
Symptoms
Its proper name is de Quervain's tenosynovitis, but you could also hear it called de Quervain’s disease or de Quervain’s syndrome. It’s a painful inflammation of tendons in your wrist and lower thumb.
Causes
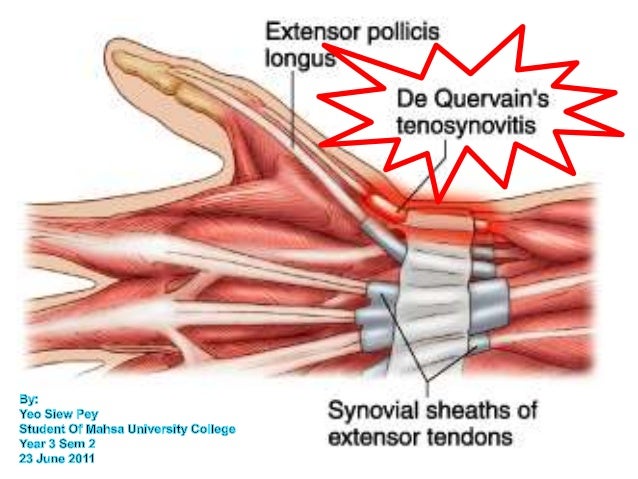
De Quervain’s tendinosis is a painful swelling (inflammation) of specific tendons of the thumb. The condition is also known as de Quervain tendinitis or de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. DeQuervain’s was named after the Swiss surgeon who first described the condition in 1895. Tendons are bands of tissue that attach muscles to bones.
Prevention
If you have de Quervain’s, you’ll probably notice: Pain along the back of your thumb, directly over the two tendons. The condition can happen gradually or start suddenly. In either case, the pain may travel into your thumb or up your forearm.
Complications
De Quervain's (say "duh-kair-VAZ") tendon release is surgery to reduce pressure on a tendon that runs along the side of the wrist near the thumb. The doctor made a cut, called an incision, in the skin on the side of your wrist near the base of your thumb. The surgery opens the tissue over the swollen part of the tendon.
What is de Quervain’s disease?
What is dequervain’s tendinosis?
How do you know if you have de Quervain’s?
What is Dede Quervain's tendon release surgery?
Why is it called de Quervain's?
De Quervain's tendinosis is a painful swelling (inflammation) of specific tendons of the thumb. The condition is also known as de Quervain tendinitis or de Quervain's tenosynovitis. DeQuervain's was named after the Swiss surgeon who first described the condition in 1895.
How do you fix de Quervain's?
TherapiesImmobilizing the thumb and wrist, keeping them straight with a splint or brace to help rest the tendons.Avoiding repetitive thumb movements as much as possible.Avoiding pinching with the thumb when moving the wrist from side to side.Applying ice to the affected area.
What causes de Quervain syndrome symptoms?
De Quervain tenosynovitis affects the two tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. Tendons are ropelike structures that attach muscle to bone. Chronic overuse, such as repeating a particular hand motion day after day, may irritate the covering around the tendons.
Can De Quervain's be cured?
If you start treatment early, your symptoms should improve within 4 to 6 weeks. If de Quervain tenosynovitis starts during pregnancy, symptoms are likely to end around the end of either pregnancy or breastfeeding.
How long does it take for de Quervain to heal?
It may take 6 to 12 weeks for your hand to heal completely. After you heal, you may be able to move your wrist and thumb without pain. How soon you can return to work depends on your job. If you can do your job without using your hand, you may be able to go back after 1 or 2 days.
What happens if De Quervain's goes untreated?
It is important to treat de Quervain's tenosynovitis. If this condition isn't treated, it can permanently limit your movement or cause the tendon sheath to burst. Once your symptoms are better, work to prevent the condition from happening again.
How does De Quervain's develop?
De Quervain's tenosynovitis develops from chronic overuse of the wrist. Examples of repetitive movements that may cause de Quervain's tenosynovitis include: Repetitive hand/wrist movements from an assembly line job. Moving a child in and out of a car seat.
Is surgery necessary for de Quervain?
Summary. De Quervain's disease causes pain when you move your wrist and thumb, and usually a tender swelling at the base of your thumb. If treatment with steroid injections has failed, surgery should relieve your pain.
What is the difference between carpal tunnel and de Quervain's?
Both CTS and de Quervains' tenosynovitis responds well to modalities such as heat or cold. Unlike de Quervains' tenosynovitis, CTS has a nerve that is being compressed. So additional nerve gliding exercises are utilized with the treatment of CTS.
Do cortisone shots work for de Quervain's?
People do get pain relief from cortisone injections for De Quervain's Tenosynovitis. Sometimes one injection can provide months of relief.
