Causes
Definition of cytomegalic : characterized by or causing the formation of enlarged cells : characterized by or causing the formation of enlarged cells
Symptoms
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a common virus. Once infected, your body retains the virus for life. Most people don't know they have CMV because it rarely causes problems in healthy people.
Prevention
That’s because a healthy person’s immune system usually keeps the virus from causing illness. However, CMV infection can cause serious health problems for people with weakened immune systems and for unborn babies (congenital CMV).
Complications
This is called "latent" infection. Latent infection can "reactivate" later in life to cause disease again. Primary infection with CMV is common and may be asymptomatic. Primary CMV is one of the common causes of a mononucleosis-like syndrome, including fever, fatigue or tiredness, malaise, and other symptoms.
What is the meaning of cytomegalic?
What is cytomegalovirus (CMV)?
Why is cytomegalovirus so dangerous?
What is a latent infection of cytomegalovirus?
What causes Cytomegaly?
How cytomegalovirus (CMV) is spread. CMV is mainly spread through close contact with someone who already has CMV. It can be passed on through sexual contact and contact with other body fluids including saliva, blood, breast milk, tears, pee and poo. CMV can only be passed on when it's "active".
Is CMV a serious disease?
For people who have weakened immune systems, CMV infection can be serious or even fatal. People who have undergone stem cell or organ transplants seem to be at greatest risk. You develop a mononucleosis-like illness while you're pregnant.
What does having CMV mean?
Summary. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a virus found around the world. It is related to the viruses that cause chickenpox and infectious mononucleosis (mono). Between 50% and 80% of adults in the United States have had a CMV infection by age 40. Once CMV is in a person's body, it stays there for life.
What happens if you are CMV positive?
Most people will get infected with the virus during childhood or early adulthood. The majority are without any symptoms but a few may develop fever, sore throat and headache. Once infected, the virus lies dormant in the body forever, with a little risk of getting reactivated.
Is CMV a STD?
While all members of the herpes virus family are contagious, CMV isn't considered a sexually transmitted infection (STI) like certain forms of herpes simplex are. Additionally, CMV is considered the only member of the herpes virus family to spread directly from mother to child through the placenta during pregnancy.
How do adults get CMV?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a common virus. Over half of adults in the U.S. have it in their body by age 40. CMV spreads easily through an infected person's saliva or other body fluids. It's related to the herpes virus, which gives you cold sores.
How do I know if I have CMV?
How do you know if you have CMV? CMV usually doesn't cause any noticeable symptoms. However, in some people, it can cause mild symptoms similar to those of glandular fever, such as fever, swollen glands, and a cough or cold.
What are the symptoms of CMV in adults?
Most people with acquired CMV have no noticeable symptoms, but if symptoms do occur, they may include:fever.night sweats.tiredness and uneasiness.sore throat.swollen glands.joint and muscle pain.low appetite and weight loss.
Is CMV contagious forever?
Once you've got CMV, it stays in your system forever. A type of herpes virus, CMV remains dormant in your body just like chickenpox and mono, laying low even after any noticeable symptoms subside. When dormant, it's not contagious, but can reactivate and become contagious at any time, unbeknown to the carrier.
What is the treatment for CMV?
The drug of choice for treatment of CMV disease is intravenous ganciclovir, although valganciclovir may be used for nonsevere CMV treatment in selected cases. Ganciclovir is a nucleoside analogue that inhibits DNA synthesis in the same manner as acyclovir.
How long are you contagious with CMV?
Probably several weeks to months. Once a person is infected, the virus is shed intermittently in the saliva and urine for the rest of that person's life. Up to 70% and usually 30% to 40% of normal children aged 1 to 3 years in group care settings excrete CMV in their saliva and urine, respectively.
Is CMV curable?
There's no cure for CMV. The virus stays inactive in your body and can cause more problems later. This reactivation is most common in people who've had stem cell and organ transplants.
Is CMV curable?
There's no cure for CMV. The virus stays inactive in your body and can cause more problems later. This reactivation is most common in people who've had stem cell and organ transplants.
Do most people have CMV?
Cytomegalovirus (pronounced sy-toe-MEG-a-low-vy-rus), or CMV, is a common virus that infects people of all ages. Over half of adults have been infected with CMV by age 40. Most people infected with CMV show no signs or symptoms.
Is CMV permanent?
CMV infection is permanent Once a person has contracted CMV, they will carry it for life. This is because the virus lies dormant inside the body and may or may not reactivate itself at any time.
How do you know when CMV is active?
A blood test can detect the antibodies that the body creates when the immune system responds to CMV's presence. A pregnant person has a minimal risk that reactivation of CMV may affect her developing baby. If a doctor suspects that a pregnant person has CMV, they may suggest an amniocentesis.
