
What do you mean by denitrification?
The phenomenon of reduction of nitrates and nitrites into atmospheric nitrogen or as an oxide of nitrogen by the action of denitrifying bacteria is known as Denitrification. In this process, nitrogen in the combined state is reduced to its gaseous state.
What are denitrifying bacteria and how do they work?
Denitrifying bacteria are bacteria capable of performing denitrification as part of the nitrogen cycle. They metabolise nitrogenous compounds using the enzyme nitrate reductase, turning nitrogen oxides back to nitrogen gas or nitrous oxide.
What is the impact of denitrification on the atmosphere?
For the purposes of nutrient management, denitrification results in a loss of valuable nitrogen (N), but the impact in the atmosphere will vary. The complete process of denitrification is influenced by the following factors:
What is the product of denitrification?
nitrogen gasThe end product of denitrification is nitrogen gas, which returns to the atmosphere. Nitrate is reduced ultimately to N2 by a series of intermediates such as N2O. Examples of denitrifying bacteria are Pseudomonas and Thiobacillus.
What does denitrification cause?
Denitrification results in the reduction of nitrate to a variety of gases (including NO, N2O, or N2). One of these gases is nitrous oxide (N2O), a potent greenhouse gas that can remain in the air for over 100 years. Nitrous oxide has also been linked with depleting stratospheric ozone.
What does denitrification produce for plants?
Denitrification is a microbial process occurring in soils, both producing and consuming the potent greenhouse gas nitrous oxide (NO), competing for nitrate with plants and hydrological leaching pathways, removing nutrients and reactive nitrogen from the biosphere, and closing the global nitrogen cycle.
What happens during denitrification?
Denitrification is the microbial process of reducing nitrate and nitrite to gaseous forms of nitrogen, principally nitrous oxide (N2O) and nitrogen (N2). A large range of microorganims can denitrify. Denitrification is a response to changes in the oxygen (O2) concentration of their immediate environment.
What happens in denitrification process?
Denitrification. Denitrification is the process that converts nitrate to nitrogen gas, thus removing bioavailable nitrogen and returning it to the atmosphere. Dinitrogen gas (N2) is the ultimate end product of denitrification, but other intermediate gaseous forms of nitrogen exist (Figure 7).
What is the benefit of denitrification?
Denitrification reduces the amount of nitrite ions discharged to the receiving water. The reduction of nitrite ions discharged to the receiving water reduces tox-icity concerns related to aquatic life. Activated sludge processes that have a total nitrogen discharge limit must denitrify.
Which molecules are created during denitrification?
The resulting denitrification products are molecular nitrogen (N2) and nitrogen oxide (NOx). This process is carried out by the anaerobic such as Pseudomonas spp., Clostridium spp., Bacillus spp., and Alcaligenes spp. (Struwe & Kjøller, 1989).
What is denitrification short answer?
Definition of denitrification : the loss or removal of nitrogen or nitrogen compounds specifically : reduction of nitrates or nitrites commonly by bacteria (as in soil) that usually results in the escape of nitrogen into the air.
What is a negative result of denitrification?
The negative aspect of denitrification is that it takes place in soils that are waterlogged. In this situation, water will move downward in the soil. Because nitrate can move easily with water, nitrate can move below the root zone of plants and potentially on down into groundwater.
What type of reaction is denitrification?
Denitrification is a type of anaerobic respiration that uses nitrate as an electron acceptor.
What happens to nitrogen during the process of denitrification?
Denitrification is the process during which the nitrogen compound is released back into the atmosphere by converting nitrate (NO3-) into gaseous nitrogen (N). The process of denitrification is carried out during the absence of oxygen by Thiobacillus species and Pseudomonas bacteria present in the soil.
What happens during the denitrification stage of the nitrogen cycle?
Denitrification. Denitrification is the process in which the nitrogen compounds make their way back into the atmosphere by converting nitrate (NO3-) into gaseous nitrogen (N). This process of the nitrogen cycle is the final stage and occurs in the absence of oxygen.
What happens during denitrification?
Denitrification is the process of the reduction of nitrates or nitrites into gaseous nitrogen with the help of facultative anaerobic bacterias.
