
What do each of the waves on an ECG mean?
What does each wave of an ECG measure? An electrocardiogram — abbreviated as EKG or ECG — is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. A normal heartbeat on ECG will show the timing of the top and lower chambers.
What is normal ECG Wave?
Normal ECG wave: A normal ECG makes a specific pattern of three recognizable waves in a cardiac cycle. These wave are- P wave, QRS wave and T-wave, P-R interval, S-T segment; P-wave: It is a small upward wave that appears first;
What are EKG waves?
Electrocardiogram. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical signal from your heart to check for different heart conditions. Electrodes are placed on your chest to record your heart's electrical signals, which cause your heart to beat. The signals are shown as waves on an attached computer monitor or printer.
What does a wave in an ECG tracing indicate?
leads and their geometry. The EKG waveform comes from a measurement of surface voltages between 2 leads. A wave that is travelling towards the positive (+) lead will inscribe an upwards deflection of the EKG; conversely a wave traveling away from the positive lead will inscribe a downward deflection.
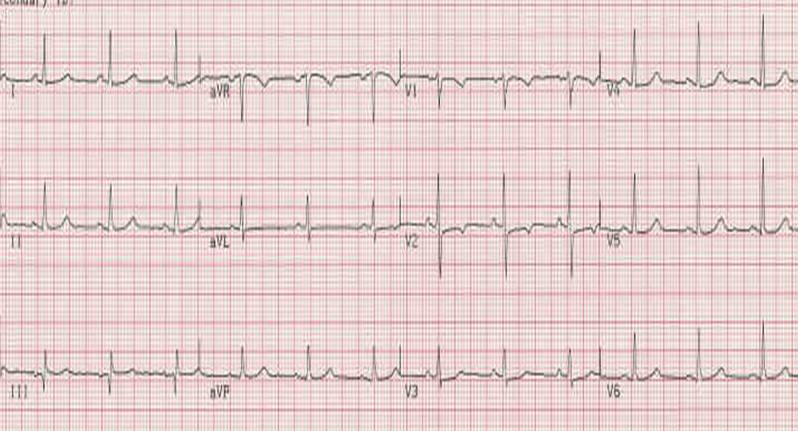
What do the P QRS and T waves represent?
The P wave in an ECG complex indicates atrial depolarization. The QRS is responsible for ventricular depolarization and the T wave is ventricular repolarization.
What are the 3 waves of the ECG called and what do they represent?
Components of ECG The P wave represents the normal atrium (upper heart chambers) depolarization; the QRS complex (one single heart beat) corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles (lower heart chambers); the T wave represents the re-polarization (or recovery) of the ventricles.
What do the T wave represent?
Introduction. The T wave on the ECG (T-ECG) represents repolarization of the ventricular myocardium. Its morphology and duration are commonly used to diagnose pathology and assess risk of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
What does QRS stand for?
QRSAcronymDefinitionQRSQuantronic Resonance SystemQRSQuality of Reading SurveyQRSQuality Review Services, IncQRSQuick Reference System22 more rows
Why is the T wave positive?
In most leads, the T wave is positive. This is due to the repolarization of the membrane. During ventricle contraction (QRS complex), the heart depolarizes.
How does the U wave appear?
This is known as a U wave. In a normal heart beat, the T wave represents repolarisation of the ventricles, specifically the repolarisation of the AV node and bundle branches. The U wave occurs when the ECG machine picks up repolarisation of the Purkinje fibres.
What is ST and T wave abnormality?
"Primary" ST-T Wave Abnormalities (ST-T wave changes that are independent of changes in ventricular activation and that may be the result of global or segmental pathologic processes that affect ventricular repolarization): Drug effects (e.g., digoxin, quinidine, etc) Electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hypokalemia)
What does high T wave mean?
Tall T-waves (also called hyper-acute T waves) can be an early sign of ST-elevation myocardial infarction. The morphology of the T waves can begin to broaden and peak within 30 minutes of complete coronary artery occlusion, and thus may be the earliest sign of myocardial infarction on the EKG.
What does the T wave in an electrocardiogram represent quizlet?
Correct: The T wave of the ECG represents ventricular repolarization as the heart rests and prepares to contract again. As pressure in the aorta rises due to atherosclerosis, more ventricular pressure is required to open the aortic valve.