What is perinatal CMV?
Infants who become infected during birth or shortly afterward (perinatal CMV ). This group includes babies infected through breast milk. People who have weakened immune systems, such as those who have had an organ, bone marrow or stem cell transplant, or those who are infected with HIV.
Why does CMV stay dormant?
CMV may cycle through periods when it lies dormant and then reactivates. If you're healthy, CMV mainly stays dormant. When the virus is active in your body, you can pass the virus to other people.
Why do people not know they have CMV?
Once infected, your body retains the virus for life. Most people don't know they have CMV because it rarely causes problems in healthy people. If you're pregnant or if your immune system is weakened, CMV is cause for concern. Women who develop an active CMV infection during pregnancy can pass ...
How does CMV spread?
CMV spreads from person to person through body fluids, such as blood, saliva, urine, semen and breast milk. There is no cure, but there are medications that can help treat the symptoms.
What are the complications of CMV?
Complications of CMV infection can include: Vision loss, due to inflammation of the light-sensing layer of the eye (retinitis) Digestive system problems, including inflammation of the colon (colitis), esophagus (esophagitis) and liver (hepatitis) Nervous system problems, including brain inflammation (encephalitis) Pneumonia.
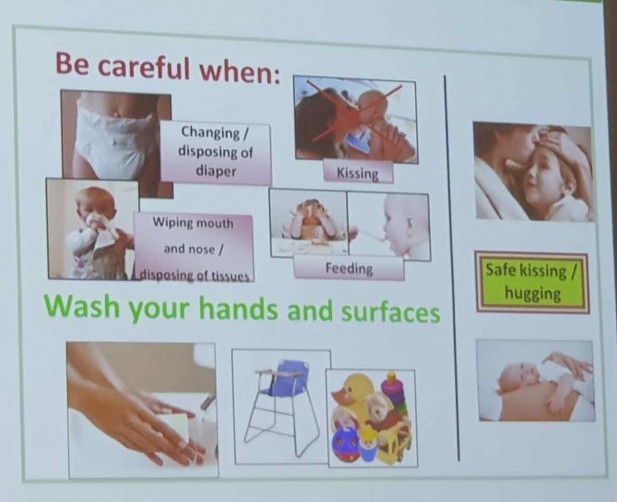
How to prevent CMV?
Careful hygiene is the best prevention against CMV. You can take these precautions: Wash your hands often. Use soap and water for 15 to 20 seconds, especially if you have contact with young children or their diapers, saliva or other oral secretions. This is especially important if the children attend child care.
Is a baby born with congenital CMV healthy?
Most babies who have congenital CMV appear healthy at birth.
What Is Cytomegalovirus?
Cytomegalovirus ( CMV) is a common virus. Over half of adults in the U.S. have it in their body by age 40. CMV spreads easily through an infected person’s saliva or other body fluids. It’s related to the herpes virus, which gives you cold sores.
What test is used to test for CMV?
These include CMV antigen (a part of the virus), a virus culture, or PCR (a molecular test). Serologic tests look for things your immune system makes to fight CMV, called IgM and IgG antibodies, although most healthy people also have them. A biopsy.
What is CMV retinitis?
CMV retinitis is what’s known as an AIDS-defining condition. The virus could also affect your intestines , esophagus , lungs , brain, or nerves. There are different types of cytomegalovirus infection. Congenital. This is when a baby gets CMV from its mother before birth. Primary.
Where does CMV spread?
CMV spreads easily in places with lots of young children, like day-care centers, so anyone who spends time there is at higher risk of getting it. You’re also more likely to get the virus if your immune system is weakened because of a medication or another health condition.
What is the procedure to take a sample of tissue from your intestines?
A biopsy. Your doctor takes a small sample of tissue from your intestines, your esophagus, or your lung and look at it under a microscope.
Does CMV go away on its own?
Your outlook depends on your overall health. In people who have strong immune systems, CMV symptoms almost always go away on their own. Congenital CMV can have lifelong effects. The risks are highest when the mother has their first CMV infection during a pregnancy.
What is the most common treatment for CMV?
Antiviral medications are the most common type of treatment. They can slow reproduction of the virus, but can't eliminate it. Researchers are studying new medications and vaccines to treat and prevent CMV.
Why is CMV testing important?
Testing for CMV can also be important if you have a weakened immune system. For example, if you have HIV or AIDS, or if you've had a transplant, your doctor may want to monitor you regularly.
What tests can detect CMV?
Diagnosis. Laboratory tests — including tests of blood and other body fluids or tests of tissue samples — can detect CMV.
Can a CMV infection be detected while pregnant?