What is the importance of denitrification?
Denitrification is an essential step of the nitrogen cycle which is one of the most nutrient cycles in the environment to maintain the balance of n...
What is the denitrification equation?
The denitrification process is a redox reaction which can be written as: ({rm{2 N}}{{rm{O}}{rm{3}}}^{rm{ - }}{rm{ + 10}}{{rm{e}}^{rm{ - }}}{rm{ + 1...
What is the difference between nitrification and denitrification?
Nitrification and denitrification are the two important processes of the nitrogen cycle. In the process of Nitrification, nitrifying bacteria oxidi...
What is the difference between Denitrification and Ammonification?
Denitrification process is carried by bacteria, they convert nitrates (left( {{rm{N}}{{rm{O}}_{rm{3}}}^{rm{ - }}} right)) to nitrogen gas (left( {{...
What is denitrification?
Denitrification is the process during which the nitrogen compound is released back into the atmosphere by converting nitrate (NO3-) into gaseous ni...
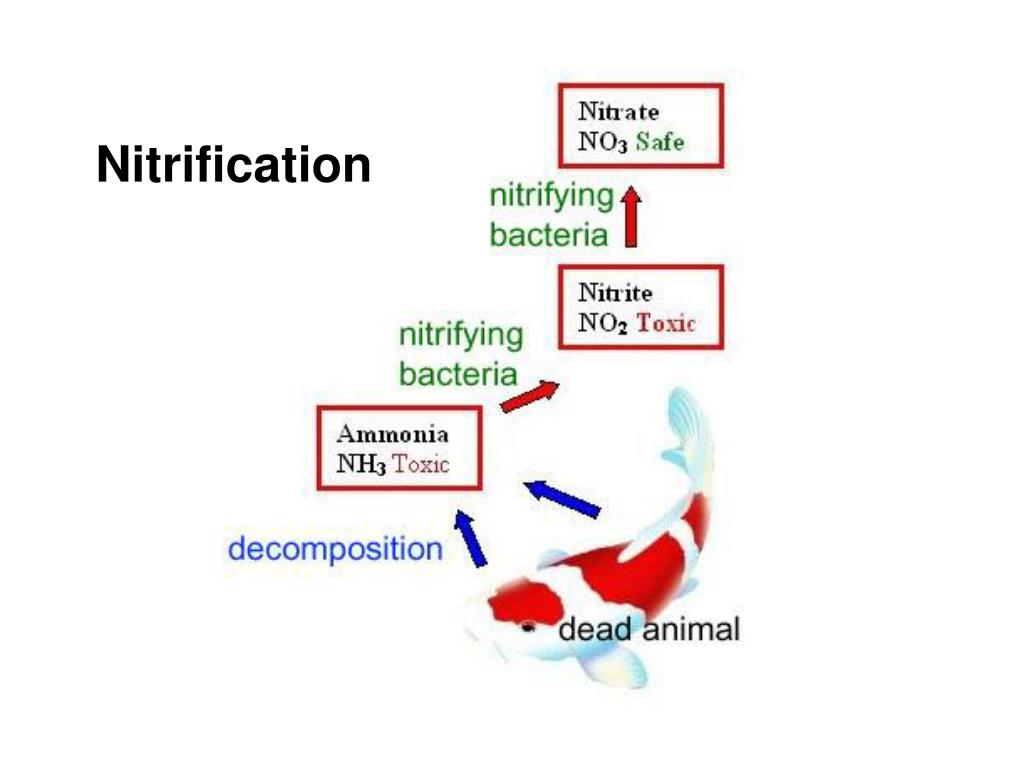
What is nitrification?
The fixing of atmospheric nitrogen in the form of nitrites and nitrates by microorganisms is called nitrogen fixation. It is utilized by plants and...
Name some denitrifying microorganisms?
Thiobacillus denitrificans and Micrococcus denitrificans are the examples of denitrifying microorganisms.
What is the effect of denitrification?
Denitrification reduces the amount of fixed nitrogen present in the soil.
What is Denitrification Process?