What causes an abnormal T wave reading?
Primary T-wave abnormalities (ischemia or injury) are due to alterations in myocardial cellular electrophysiology and secondary T-wave abnormalities (bundle branch block or ventricular Hypertrophy) are subsequent to alterations of sequence of ventricular activation.
What does a peaked T wave mean?
Overview. Peaked T waves refers to the pointed, tall, peaked shape of T waves on the EKG in the setting of certain abnormalities such as hyperkalemia.
What is the P wave in ECG?
ECG interpretation starts with assessment of the P-wave and PR interval. The P-wave is generated by depolarization (activation, contraction) of the atria. The PR interval is the interval between the start of the P-wave and the start of the QRS complex. The PR interval determines whether impulse transmission from atria to ventricles is normal. The isoelectric (flat) line between the end of the P-wave and the start of the QRS complex is called the PR segment. The PR segment is the baseline (also referred to as reference line or isoelectric line) of the ECG curve. Thus, when measuring the amplitude of a wave on the ECG, the PR segment is the baseline. Refer to Figure 1.
What is the T wave?
The T-wave reflects the rapid repolarization (recovery) of the myocardium and T-wave changes occur in numerous conditions. T-wave changes are frequently misunderstood. The transition from the ST segment to the T-wave should be smooth. The normal T-wave is somewhat asymmetric, with a steeper downward slope.
What is the QT interval?
QT duration reflects the total duration of ventricular depolarization (activation) and repolarization (recovery). It is measured from the start of the QRS complex to the end of the T-wave. The QT interval increases at slower heart rates and vice versa (i.e it decreases at higher heart rates). Therefore, to judge whether the QT interval is normal it is necessary to take the heart rate into account. The heart rate adjusted QT interval is the corrected QT interval, or simply the QTc interval. A long QTc interval causes electrical instability in the ventricles and this may cause lethal ventricular arrhythmias.
What is the heart rate adjusted QT interval?
The heart rate adjusted QT interval is the corrected QT interval, or simply the QTc interval. A long QTc interval causes electrical instability in the ventricles and this may cause lethal ventricular arrhythmias.
Which ventricle is larger, the QRS or the adipose?
Because the left ventricle is usually considerably larger than the right ventricle, the QRS complex is actually a reflection of the electrical potentials generated by the left ventricle.
Is ventricular depolarization a QRS complex?
In other words, if ventricular depolarization only generates a Q-wave and an R-wave, that complex may still be referred to as a QRS complex. However, one may also be more explicit and refer to such a complex as a QR complex.
What is the basic of ECG?
Basics of ECG- Interpretation of waves and intervals. A normal ECG is electrical representation of a normal heart beat or sinus rhythm. The cardiac action potential causing deporalization and repolarization of various cardiac tissues gives a pattern of rhythic change is Electrocardiograph which can be used to diagnose different diseases of the CVS.
What is normal ECG?
A normal ECG is electrical representation of a normal heart beat or sinus rhythm. The cardiac action potential causing deporalization and repolarization of various cardiac tissues gives a pattern of rhythic change is Electrocardiograph which can be used to diagnose different diseases of the CVS.
Where does the P wave originate?
A normal P wave originates from the Sinoatrial Node , SA node. It represents atrial depolarization.Normal P wave has a
What is the J point in a QRS?
The J point is the the junction between the termination of the QRS complex and the beginning of the ST segment. Abnormal J (slurring elevation) is seen in Hypothermia -” Osborne Wave.”
What is the EKG waveform?
In order to successfully read an EKG, you have to first understand the basics of an EKG waveform. The main components of an EKG wave include the P wave, PR segment, QRS complex, ST segment, T wave, and TP segment.
What are the components of an EKG wave?
The main components of an EKG wave include the P wave, PR segment, QRS complex, ST segment, T wave, and TP segment.
What is the difference between diastole and systole?
Diastole occurs when the heart is at rest, especially the ventricles, allowing blood to fill the cardiac chambers. Systole occurs when the heart is contracting, especially the ventricles, pushing blood forward into the pulmonary artery and aorta.
Why is conduction velocity slowed through the AV node?