How do you massage De Quervain?
Cross Friction Massage over Muscle Belly/Tendons: Gently push into the tissues at the base of your thumb. Move your fingers around until you find the area that is most tender. Begin with applying a gentle force into the tissues and rubbing back and forth (not up and down the arm) and increase intensity as able.
How is de Quervain's diagnosed?
The doctor will ask you to bend your thumb across your palm. Then you'll bend your fingers down over your thumb to make a fist. This movement stretches your tendons. If it hurts on the thumb side of your wrist, you probably have de Quervain's tenosynovitis.
Should I have surgery for de Quervain's?
If individuals with De Quervain's tenosynovitis have pursued nonsurgical treatment for several weeks or months without relief from symptoms—or if the condition is severe—a surgical procedure is typically the next course of action.
Does wrist tendonitis ever go away?
The doctor will examine the wrist and recommend additional treatment options. In rare cases, a person may need surgery to correct wrist tendonitis. Tendonitis can go away completely in time, but some people may need to learn to manage chronic tendonitis.
How successful is surgery for de Quervain?
Results in the present series of 80 cases of De Quervain's tenosynovitis, treated using Le Viet's technique [9] and assessed at a mean 9.5 years, were favorable, with complete resolution in 85% of cases and a 97.5% satisfaction rate (72 very satisfied and 6 satisfied).
How do you massage De Quervain?
Cross Friction Massage over Muscle Belly/Tendons: Gently push into the tissues at the base of your thumb. Move your fingers around until you find the area that is most tender. Begin with applying a gentle force into the tissues and rubbing back and forth (not up and down the arm) and increase intensity as able.
What is de Quervain's tendinitis?
What is de Quervain’s tendinosis? De Quervain’s tendinosis is a painful swelling (inflammation) of specific tendons of the thumb. The condition is also known as de Quervain tendinitis or de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. DeQuervain’s was named after the Swiss surgeon who first described the condition in 1895.
How common is de Quervain's tendinosis?
This condition affects women eight to 10 times more often than men.
How is de Quervain's tendinosis diagnosed?
How is de Quervain’s tendinosis diagnosed? The test most often used to diagnose de Quervain’s tendinosis is the Finkelstein test. Your doctor will ask you to make a fist with your fingers wrapped over your thumb.
Do you need surgery for de Quervain's tendonitis?
De Quervain’s tendinosis usually responds very well to treatment. Many people do not need surgery. Treatment with braces, anti-inflammatory medications and rest often corrects the condition. Cases that require surgery have a high success rate. However, de Quervain’s tendinosis does need to be treated.
Can de Quervain's tendon be treated with anesthesia?
If non-surgical treatments do not help relieve pain and swelling, surgery may be recommended. Surgery for de Que rvain’s tendinosis is an outpatient procedure typically done under local anesthesia or with mild sedation. During the surgery, a tiny cut is made in the sheath through which the tendons pass.
How to diagnose de Quervain syndrome?
De Quervain syndrome is diagnosed clinically, based on history and physical examination, though diagnostic imaging such as X-ray may be used to rule out fracture, arthritis, or other causes, based on the person's history and presentation. The modified Eichoff maneuver, commonly called the Finkelstein's test, is a physical exam maneuver used to diagnose de Quervain syndrome. To perform the test, the examiner grasps and ulnar deviates the hand when the person has their thumb held within their fist. If sharp pain occurs along the distal radius (top of forearm, about an inch below the wrist), de Quervain's syndrome is likely. While a positive Finkelstein's test is often considered pathognomonic for de Quervain syndrome, the maneuver can also cause pain in those with osteoarthritis at the base of the thumb.
What are the most significant work related factors associated with de Quervain's disease?
However, researchers in France found personal and work-related factors were associated with de Quervain's disease in the working population; wrist bending and movements associated with the twisting or driving of screws were the most significant of the work-related factors.
Is de Quervain's disease a conservative disease?
A systematic review and meta-analysis published in 2013 found that corticosteroid injection seems to be an effective form of conservative management of de Quervain's syndrome in approximately 50% of patients, although more research is needed regarding the extent of any clinical benefits. Efficacy data are relatively sparse and it is not clear whether benefits affect the overall natural history of the illness. One of the most common causes of corticosteroid injection failure are subcompartments of the extensor pollicis brevis tendon.
Is de Quervain's disease a causal relationship?
The cause of de Quervain's disease is not established. Evidence regarding a possible relation with occupational risk factors is debated. A systematic review of potential risk factors discussed in the literature did not find any evidence of a causal relationship with occupational factors. However, researchers in France found personal ...
Is De Quervain syndrome a repetitive strain injury?
