) But instead, the sun heating us from so far away because it’s that hot! Or like the radiator in a room that heats up and therefore heats up the whole room.
Does convection depend on heat transfer?
Before we get into the meat and potatoes of this, let me just reiterate that convection greatly depends on the other two types of heat transfer in order to occur .
Is convection a thunderstorm?
In a meteorologist’s vocabulary, convection and thunderstorm are practically interchangeable. The upward vertical motion of the warm, moist air is what fuels thunderstorms and on a much larger scale– even hurricanes!
How does convection work?
Convection works by areas of a liquid or gas heating or cooling greater than their surroundings, causing differences in temperature. These temperature differences then cause the areas to move as the hotter, less dense areas rise, and the cooler, more dense areas sink.
Why is convection important?
Convection is a vital process which helps to redistribute energy away from hotter areas to cooler areas of the Earth, aiding temperature circulation and reducing sharp temperature differences . Without convection simple tasks such as boiling water in a kettle would be much slower as only the water directly in contact with the heat ring at the bottom of the kettle would be able to be heated, with the water at the top staying cool.
How is convection different from conduction?
Conduction however, doesn’t necessarily involve particles moving. Instead energy is passed from one particle to another upon contact, transferring heat. As a result, conduction in liquids and gases is a much slower process than convection, as particles are free to move and direct contact is reduced. However, conduction is much more effective in solids than convection, as the particles are densely packed, continuously touching one another to allow an efficient transfer of heat. Additionally, in solids particles fixed and unable to move, stopping the transfer of energy via convection.
How does convection affect ocean currents?
However, these currents are affected by convection due to the influence of ocean temperature and salinity (concentration of salt within the water) on density.
How does convective current work?
Often the areas of heating and cooling are fixed, and allow convective cycles or currents to become established. For example, a saucepan of water over a flame may develop convective currents as the water is heated from below, rises to the surface, and cools. Once cooled enough, the water then sinks back to the bottom of the saucepan where the cycle is repeated, and the convective overturning continues.
What happens to the air above the Earth's surface when the sun heats up?
For example, as the sun heats the Earth’s surface, the air above it heats up and rises. If conditions allow, this air can continue to rise, cooling as it does so, forming Cumulus clouds. Stronger convection can result in much larger clouds developing as the air rises higher before it is cooled, sometimes producing Cumulonimbus clouds ...
Which is more effective, conduction or convection?
However, conduction is much more effective in solids than convection, as the particles are densely packed, continuously touching one another to allow an efficient transfer of heat. Additionally, in solids particles fixed and unable to move, stopping the transfer of energy via convection.
What is Convection?
Convection is the process of heat transfer by the bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids. The initial heat transfer between the object and the fluid takes place through conduction, but the bulk heat transfer happens due to the motion of the fluid.
How many types of convection are there?
There are two types of convection, and they are:
What is the process of heat transfer in fluids by the actual motion of matter?
Convection is the process of heat transfer in fluids by the actual motion of matter.
What is the process of heat?
According to the heat definition, heat is a form of energy that can be transferred from one medium to another through various processes like conduction, convection and radiation.
Why does land lose heat?
The land quickly loses heat when compared to water due to the differences in heat capacity. Consequently, the temperature of the sea is relatively higher, which creates low air pressure there. This sets up a flow of cool breeze offshore, known as the land breeze.
Why does coffee get cold?
You may have noticed that if you leave a cup of hot coffee on a table, it gets cold in some time. This is because heat is lost to the surroundings. Thus, heat transfer is the transfer of heat or thermal energy between physical systems. So when there is a temperature difference between two bodies, heat is transferred from the hot body to ...
What are some examples of forced convection?
Examples of forced convection are using water heaters or geysers for instant heating of water and using a fan on a hot summer day.
How do convection currents affect the weather?
How Do Convection Currents aFFECT wEAther? Convection Currents affect the weather all over the Earth. Convection currents can affect. even the smallest amount of weather, like wind. An example of this occurs when a. land mass is adjacent to a body of water. When a land mass is adjacent to a body. of water during the day it causes a sea breeze.
Why does the sea breeze happen?
of water during the day it causes a sea breeze. A Sea Breeze happens when the. land heats up faster than the water which means the air over the land is warmer. and less dense than the air over the water. Since the air is less dense it. rises, then the colder more dense air from the water replaces it and causes an.
What happens when you mix moisture with thermal conditions?