Pregnant women who have already developed CMV antibodies have a very small chance of a reactivation infecting their unborn children. If your doctor detects a new CMV infection while you're pregnant, a prenatal test (amniocentesis) can determine whether the fetus has been infected.
What are cytomegalovirus infection symptoms and signs?
Mono-like symptoms may include fever, malaise (feeling unwell), enlarged lymph nodes, sore throat, muscle aches, loss of appetite, enlarged liver or spleen, and fatigue. Hepatitis-like symptoms and signs may include appetite loss, yellow eyes ( jaundice ), nausea, and diarrhea.
What is cytomegalovirus (CMV) and cytomegalovirus disease?
Cytomegalovirus (pronounced si-to-MEG-a-lo-vi-rus), or CMV, is a virus that belongs to the Herpesviridae family, hence its older name, "human herpes virus 5 (HHV 5)". Other members of this family include herpes simplex viruses (which cause cold sores and genital herpes ), varicella-zoster virus (which causes chickenpox and shingles ), and Epstein-Barr virus (which causes infectious mononucleosis, also known as " mono "). After primary infection, this group of viruses can infect many body systems and remain dormant in those cells for life. This is called "latent" infection. Latent infection can "reactivate" later in life to cause disease again. Primary infection with CMV is common and may be asymptomatic. Primary CMV is one of the common causes of a mononucleosis, or flu-like syndrome, including fever, fatigue, or tiredness, malaise, and other symptoms. Primary infection with CMV has been referred to as "heterophile-negative" mononucleosis because it causes an illness similar to Epstein-Barr virus, but results of heterophile antibody test for EBV will be negative.
What are the risk factors for cytomegalovirus infection?
Those at risk for CMV include young children and adults who work closely with them, people who undergo blood transfusions, people who have multiple sex partners, and previously uninfected people who receive a CMV-infected organ or bone marrow transplant.
What types of disease does reactivation of latent cytomegalovirus cause?
Adults at risk for life-threatening reactivation with CMV disease include those who are immunosuppressed due to advanced HIV disease, those who receive intensive chemotherapy or immune-suppressing drugs, or those who receive organ or bone marrow transplants.
What specialists treat cytomegalovirus infections?
Because CMV may affect any organ system, multiple specialists may take part in the management, such as gastroenterologists ( digestive system specialists) or pulmonologists (lung specialists). An infectious-disease specialist is often consulted as part of the care team to assist with monitoring, preventive antivirals, diagnosis, or treatment of active infection. Pediatric infectious-disease specialists may manage the care of infants with congenital CMV.
How do physicians diagnose cytomegalovirus infection?
A blood test to detect the antibodies will be positive if the person has had a CMV infection. If the antibody test is negative, the person is considered to be uninfected with CMV.
What type of CMV disease is associated with HIV infection?
One of the most common types of CMV disease in people with advanced HIV/AIDS is CMV retinitis, which may cause permanent blindness. Once highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART, or ART) was introduced in 1996, the incidence of CMV retinitis dropped almost 90%. However, some individuals still develop CMV. Some are not able to tolerate ART, or develop resistance, or simply do not adhere to treatment. CMV retinitis is a marker for 60% increased overall mortality in patients with HIV. For those whose T cell count remains low, overall mortality is 100%. In those whose T cells are under 100/microL, a dilated eye exam is recommended every six months for CMV; if T cells are under 50/microL, screening should occur every three months. CMV reactivation in these patients is not limited to the eye and may be difficult to diagnose. Other manifestations of CMV in advanced HIV disease includes encephalitis, peripheral nerve damage, and disease of the gastrointestinal tract ( esophagitis, enteritis, or colitis).
How do you get CMV?
People with CMV may pass the virus in body fluids, such as saliva, urine, blood, tears, semen, and breast milk. CMV is spread from an infected person in the following ways: 1 From direct contact with saliva or urine, especially from babies and young children 2 Through sexual contact 3 From breast milk to nursing infants 4 Through transplanted organs and blood transfusions
How does CMV spread?
CMV is spread from an infected person in the following ways: From direct contact with saliva or urine, especially from babies and young children. Through sexual contact.
What are the long term effects of CMV?
Babies born with CMV can have brain, liver, spleen, lung, and growth problems. The most common long-term health problem in babies born with congenital CMV infection is hearing loss, ...
Can you be infected with CMV?
A person can also be re-infected with a different strain (variety) of the virus. Most people with CMV infection have no symptoms and aren’t aware that they have been infected.
Can valganciclovir be used for CMV?
For babies with signs of congenital CMV infection at birth, antiviral medications, primarily valganciclovir, may improve hearing and developmental outcomes. Valganciclovir can have serious side effects and has only been studied in babies with signs of congenital CMV infection. There is limited information on the effectiveness ...