Proponents of the view that De Quervain syndrome is a repetitive strain injury consider postures where the thumb is held in abduction and extension to be predisposing factors. Workers who perform rapid repetitive activities involving pinching, grasping, pulling or pushing have been considered at increased risk.
How to treat de Quervain's disease?
Home remedies and lifestyle changes. See your doctor if you think you have de Quervain’s. But try these methods at home to feel better and keep your thumb healthy: 1 Ice the area to ease inflammation. 2 Stop doing anything that makes it worse. Avoid repeated motions and pinching moves with your fingers and thumb. 3 Wear the splint as long as your doctor tells you to. 4 Keep doing your exercises.
How old is the most likely person to get de Quervain's tenosynovitis?
Anyone can get de Quervain's tenosynovitis. But these things make it more likely: Age. Adults between 30 and 50 are most likely to get it. Gender. Women are 8 to 10 times more likely to get it than men. Motherhood. It often happens just after pregnancy. Lifting your little bundle of joy repeatedly might bring it on.
Can anyone get de Quervain's tenosynovitis?
Anyone can get de Quervain's tenosynovitis. But these things make it more likely:
Can you go home after de Quervain surgery?
It’s an outpatient procedure, which means you go home just afterward. You'll probably see the physical therapist again for post-surgery exercises to strengthen your thumb and wrist. Home remedies and lifestyle changes. See your doctor if you think you have de Quervain’s.
What Does De Quervain’s Disease Mean?
De Quervain's disease is a condition where there is an inflammation of the tendons of the wrist nearest the thumb. These tendons are encased and normally glide smoothly within synovial sheaths when healthy. While not proven beyond a shadow of a doubt, repetitive tasks are thought to contribute to the development of de Quervain's disease. Once inflammation occurs, movement of the afflicted digits is restricted and causes pain and swelling. The condition may also be referred to as de Quervain's tendinosis, de Quervain's stenosing tenosynovitis, radial styloid tenosynovitis, mother's wrist, mommy thumb, washer woman's syndrome or gamer's thumb.
Who first identified de Quervain's disease?
De Quervain's disease was initially identified by Dr. Fritz de Quervain in 1895. The unusual nature of its other names stems from the fact that the condition is more prevalent in women than men. New mothers are especially susceptible to developing de Quervain's disease due to swelling caused by excess fluids retained during pregnancy.
Why does De Quervain tendonitis occur?
Causes. De Quervain's tendinosis may be caused by overuse. It also is associated with pregnancy and rheumatoid disease. It is most common in middle-aged women.
How to test for de Quervain's tendinosis?
To determine whether or not you have De Quervain's tendinosis, your physician may ask you to perform the Finkelstein test by placing your thumb against your hand, making a fist with your fingers closed over your thumb, and then bending your wrist toward your little finger.
What side of the wrist does De Quervain's tendon pain occur?
If you have De Quervain's tendinosis, this test is quite painful, causing tendon pain on the thumb side of the wrist.
Your Recovery
De Quervain's (say "duh-kair-VAZ") tendon release is surgery to reduce pressure on a tendon that runs along the side of the wrist near the thumb. The doctor made a cut, called an incision, in the skin on the side of your wrist near the base of your thumb. The surgery opens the tissue over the swollen part of the tendon.
When should you call for help?
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if:
Where can you learn more?
Enter G293 in the search box to learn more about "De Quervain's Tendon Release: What to Expect at Home".
Overview
Signs and symptoms
Causes
Pathophysiology
Diagnosis
De Quervain syndrome is mucoid degeneration of two tendons that control movement of the thumb and their tendon sheath. This results in pain and tenderness on the thumb side of the wrist. Radial abduction of the thumb is painful. On occasion, there is uneven movement or triggering the thumb with radial abduction. Symptoms can come on gradually or be noted suddenly.
Treatment
Symptoms are pain and tenderness at the radial side of the wrist, fullness or thickening over the thumb side of the wrist, and difficulty gripping with the affected side of the hand. The onset is often gradual. Pain is made worse by movement of the thumb and wrist, and may radiate to the thumb or the forearm.
History
The cause of de Quervain's disease is not established. Evidence regarding a possible relation with activity and occupation is debated. A systematic review of potential risk factors discussed in the literature did not find any evidence of a causal relationship with activity or occupation. However, researchers in France found personal and work-related factors were associated with de Quervain's disease in the working population; wrist bending and movements associated with th…
Society and culture
De Quervain syndrome involves noninflammatory thickening of the tendons and the synovial sheaths that the tendons run through. The two tendons concerned are those of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus muscles. These two muscles run side by side and function to bring the thumb away from the hand; the extensor pollicis brevis brings the thumb outwards radially, and t…