Elasticity is an economic concept used to measure the change in the aggregate quantity demanded of a good or service in relation to price movements of that good or service. A product is considered to be elastic if the quantity demand of the product changes drastically when its price increases or decreases.
Full Answer
Why do economists use elasticity?
- It allows a firm or business to predict the change in total revenue with a projected change in price.
- Firms can charge different prices in different markets if elasticities differ in income groups.
- It allows a firm to decide how much tax to pass on to a consumer.
What are some examples of elasticity in economics?
Elasticity Elasticity is how much supply and demand changes in response to variables such as wages. For example, a high wage in a particular profession will increase the supply of workers with time as people who are attracted to the high salary will learn the skills necessary to enter the profession.
How to calculate elasticity economics?
- Take the partial derivative of Q with respect to P, ∂ Q /∂ P. For your demand equation, this equals –4,000.
- Determine P 0 divided by Q 0. Because P is $1.50, and Q is 2,000, P 0 /Q 0 equals 0.00075.
- Multiply the partial derivative, –4,000, by P 0 /Q 0, 0.00075. The point price elasticity of demand equals –3.
What is the importance of elasticity in economics?
##Importance of elasticity:-
- Helps business firms in analysing effect of change in price on total revenue and expenditure.
- Helps business firms in determining price of a commodites
- Helps firms in reducing risks of uncertainties.

How does elasticity help in economics?
As an economic tool, elasticity can help determine whether the tax costs can be passed on to the customer through a price increase.
What is income elasticity?
Income elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of the demand for a particular good or service, as a result of a change in income of the target market or ceteris paribus. Ceteris paribus is a Latin phrase used in economics, meaning 'with all other factors held constant'.
What is the red slanting line in Mabel's candy?
The red slanting line is called the demand curve. At a price of $1.50, the quantity demanded is three units. When the price is lowered to $0.50, the quantity in demand increased to five units. Ms. Mabel can then make the assumption that every increase in price will result in fewer purchases of her candy.
Why is elasticity important in business?
Among the many advantages of using elasticity to make business and marketing decisions, some include the simplicity of the process, or its usefulness in predicting the effect of price changes on revenue and expenditure.
What are the disadvantages of using elasticity?
Some economists believe that the only disadvantage of using elasticity for decision-making is if the marketer does not know how to interpret and apply the results. However, when using the theory, marketers should consider other factors that may affect the quantity demanded, aside from changes in price.
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
Do you have to be a Study.com member to unlock this lesson?
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
What Is Elasticity?
Elasticity is a measure of a variable's sensitivity to a change in another variable, most commonly this sensitivity is the change in quantity demanded relative to changes in other factors, such as price. In business and economics, price elasticity refers to the degree to which individuals, consumers, or producers change their demand or the amount supplied in response to price or income changes. It is predominantly used to assess the change in consumer demand as a result of a change in a good or service's price.
What is the relationship between the quantity demanded and the price of a good or service?
Whenever there is a change in these variables, it causes a change in the quantity demanded of the good or service. For example, when there is a relationship between the change in the quantity demanded and the price of a good or service, the elasticity is known as price elasticity of demand.
How does elasticity affect customer retention?
Beyond prices, the elasticity of a good or service directly affects the customer retention rates of a company. Businesses often strive to sell goods or services that have inelastic demand; doing so means that customers will remain loyal and continue to purchase the good or service even in the face of a price increase.
Why is tobacco inelastic?
This means that tobacco is inelastic because the change in price will not have a significant influence on the quantity demanded. However, if that smoker finds that they cannot afford to spend the extra $2 per day and begins to kick the habit over a period of time, the price of cigarettes for that consumer becomes elastic in the long run.
How to calculate income elasticity of demand?
The formula for calculating income elasticity of demand is the percent change in quantity demanded divided by the percent change in income. With income elasticity of demand, you can tell if a particular good represents a necessity or a luxury.
What does it mean when elasticity is zero?
If elasticity = 0, then it is said to be 'perfectly' inelastic, meaning its demand will remain unchanged at any price. There are probably no real-world examples of perfectly inelastic goods. If there were, that means producers and suppliers would be able to charge whatever they felt like and consumers would still need to buy them. The only thing close to a perfectly inelastic good would be air and water, which no one controls.
What are some examples of elastic goods?