Conduction velocity is slowed through the AV node to allow time for the atria to contract before depolarizing the ventricles.
Which bundle branch depolarizes the right ventricle?
The right bundle branch mainly depolarizes the right ventricle, and the left bundle branch mainly depolarizes the left ventricle.
Where does cardiac action potential exit?
The cardiac action potential will then exit the AV node, and enters the bundle of His, followed by the right and left bundle branches, and lastly through the Purkinje fibers.
Where does the venous blood enter the right atrium?
The venous blood from the systemic vasculature enters the right atrium via the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava.
What is the first wave of ECG?
In a normal ECG, there's three distinct waves. The first wave is the P wave, which represents the depolarization of the atria. This happens right before the atria contract and push blood into the ventricles. The next wave is called the QRS wave.
What is an ECG?
Let's review. The electrocardiogram or ECG is a test that records the electrical activity of your heart. It can detect the electrical impulses that move through the heart, providing a graphic tracing of how your heart is performing. In a normal ECG, there's three distinct waves.
What does the QRS wave represent?
In contrast, the ventricles are the muscular pumps of the heart, and the QRS wave represents their depolarization - it is much larger of a wave. T Wave. After the QRS complex, we see another small peak, and this is called the T wave. The T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles.
Why is the QRS wave associated with the first heart sound?
We remember that the contraction of the ventricles causes the AV valves to close, and this causes the first heart sound, 'lub.' So the first heart sound is also associated with the QRS wave.
What does it mean when an ECG is flatlined?
You've probably seen one if you've ever watched a television drama based in a hospital, because when one of your favorite characters 'flatlined,' that meant that the ECG was no longer detecting an electrical charge, and you heard that familiar flatline 'beeeeep' of the ECG monitor.
How does an ECG work?
Now, you don't feel these impulses, but they can be picked up and graphed as an electrocardiogram or ECG, which is simply a recording of the flow of the electrical current through the heart. This is a common test used to detect problems in the heart. You've probably seen one if you've ever watched a television drama based in a hospital, because when one of your favorite characters 'flatlined,' that meant that the ECG was no longer detecting an electrical charge, and you heard that familiar flatline 'beeeeep' of the ECG monitor.
What is the second heart sound?
This means that the ventricles are relaxed and under less pressure. This causes the semilunar valves to close, so the second heart sound, 'dub, ' happens shortly after the T wave appears on the ECG.
What is wave on EKG?
Waves are the different upward or downward deflections represented on the EKG tracing. They are the product of the action potentials created during the cardiac stimulation, and repeated from one heart beat to another, barring alterations.
What is the Q wave in precordial leads?
Precordial Leads: Q waves are not to be seen in leads V1-V2. Normally a Q wave can be seen in leads V5-V6, usually less that 0.04 s wide, 2 mm deep and it should never exceed 15% of the QRS complex.
What is the second negative wave in the QRS complex?
S wave: it is the second negative wave in the QRS complex, appearing after the R wave.
What is the Q wave?
Q wave: if the first wave of the QRS complex is negative, it is referred to as Q wave.
What is the maximum amplitude of a T wave?
Its maximum amplitud is less than 5 mm in limb leads and less than 15 mm in precordial leads.
How long is the duration of a QRS wave?
It consists of a collection of waves which represents the ventricular depolarisation. Its duration ranges from 0.06 s and 0.10 s. It can present different morphologies depending on the lead (read QRS complex morphology ).
How deep is a Q wave?
A normal Q wave is usually narrow and shallow (less that 0.04 s wide, 2 mm deep). Generally it does not exceed 25% of the QRS complex. A relatively deep Q wave can be seen in lead III in horizontally positioned hearts; a QS pattern can be seen in lead aVL in vertically positioned hearts.
What is EKG interpretation?
ECG (EKG) Interpretation. As with all investigations the most important things are your findings on history, examination and basic observations. Having a good system will avoid making errors. To start with we will cover the basics of the ECG, how it is recorded and the basic physiology. The 12-lead ECG misleadingly only has 10 electrodes (sometimes ...
How many ECGs are recorded 10 minutes apart?