Combined nitrogen is the nitrogen along with any other element, e.g., nitrate, nitrite, ammonium, amines, etc. This process is facilitated by microorganisms. The common organisms that facilitate denitrification are facultative anaerobic bacteria. Denitrification is a process of respiration and the acquisition of energy for these bacteria.
How does denitrification affect the environment?
Following are some of the significance of denitrification in our environment:#N#1. Denitrification maintains homeostasis in the environment, although it is naturally unfavorable for soil fertil ity and plant growth it maintains the balance in the soil by converting nitrates into gaseous nitrogen thereby maintaining the concentration of atmospheric nitrogen content.#N#2. It plays a vital role in industrial and sewage water treatment by scavenging all the waste materials containing nitrogen content.#N#3. Also helps in maintaining nitrogen concentration in aquatic environments as well.#N#4. Since this process converts nitrates into free atmospheric nitrogen, it depletes fertility in the soil, thereby, reducing agricultural productivity.
What is the process of nitrogen in soil?
In wet soils, these soil bacteria convert nitrates and nitrites into various nitrogen gases like nitrous oxide, nitric oxide, etc as a result of their reduction mechanisms by the action of several enzymes.
What is the process of reducing nitrates into gaseous nitrogen?
Denitrification : Denitrification is the process of the reduction of nitrates or nitrites into gaseous nitrogen by facultative anaerobes. This process usually takes place when there is no oxygen or very little oxygen in the environment such as in the deep soil near the water table.
What are the steps of the nitrogen cycle?
The steps of the nitrogen cycle are nitrogen fixation, nitrification, nitrogen assimilation, ammonification, and denitrification. Let us study in brief the nitrogen cycle before studying denitrification in detail.#N#1. Nitrogen Fixation : It is the process of fixing atmospheric nitrogen into the soil mainly through biological processes via bacteria or sometimes by physical processes which require a lot of energy with the release of enormous amounts of heat, pressure, and energy. In this process, nitrogen is converted to either ammonia or nitrate.#N#2. Nitrification: It is a two step process where the first reaction is the conversion of ammonia into nitrate and the second reaction is the further conversion of nitrate into nitrite.#N#3. Nitrogen Assimilation : The process in which the nitrates and ammonia produced in the process of nitrogen fixation and nitrification are assimilated or incorporated or absorbed by plants and animals is referred to as nitrogen assimilation.#N#4. Ammonification: Large amounts of organic nitrogen compounds are formed during assimilation like amino acids, proteins, a, and nucleic acids. In this process, these organic nitrogen are converted back to ammonia which is then available for either assimilation or nitrification.#N#5. Denitrification: Denitrification is the process of the reduction of nitrates or nitrites into gaseous nitrogen by facultative anaerobes. This process usually takes place when there is no oxygen or very little oxygen in the environment such as in the deep soil near the water table. Therefore, wetlands are the areas where excess nitrogen is reduced through denitrification processes.#N#Since nitrogen is a source of energy for most anaerobes, this is a significant process in the nitrogen cycle. In wet soils, these soil bacteria convert nitrates and nitrites into various nitrogen gases like nitrous oxide, nitric oxide, etc as a result of their reduction mechanisms by the action of several enzymes.
What is the opposite of nitrification?
In the process of Nitrification, nitrifying bacteria oxidise ammonia to nitrite which is further oxidised into nitrate. On the other hand, denitrification is the opposite of nitrification. In the denitrification process, microorganisms reduce nitrate back to nitrogen. Q.5.
What are the factors that determine the rate of denitrification?
