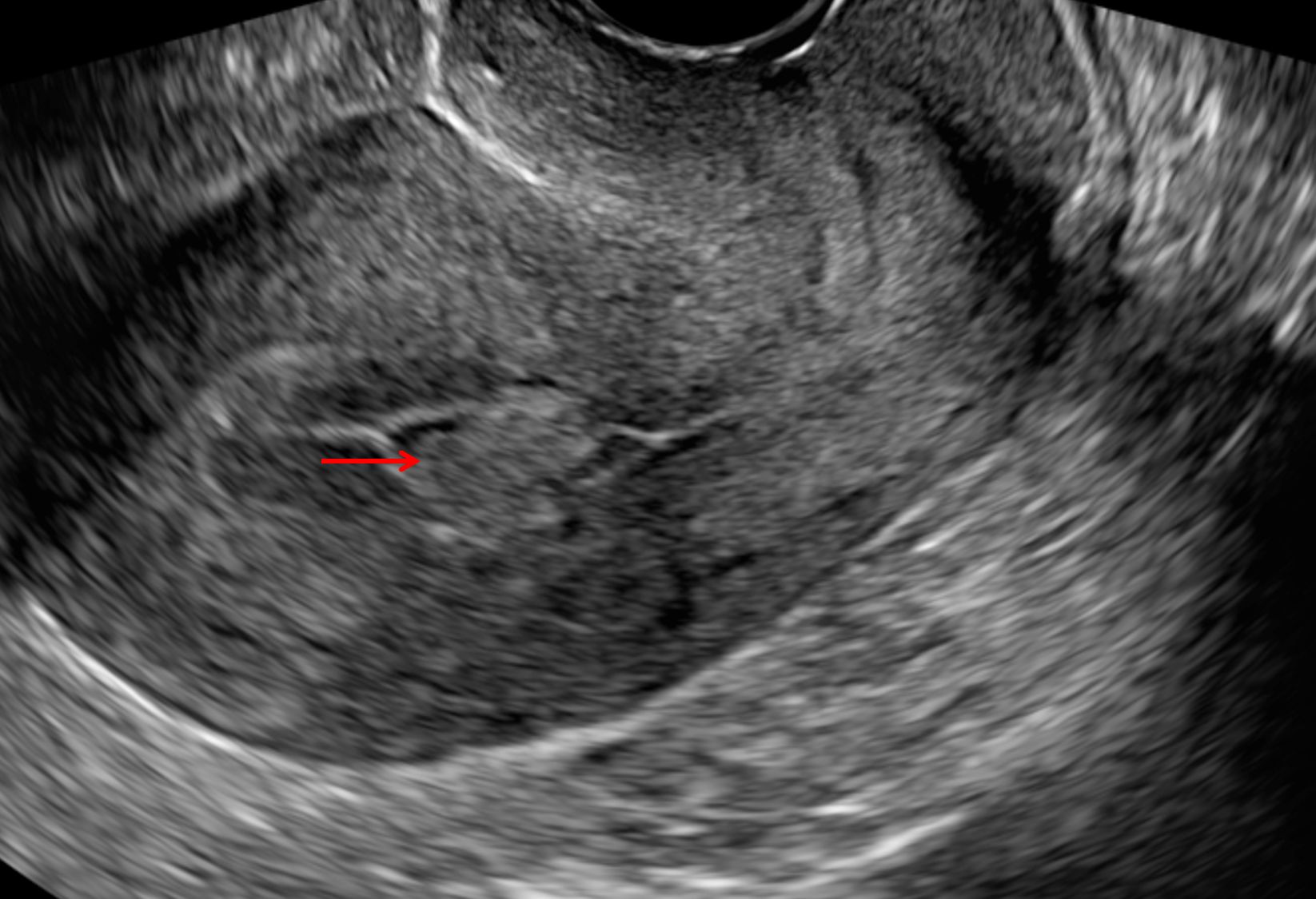
Ultrasound is used to diagnose the presence and monitor the growth of fibroids: uncomplicated leiomyomas are usually hypoechoic, but can be isoechoic, or even hyperechoic compared to normal myometrium. calcification is seen as echogenic foci with shadowing. Is hyperechoic endometrium
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer; the functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, and the elephant shrew. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrou…
Full Answer
What does echogenic endometrium mean?
What does endometrium homogeneous mean? The endometrial echogenicity should be defined as ‘uniform‘, if the endometrium is homogeneous and with symmetrical anterior and posterior sides. This definition includes the different appearances seen throughout the menstrual cycle and the monolayer pattern found in most postmenopausal patients.
What does hyperechoic lesion in uterus indicate?