If you are concerned that there are dynamic changes in an ECG it is helpful to ask for serial ECGs (usually three ECGs recorded 10 minutes apart) so they can be compared. These should always be labelled 1, 2 and 3.
What is Q wave?
A q-wave is an initial downward deflection in the QRS complex. These are normal in left-sided chest leads (V5, 6, lead I, aVL) as they represent septal depolarization from left to right. This is as long as they are <0.04secs long (1 small square) and <2mm deep.
What does it mean when a P wave is not associated with a QRS complex?
At this point you can also assess whether each p wave is associated with a QRS complex. P-waves not in association with QRS complexes indicate complete heart block.
How many electrodes are in the heart?
The leads can be thought of as taking a picture of the heart’s electrical activity from 12 different positions using information picked up by the 10 electrodes. These comprise 4 limb electrodes and 6 chest electrodes.
What is the axis of the heart?
Axis is the sum of all the electrical activity in the heart. The contraction travels from the atria to the right and left ventricles. As the left ventricle is larger and more muscular normal axis lies to the left (at -30 degrees to 90 degrees – see Figure 5).
When electrical activity travels towards a lead, the deflection is net positive?
When electrical activity (or depolarisation) travels towards a lead, the deflection is net positive. When the activity travels away from the lead the deflection is net negative. If it is at 90 degrees then the complex is ‘isoelectric’ i.e. the R and S wave are the same size. This can often be seen in V4 (see Figure 3).
What is ECG interpretation?
ECG interpretation includes an assessment of the morphology (appearance) of the waves and intervals on the ECG curve. Therefore, ECG interpretation requires a structured assessment of the waves and intervals. Before discussing each component in detail, a brief overview of the waves and intervals is given.
Which wave progression follows the same rules as R wave progression?
T-wave progression follows the same rules as R-wave progression (see earlier discussion).
How many vectors are generated by depolarization of the ventricles?
Depolarization of the ventricles generates three large vectors, which explains why the QRS complex is composed of three waves. It is fundamental to understand the genesis of these waves and although it has been discussed previously a brief rehearsal is warranted. Figure 7 illustrates the vectors in the horizontal plane. Study Figure 7 carefully, as it illustrates how the P-wave and QRS complex are generated by the electrical vectors.
Why are R waves high?
It is important to assess the amplitude of the R-waves. High amplitudes may be due to ventricular enlargement or hypertrophy. To determine whether the amplitudes are enlarged, the following references are at hand:
Which side of the ventricular septum is depolarized?
The ventricular septum receives Purkinje fibers from the left bundle branch and therefore depolarization proceeds from its left side towards its right side . The vector is directed forward and to the right. The ventricular septum is relatively small, which is why V1 displays a small positive wave (r-wave) and V5 displays a small negative wave (q-wave). Thus, it is the same electrical vector that results in an r-wave in V1 and q-wave in V5.
Why is Q wave important?
The Q-wave. It is crucial to differentiate normal from pathological Q-waves, particularly because pathological Q-waves are rather firm evidence of previous myocardial infarction. However, there are numerous other causes of Q-waves, both normal and pathological and it is important to differentiate these.
Which direction do vectors resulting from activation of the ventricular free walls go?
The vectors resulting from activation of the ventricular free walls are directed to the left and downwards ( Figure 7 ). The explanation for this is as follows:
The Normal ECG (EKG) Waves, Intervals, Durations and Rhythm
Overview of The Normal Electrocardiogram
- Figure 1. The classical ECG curve with its most common waveforms. Important intervals and points of measurement are depicted. ECG interpretation requires knowledge of these waves and intervals.
The P-Wave, PR Interval and PR Segment
- ECG interpretation starts with assessment of the P-wave and PR interval. The P-wave is generated by depolarization (activation, contraction) of the atria. The PR interval is the interval between the start of the P-wave and the start of the QRS complex. The PR interval determines whether impulse transmission from atria to ventricles is normal. The i...
The QRS Complex
- The QRS complex reflects the depolarization (activation, contraction) of the ventricles. Although it may not always include a Q-wave, R-wave and S-wave, it is still referred to as a QRS complex. In other words, if ventricular depolarization only generates a Q-wave and an R-wave, that complex may still be referred to as a QRS complex. However, one may also be more explicit and refer to …