Various factors govern the process of denitrification such as pH, temperature, hydraulic conditions, quantity and quality of organic carbon content, microbial population, and nitrate concentration. #N#1. pH – The rate of denitrification is greatly affected by soil pH. The rate of denitrification is very low below the pH of 4.8 and the rate increases with an increase in soil pH and the reactions were very rapid at a p H range of 8.0 to 8.6.#N#2. Temperature- The rate of denitrification is raised rapidly with an increase in temperature from 2 o C to 2 5 o C. The optimum temperature for the process of denitrification is about 6 0 o C.#N#3. Hydraulic conditions – The degree of the water content (moisture content) of the soil has a deep influence on the rate of denitrification. Lower the moisture content, lower the process of denitrification. The higher the moisture content, the greater is the rate of denitrification, up to a certain level. The critical moisture content in the soil must be 60 of the water holding capacity of the soil.#N#4. Quantity and quality of organic content- Carbon content plays a very important role in the denitrification process. The quality and quantity of carbon content greatly affect the growth of denitrifying bacteria which in contrast affects denitrification. The greater the organic content in the soil the more is the growth of denitrifiers, and therefore denitrification progresses rapidly and vice versa. A similar thesis applies to nitrate concentration as well.#N#5. Microbial communities- The number of microbes greatly affects the process of denitrification. Under optimum conditions, microbes grow luxuriantly. As the number of bacteria increases, the rate of denitrification increases tremendously as well.
How does denitrification occur?
It is a naturally occurring, microbially mediated process, where nitrate is used as a form of energy for denitrifiers.
What is the process of denitrification?
Denitrification is a universal process for both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, which occurs naturally under the extreme concentrations in managed ecosystems – marine and freshwater environments, ...
When does the Denitrification process occur?
Denitrification is more active in the regions where water-filled pore space in the soil exceeds 60 per cent. The end-product gas depends on the soil conditions and the microbial community. As the deficiency of oxygen increases, microbes perform its functions by converting more of the nitrate to dinitrogen (N 2) gas. For the purposes of nutrient management, denitrification results in a loss of valuable nitrogen (N), but the impact in the atmosphere will vary.
What is the process of removing nitrogen from soil?
Denitrification is a microbial process of removing valuable nitrogen from the soil and releasing the greenhouse gas nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and the tropospheric pollutant nitric oxide (NO). The biological cycle of denitrification involves a cascade of different enzymes, which reduces nitrate to dinitrogen. Also Read: Biogeochemical Cycles.
How does denitrification affect the atmosphere?
For the purposes of nutrient management, denitrification results in a loss of valuable nitrogen (N), but the impact in the atmosphere will vary.
What bacteria are responsible for denitrification?
The process of denitrification is carried out during the absence of oxygen by Thiobacillus species such as Clostridium and Pseudomonas bacteria present in the soil. In this process, the genus of Gram-negative bacteria degrades nitrate compounds present in the soil and aquatic systems into nitrous oxide (N 2 O)and nitrogen gas, ...
What is the main factor that influences the process of denitrification?
The main factor which influences the process of denitrification is the organic content in the soil. The organic matter available within the soil is the only source of nutrition for the bacteria. Therefore, the soil bacteria require a source of readily available organic matter, either from the plants, from the soil or from other additional sources.
What is Denitrification?
Denitrification is the process by which nitrogen is taken from soil or aquatic systems, converted into a gas and released into the atmosphere. Simply explained, nitrogen is found in compounds in the ground and aquatic systems in the form of nitrate and nitrite.
Denitrification in Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the cycle nitrogen goes through on planet Earth. It is a biogeochemical process where nitrogen is converted into different forms as it passes through the soil to organisms to the atmosphere and back to the soil again and again. It includes many stages and processes typically listed in the following order:
Where does nitrification occur?
Nitrifying bacteria are slow growing organisms, and nitrification problems usually occur in large reservoirs or low-flow sections in the system. Operational practices that ensure short residence time and circulation within the system can minimize nitrification problems. Low circulation areas of the system , such as dead-ends and reservoirs are prime areas for nitrification occurrence since detention time and sediment buildup can be much greater than in other parts of the system.
What is the main cause of nitrification?
Excess nitrogen in the form of ammonia in finished water can be the principal cause of nitrification since ammonia serves as the primary substrate in the nitrificaiton process. Ammonia, nitrate and nitrite can typically be found in surface water supplies as a result of natural processes.
Why do we need to nitrify wastewater treatment plants?
Why do we need to do nitrification in the wastewater treatment plant? For one thing, ammonia left in the treated effluent can be toxic to fish. Also, the nitrifiers in the receiving waters will be working to convert that ammonia to nitrate. That conversion will use up oxygen. By nitrifying the plant effluent, the oxygen demand on the receiving waters will be reduced.