It is a very small fibroid - the hyperechoic lesion in uterus is the fibroid. It is a small growth of the uterine muscle. It does NOT need any surgery at all. It is small, as small as a small pea ( matar in Hindi ). Do you have any complaints because of it ? Looking forward to hearing from you.
What is foci of endometrium?
Thus, focal glandular hyperplasia of the endometrium is a local multiplication of cells of the glandular tissue, when a thickening of the endometrium is noted on this site. The background disease for the development of pathology can be endocrine, vascular pathology, as a result of which hormonal disorders occur.
What does a hyperechoic foci in nodule mean?
The term “ hypoechoic ” refers to the way a nodule looks on an ultrasound, also called a sonogram. Ultrasound machines produce sound waves that penetrate your body, bouncing off tissues, bones, muscles, and other substances. The way that these sounds bounce back to form an image is known as echogenicity.
See more

What causes echogenic foci in endometrium?
Endometrial microcalcifications are the most common cause of the echogenic foci seen on our ultrasound examinations. They appear to be stable or to regress with time and are associated mostly with benign endometrial conditions.
What does echogenic foci mean on ultrasound uterus?
The histopathologic features of these foci are unconfirmed, but we suspect they represent calcification or fibrosis at sites of mechanical injury to myometrium. The presence of these foci serves as a marker of prior instrumentation and probably has no clinical significance.
Is echogenic endometrium normal?
Whereas a thickened echogenic endometrium up to 16 mm can be normal in premenopausal patients, this degree of thickening would be abnormal in a postmenopausal patient, with causes such as tamoxifen-induced endometrial hyperplasia (Fig 2) and endometrial carcinoma serving as important differential considerations.
What does endometrium echogenic mean?
The endometrial echogenicity should be defined as 'uniform', if the endometrium is homogeneous and with symmetrical anterior and posterior sides. This definition includes the different appearances seen throughout the menstrual cycle and the monolayer pattern found in most postmenopausal patients.
Should I worry about echogenic focus?
But echogenic intracardiac focus (EIF) is almost never something to worry about. It shows up as a bright spot on the heart in imaging, and it's thought to be a microcalcification on the heart muscle. EIF occurs in as many as 5 percent of all pregnancies.
Will echogenic focus go away?
An echogenic intracardiac focus is found in 1 out of every 20 to 30 pregnancies. It does not affect the health of your baby or how his or her heart develops. The spots usually do not go away before your baby is born.
What does endometrium is thickened and echogenic mean?
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition of the female reproductive system. The lining of the uterus (endometrium) becomes unusually thick because of having too many cells (hyperplasia). It's not cancer, but in certain women, it raises the risk of developing endometrial cancer, a type of uterine cancer.
What is echogenic structure in uterus?
The outer (basal layer) endometrium is echogenic. The inner functional endometrium is hypoechoic, and the line demarcating the uterine cavity is echogenic.
What is echogenic material in uterus?
An echogenic mass is seen as a large well-defined mass with lobulated appearance and without fluid component. Calipers 1 and 2 indicate anteroposterior (AP) diameters of the uterus and uterine cavity, respectively.
What does echogenic mean in ultrasound?
Echogenicity. Echogenicity of the tissue refers to the ability to reflect or transmit US waves in the context of surrounding tissues. [7–9] Whenever there is an interface of structures with different echogenicities, a visible difference in contrast will be apparent on the screen.
What does echogenic mean in medical terms?
Adjective. echogenic (comparative more echogenic, superlative most echogenic) (medicine) Describing any inner part of the body that reflects sound waves and thus produces echos that may be detected using ultrasound scanners.
What is the most common age to get endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial hyperplasia is most common among women in their 50s and 60s who have experienced menopause. It may also occur in women who are in perimenopause, a transitional state during which women still have their menstrual periods but on an irregular basis.
What is foci in ovaries?
Small echogenic foci in the ovaries are most frequently due to hemosiderin or calcification. A few small echogenic foci in the ovaries are associated with benign histologic changes and do not appear to be reliable indicators of endosalpingiosis or endometriosis. Key words: calcification; hemosiderin; ovary; sonography.
What does a white spot on an ultrasound mean?
An intracardiac echogenic focus (ICEF) is a bright white spot seen in the baby's heart during an ultrasound. There can be one or multiple bright spots and they occur when an area of the heart muscle has extra calcium. Calcium is a natural mineral found in the body.
What is echogenic lesion in ovary?
These ovarian echogenic foci are found both in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. They are generally of no significance and may occasionally be helpful in identifying an ovary. Larger echogenic foci in the ovary, usually from isolated calcifications, are also typically benign findings ( Fig. 30-3 ).