Examples of elastic goods include clothing or electronics, while inelastic goods are items like food and prescription drugs.
What is Elasticity?
Elasticity measures the sensitivity of change of one variable in response to another, causal variable. We call variables that respond drastically to change as ‘elastic’, and ones that don’t respond a lot as ‘inelastic’.
How to calculate elasticity?
You can calculate the elasticity of a variable by dividing the percentage change in quantity by the percentage change in price.
Does belief affect student performance?
If you’re a teacher, the belief you have in your students will affect their performance. In fact, economist, Tyler Cowen, references an educational research paper that suggests an elastic relationship between teacher expectations and college completion among their students.
What is Elasticity?
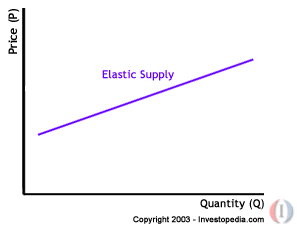
Elasticity refers to the degree of responsiveness in supply or demand in relation to changes in price. If a curve is more elastic, then small changes in price will cause large changes in quantity consumed. If a curve is less elastic, then it will take large changes in price to effect a change in quantity consumed. Graphically, elasticity can be represented by the appearance of the supply or demand curve. A more elastic curve will be horizontal, and a less elastic curve will tilt more vertically. When talking about elasticity, the term "flat" refers to curves that are horizontal; a "flatter" elastic curve is closer to perfectly horizontal.
What is the difference between an elastic and an inelastic supplier?
An inelastic supplier (one with a steeper supply curve) will always supply the same amount of goods, regardless of the price, and an elastic supplier (one with a flatter supply curve) will change quantity supplied in response to changes in price.
What is the elasticity of demand?
Price elasticity of demand, also called the elasticity of demand, refers to the degree of responsiveness in demand quantity with respect to price. Consider a case in the figure below where demand is very elastic, that is, when the curve is almost flat. You can see that if the price changes from $.75 to $1, the quantity decreases by a lot. There are many possible reasons for this phenomenon. Buyers might be able to easily substitute away from the good, so that when the price increases, they have little tolerance for the price change. Maybe the buyers don't want the good that much, so a small change in price has a large effect on their demand for the good.
What does an I nelastic curve look like?
Hint: You can use perfectly inelastic and perfectly elastic curves to help you remember what inelastic and elastic curves look like: an I nelastic curve is more vertical, like the letter I. An E lastic curve is flatter, like the horizontal lines in the letter E .
How does inelastic demand affect demand?
If demand is very inelastic, then large changes in price won't do very much to the quantity demanded. For instance, whereas a change of 25 cents reduced quantity by 6 units in the elastic curve in the figure above, in the inelastic curve below, a price jump of a full dollar reduces the demand by just 2 units. With inelastic curves, it takes a very big jump in price to change how much demand there is in the graph below. Possible explanations for this situation could be that the good is an essential good that is not easily substituted for by other goods. That is, for a good with an inelastic curve, customers really want or really need the good, and they can't get want that good offers from anywhere else. This means that consumers will need to buy the same amount of the good from week to week, regardless of the price.
What happens when a curve is less elastic?
If a curve is less elastic, then it will take large changes in price to effect a change in quantity consumed. Graphically, elasticity can be represented by the appearance of the supply or demand curve. A more elastic curve will be horizontal, and a less elastic curve will tilt more vertically.
What happens when the price of a product changes from $.75 to $1?
You can see that if the price changes from $.75 to $1, the quantity decreases by a lot. There are many possible reasons for this phenomenon. Buyers might be able to easily substitute away from the good, so that when the price increases, they have little tolerance for the price change.
What is the measure of price elasticity of demand?
Price elasticity of demand: also known as PED or E d, is a measure in economics to show how demand responds to a change in the price of a product or service.
What is the elasticity of a PED?
The PED is -1 (minus one) Price elasticity may vary from minus one to plus one. Most products and services range from minus one to zero. Giffen or Veblen goods, on the other hand, range from zero to plus one.
Why is diet coke elastic?
Demand for one can of diet coke is elastic because there are other cheap alternatives available.
What are some examples of Giffen goods?
Giffen goods are very basic products which low-income households rely on. Examples of Giffen goods are rice in China, bread in Europe and North America, and tortillas in Mexico. If the price of tortillas rises in Mexico, poor people will cut back on more expensive foods.