How to maintain nitrifying microbes?
To maintain nitrifying microbes in a process, the sludge age must be kept high enough to retain a sufficient population of these organisms. Under toxic and/or cold weather conditions, the growth rate of natural nitrifying populations tends to slow appreciably, causing nitrifiers to wash out of the system. Thus, it can be a problem to maintain ammonia removal if such conditions persist.
Why is pH important in nitrification?
First, a reduction of total alkalinity may accompany nitrification because a significant amount of bicarbonate is consumed in the conversion of ammonia to nitrite. A model that was developed in 1974 indicates that 8.64 mg/L of bicarbonate (HCO 3) will be utilized for each mg/L of ammonia-nitrogen oxidized. While reduction in alkalinty does not impose a direct public health impact, reductions in alkalinity can cause reductions in buffering capacity, which can impact pH stability and corrosivity of the water toward lead and copper. Secondly, nitrifying bacteria are very sensitive to pH. Nitrosomonas has an optimal pH between approximately 7.0 and 8.0, and the optimum pH range for Nitrobacter is approximately 7.5 to 8.0. Some utilities have reported that an increase in pH (to greater than 9) can be used to reduce the occurrence of nitrification.
What is biological nitrification?
Biological nitrification is the microbe-mediated process of oxidizing ammonia to remove nitrogenous compounds from wastewaters. Domestic sewage typically contains 20 to 40 mg/L of ammonia nitrogen (NH 4- N). Organic matter containing nitrogen, e.g., protein and nucleic acid, also biodegrades to release ammonia.
How do bacteria remove nitrogen from wastewater?
Bacteria remove nitrogen from wastewater by a two step biological processes: nitrification followed by denitrification. Technically, it is a three step process: ammonification precedes nitrification and denitrification.
What is the process of denitrification?
Denitrifying bacteria are a part of the N cycle, and consists of sending the N back into the atmosphere. The reaction above is the overall half reaction of the process of denitrification. The reaction can be further divided into different half reactions each requiring a specific enzyme.
What is denitrification in soil?
Denitrification is performed by a variety of denitrifying bacteria that are widely distributed in soils and sediments and that utilize oxidized nitrogen compounds in absence of oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor. They metabolise nitrogenous compounds using various enzymes, turning nitrogen oxides back to nitrogen gas (.
What is the role of denitrifying bacteria in methane?
Role of denitrifying bacteria as a methane sink. Denitrifying bacteria have been found to play a significant role in the oxidation of methane (CH4) (where methane is converted to CO2, water, and energy) in deep freshwater bodies of water.
Why are denitrifying bacteria considered bioremediators?
Denitrifying bacteria are said to be high quality bioremediators because of their adaptability to a variety of different environments, as well as the lacking any toxic or undesirable leftovers, as are left by other metabolisms.
What is denitrifying bacteria?
Denitrifying bacteria are a diverse group of bacteria that encompass many different phyla. This group of bacteria, together with denitrifying fungi and archaea, is capable of performing denitrification as part of the nitrogen cycle. Denitrification is performed by a variety of denitrifying bacteria that are widely distributed in soils and sediments and that utilize oxidized nitrogen compounds in absence of oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor. They metabolise nitrogenous compounds using various enzymes, turning nitrogen oxides back to nitrogen gas (#N#N 2 {displaystyle {ce {N2}}}#N#) or nitrous oxide (#N#N 2 O {displaystyle {ce {N2O}}}#N#).
Why do denitrifying bacteria switch from aerobic respiration to denitrification?
The majority of denitrifying bacteria are facultative aerobic heterotrophs that switch from aerobic respiration to denitrification when oxygen as an available terminal electron acceptor (TEA) runs out. This forces the organism to use nitrate to be used as a TEA. Because the diversity of denitrifying bacteria is so large, ...
How does denitrification produce ATP?
Denitrifying bacteria use denitrification to generate ATP. The most common denitrification process is outlined below, with the nitrogen oxides being converted back to gaseous nitrogen: The result is one molecule of nitrogen and six molecules of water.