What are calcifications in endometrium?
Endometrial calcification (Calcific endometritis) is an uncommon finding and is an uncommon cause of infertility with ultrasonography having a high degree of precision for the diagnosis. Endometrial calcifications in relation to retained products of conception or as osseous metaplasia, have been described earlier (1).
What percentage of pregnancies have echogenic focus?
In fact, echogenic focus is found in 3% to 5% of normal pregnancies. 2 . While finding these bright spots in the heart might seem scary, an echogenic focus is actually a pretty common finding on ultrasound, and most often, is not cause for concern.
What is the name of the bright spot in the heart?
1 These bright spots seen in the heart are called echogenic intracardiac foci (multiple) or an echogenic intracardiac focus (singular), which is often shortened to EIF, a cardiac echogenic focus, or echogenic focus.
When does EIF disappear?
While the EIF might disappear during the third trimester, many times it is still present on later ultrasounds. Follow-up imaging studies aren’t typically recommended unless other abnormalities are found on the ultrasound and/or the pregnancy is at higher risk for chromosomal anomalies.
Is EIF an isolated finding?
If an EIF is the only notable finding on the ultrasound, it is considered an “isolated” finding and nothing to worry about. Additionally, the link between EIF and chromosomal abnormalities, if any, is still uncertain. 2
Does echogenic focus go away?
No treatment is required for this condition. The echogenic focus may go away on its own or it may not , but it doesn’t affect a child’s cardiac function so there is no need for treatment or even follow-up testing to see if it is still there.
Is echogenic focus bad for the fetus?
An echogenic focus on its own poses no health risk to the fetus, and when the baby is born, there are no risks to their health or cardiac functioning as a result of an EIF. It is considered a variation of normal heart anatomy and is not associated with any short- or long-term health problems.
Does EIF affect the heart?
Symptoms. EIF causes no symptoms for the fetus or pregnant person. As noted above, this condition doesn't affect the health or function of the baby's heart. Overview of Your 20-Week Level II Ultrasound.
What causes echogenic foci?
The etiologic factors for echogenic foci may be numerous. Histopathologic studies showed microcalcifications, which are the most common cause of echogenic foci.
What is the most common etiology of microcalcification?
The etiology most common was microcalcification but also included crystals, debris from laminaria, and ossified tissues. Clinical follow-up in 62 patients showed that this condition was mostly benign (endometrioid carcinoma developed in 1 patient).
What is an echogenecity ultrasound?
The term 'echogenic' is an ultrasound finding. It refers to a tissue/organ being scanned emitting echoes. Echogenecity ranges from 'hyperechoic' which emit brighter/whiter echoes in contrast to 'hypoechoic' which emit darker echoes. A hyperechoic mass may refer to a mass that is calcified or is with more dense consistency as in scarring or fibrosis or even fat. Hypoechoic ones may include air, fluid/water or even a solid mass that emits dark echoes like nodules of prostate cancer. Sometimes echogenecity present in a seemingly benign mass like a renal cyst, may indicate calcification in its walls and warrants further investigation to rule out malignancy. Herperechoic renal substance, on the other hand, may mean a renal parenchymal disorder often related to scarring as in chronic nephritis -- often a sign of deteriorating renal function.
What is an echogenecity?
The term 'echogenic' is an ultrasound finding. It refers to a tissue/organ being scanned emitting echoes. Echogenecity ranges from 'hyperechoic' which emit brighter/whiter echoes in contrast to 'hypoechoic' which emit darker echoes. A hyperechoic mass may refer to a mass that is calcified or is with more dense consistency as in scarring ...
What is hypoechoic ultrasound?
Hypoechoic ones may include air, fluid/water or even a solid mass that emits dark echoes like nodules of prostate cancer. Sometimes echogenecity present in a seemingly benign mass like a renal cyst, may indicate calcification in its w. Continue Reading. The term 'echogenic' is an ultrasound finding. It refers to a tissue/organ being scanned ...
What is a hyperechoic mass?
A hyperechoic mass may refer to a mass that is calcified or is with more dense consistency as in scarring or fibrosis or even fat. Hypoechoic ones may include air, fluid/water or even a solid mass that emits dark echoes like nodules of prostate cancer.
Who has given a nice answer explaining the significance of echogenicity?
Andy Marrero has given a nice answer explaining the significance of echogenicity…
Can an echogenic mass be biopsyd?
An echogenic mass in an ectatic duct warrants biopsy to exclude carcinoma. An echogenic skin lesion is most likely benign and can occasionally have peripheral vascularity due to surrounding inflammation. However, a skin lesion with internal vascularity is concerning for metastasis or lymphoma.