What is the difference between product C and product A?
In this image, demand for products A and B changes to a greater extent than alterations in price. Products D, E, and F have smaller demand changes than alterations in price. With product C, demand and prices change by the same proportion. Product A is a non-essential good (such as a weekend in a spa), product F is an essential good (such as milk or bread), while product C might be a Coke (people would turn to Pepsi if Coke’s price rose).
What is income elasticity of demand?
Income elasticity of demand measures how demand for a product or service changes when people’s incomes change.
What is price elasticity?
Price elasticity is a measure of how consumers react to the prices of products and services. Normally demand declines when prices rise, but depending on the product/service and the market, how consumers react to a price change can vary. There are two types price elasticities:
What Is Elasticity?
- Elasticity is a measure of a variable's sensitivity to a change in another variable, most commonl…
In business and economics, price elasticity refers to the degree to which individuals, consumers, or producers change their demand or the amount supplied in response to price or income changes. It is predominantly used to assess the change in consumer demand as a result of a ch… - Elasticity is an economic measure of how sensitive one economic factor is to changes in another.
For example, changes in supply or demand to the change in price, or changes in demand to changes in income.
How Elasticity Works
- When the value of elasticity is greater than 1.0, it suggests that the demand for the good or servi…
Inelastic means that when the price goes up, consumers’ buying habits stay about the same, and when the price goes down, consumers’ buying habits also remain unchanged. - If elasticity = 0, then it is said to be 'perfectly' inelastic, meaning its demand will remain unchang…
Elasticity is an economic concept used to measure the change in the aggregate quantity demanded of a good or service in relation to price movements of that good or service.
Types of Elasticity
- The quantity demanded of a good or service depends on multiple factors, such as price, income…
Price elasticity of demand is an economic measure of the sensitivity of demand relative to a change in price. The measure of the change in the quantity demanded due to the change in the price of a good or service is known as price elasticity of demand . - Income elasticity of demand refers to the sensitivity of the quantity demanded for a certain goo…
The cross elasticity of demand is an economic concept that measures the responsiveness in the quantity demanded of one good when the price for another good changes. Also called cross-price elasticity of demand, this measurement is calculated by taking the percentage change in the qua…
Factors Affecting Demand Elasticity
- There are three main factors that influence a good’s price elasticity of demand.
In general, the more good substitutes there are, the more elastic the demand will be. For example, if the price of a cup of coffee went up by $0.25, consumers might replace their morning caffeine fix with a cup of strong tea. This means that coffee is an elastic good because a small increase i…
The Importance of Price Elasticity in Business
- Understanding whether or not the goods or services of a business are elastic is integral to the s…
Beyond prices, the elasticity of a good or service directly affects the customer retention rates of a company. Businesses often strive to sell goods or services that have inelastic demand; doing so means that customers will remain loyal and continue to purchase the good or service even in th…
Examples of Elasticity
- There are a number of real-world examples of elasticity we interact with on a daily basis. One int…
The COVID-19 pandemic has also shone a spotlight on the price elasticity of demand through its impact on a number of industries. For example, a number of outbreaks of the coronavirus in meat processing facilities across the US, in addition to the slowdown in international trade, led to a do…
What Is Meant by Elasticity in Economics?
- Elasticity refers to the measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded or quantity supplied to one of its determinants. Goods that are elastic see their demand respond rapidly to changes in factors like price or supply. Inelastic goods, on the other hand, retain their demand even when prices rise sharply (e.g., gasoline or food).
Are Luxury Good Elastic?
- Luxury goods often have a high price elasticity of demand because they are sensitive to price changes. If prices rise, people quickly stop buying them and wait for prices to drop.
What Are the 4 Types of Elasticity?
- Four types of elasticity are demand elasticity, income elasticity, cross elasticity, and price elasticity.
What Is Price Elasticity?
- Price elasticity measures how much the supply or demand of a product changes based on a given change in price.
What Is the Elasticity of Demand Formula?
- The elasticity of demand can be calculated by dividing the percentage change in the quantity demanded of a good or service by the percentage change in price. It reflects how demand for a good or service changes as its quantity or price varies.
The Bottom Line
- Understanding whether a good or service is elastic or inelastic, and what other products could be tied to a good's elasticity can help consumers make informed decisions when they are deciding if or when to make a purchase.