But when mixed with moisture and the right thermal conditions, it brings lightning and turbulence that can bring havoc to any airspace. Disruptions due to rerouting and the aftermath of a run-in with these storms can have dramatic repercussions.
How does a thunderstorm make the Earth livable?
Convection makes the earth livable, by transporting excess heat from the surface of the earth into the upper levels of the atmosphere. Without Convection the average temperature on earth could be as high as 125 degrees ...
What is the horizontal air flow in a convective current?
The horizontal air flow in a convective current is “wind.” Convection of both large and small scales accounts for systems ranging from hemispheric circulations down to local eddies. This horizontal flow, wind, is sometimes called “advection.” However, the term “advection” more commonly applies to the transport of atmospheric properties by the wind, i.e., warm advection; cold advection; advection of water vapor, etc.
What happens when two surfaces are heated unequally?
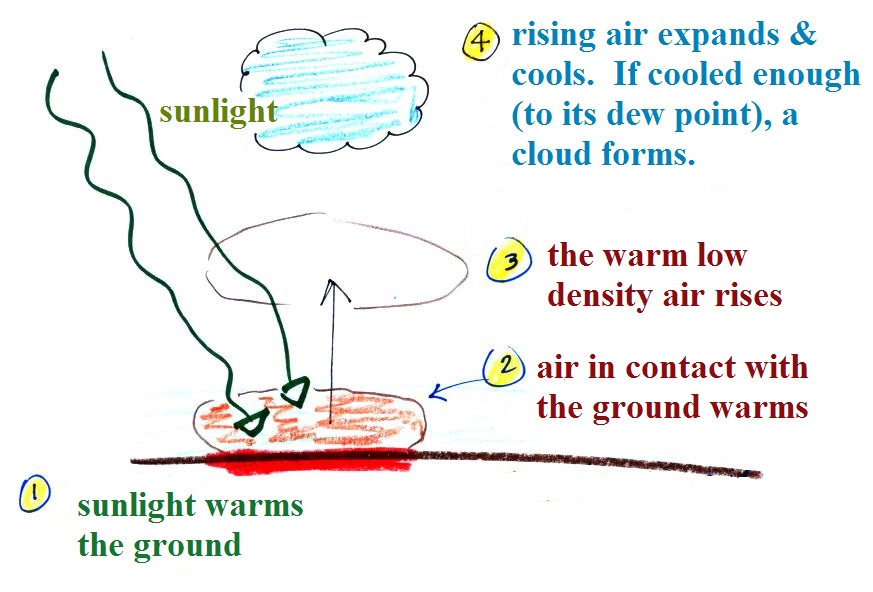
When two surfaces are heated unequally, they heat the overlying air unevenly. The warmer * air expands and becomes lighter or less dense than the cool * air. The more dense, cool air is drawn to the ground by its greater gravitational force lifting or forcing the warm air upward much as oil is forced to the top of water when the two are mixed. Figure 18 shows the convective process. The rising air spreads and cools, eventually descending to complete the convective circulation. As long as the uneven heating persists, convection maintains a continuous “convective current.”
from Your Kitchen to The Air
Steps to The Process of Convection
- The process of convection begins at sunrise and continues as follows: 1. The sun's radiation strikes the ground, heating it. 2. As the ground's temperature warms, it heats the layer of air directly above it through conduction (the transfer of heat from one substance to another). 3. Because barren surfaces like sand, rocks, and pavement become warmer faster than ground cov…
Convective Clouds
- As convection continues, the air cools as it reaches lower air pressures and may reach the point where the water vapor within it condenses and forms (you guessed it) a cumulus cloudat its top! If the air contains a lot of moisture and is quite hot, it will continue to grow vertically and will become a towering cumulus or a cumulonimbus. Cumulus, towering cumulus, Cumulonimbus, a…
Convective Precipitation
- If convective clouds have enough cloud droplets they'll produce convective precipitation. In contrast to non-convective precipitation (which results when air is lifted by force), convective precipitation requires instability, or the ability for air to continue rising on its own. It is associated with lightning, thunder, and bursts of heavy rain. (Non-convective precipitation events have less i…
Convective Winds
- All of the rising air through convection must be balanced by an equal amount of sinking air elsewhere. As the heated air rises, air from elsewhere flows in to replace it. We feel this balancing movement of air as wind. Examples of convective winds include foehns and sea breezes.
When Does Convection stop?
- Only when the pocket of warm, rising air has cooled to the same temperature of the surrounding air will it stop rising.