What you should know about endocrine disruptors?
There are several symptoms you should be aware of:
- Decreased energy levels
- Disturbed sleep patterns
- Loss of muscle mass
- Increased body fat
- Hair loss
- Erectile dysfunction
- Mood swings, irritability, or depression
What the heck are endocrine disruptors?
Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that may interfere with the body’s endocrine system and produce adverse developmental, reproductive, neurological, and immune effects in humans. Many substances, both natural and man-made, are thought to cause endocrine disruption.
How do endocrine disruptors impact women?
Disrupting the Cycles of Life. EDCs can also affect the duration of fertility. In girls, early life exposure to DDT may contribute to an earlier onset of puberty; once they become adults, this exposure may also lengthen menstrual cycles and accelerate menopause. Lead, another reproductive toxicant, may shorten a woman’s reproductive lifespan.
What causes endocrine disruption?
- Chemical exposures during development can alter disease susceptibility later in life.
- Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can produce adverse developmental, reproductive, neurological, cardiovascular, metabolic and immune effects in humans.
- EDCs interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, activity, or elimination of natural hormones.

What does an endocrine disruptor do?
Endocrine disruptors can affect the body in three main ways: They may block the pathway between a natural hormone and a receptor. They may act directly on a gland, causing it to make too much or too little of a hormone. They may mimic a hormone, causing the body to overreact or to react at the wrong time.
What are examples of endocrine disruptors?
Endocrine disruptors are found in many everyday products, including some plastic bottles and containers, liners of metal food cans, detergents, flame retardants, food, toys, cosmetics, and pesticides. Some endocrine-disrupting chemicals are slow to break-down in the environment.
What are symptoms of endocrine disruption?
While each endocrine disorder has its own set of symptoms, some of the most common symptoms found among many of them include:Mood swings.Fatigue.Weakness.Unintended weight fluctuations.Changes in blood glucose levels or cholesterol levels.
What are endocrine disruptors and where do they come from?
Endocrine disruptors are found in everyday products, including some food and beverage packaging, cosmetics, toys, flame retardants, and pesticides. Your contact with these chemicals may occur through diet, air, skin, and water. plastics and epoxy resins found in many plastic products, including food storage containers.
What foods are hormone disruptors?
4 Foods That Throw off Your Hormonal BalanceRed Meat. Red meat contains high amounts of saturated and hydrogenated fats which are considered unhealthy types of fat. ... Processed Foods. Processed and refined foods have been linked to various health issues. ... Caffeine. ... Soy and Dairy products.
Is alcohol an endocrine disruptor?
Chronic consumption of a large amount of alcohol disrupts the communication between nervous, endocrine and immune system and causes hormonal disturbances that lead to profound and serious consequences at physiological and behavioral levels.
How do you keep your endocrine system healthy?
How Can I Help Keep My Endocrine System Healthy?Get plenty of exercise.Eat a nutritious diet.Go for regular medical checkups.Talk to the doctor before taking any supplements or herbal treatments.Let the doctor know about any family history of endocrine problems, such as diabetes or thyroid problems.
What is the most common female endocrine disorder?
Polycystic ovary syndrome is the most common endocrine disorder in women.
What is the most common endocrine disorder?
In the United States, the most common endocrine disease is diabetes. There are many others. They are usually treated by controlling how much hormone your body makes. Hormone supplements can help if the problem is too little of a hormone.
Is Sugar an endocrine disruptor?
Sugar's effect on your hormones Sugar not only provides major highs and lows in mood and energy, it can also disrupt one of the most powerful hormones in the body: insulin. And insulin is closely connected to all of the other hormones in your body, including estrogen and testosterone.
Is perfume an endocrine disruptor?
Parabens are commonly found in perfumes, and parabens are synthetic preservatives. The problem with this is that they are known to disrupt the endocrine system by interfering with both hormone production as well as the release of hormones in the body.
Is nail polish an endocrine disruptor?
If you wear nail polish, you might be applying more than glossy color to your fingertips. A new study by researchers at EWG and Duke University finds that nail polishes can contain a suspected endocrine disruptor called triphenyl phopshte, or TPHP.
How can you protect yourself from endocrine disruptors?
Avoid storing canned or plastic-packaged foods in hot areas, like the trunk of a car on a summer day. Also, avoid microwaving or heating food in plastic containers. EDCs could leach out of the container and into your food and body.
How many endocrine disruptors are there?
There are over 100 substances with endocrine disrupting properties, as well as other properties, on the list, but only 32 substances have been added based solely on their endocrine-disrupting mode of action.
Are perfumes endocrine disruptors?
Parabens are commonly found in perfumes, and parabens are synthetic preservatives. The problem with this is that they are known to disrupt the endocrine system by interfering with both hormone production as well as the release of hormones in the body.
Is Dairy an endocrine disruptor?
EDCs can also be present in dairy products such as milk and cheese, as some of these chemicals build up in the milk of animals. Reducing your consumption of these products can reduce your exposure to harmful chemicals.
What are Concerns Regarding Endocrine Disruptors?
In the last two decades there has been a growing awareness of the possible adverse effects in humans and wildlife from exposure to chemicals that can interfere with the endocrine system. These effects can include:
What are Examples of Endocrine Disruption?
One example of the devastating consequences of the exposure of developing animals, including humans, to endocrine disruptors is the case of the potent drug diethylstilbestrol (DES), a synthetic estrogen. Prior to its ban in the early 1970's, doctors mistakenly prescribed DES to as many as five million pregnant women to block spontaneous abortion and promote fetal growth. It was discovered after the children went through puberty that DES affected the development of the reproductive system and caused vaginal cancer.
How does the endocrine system disrupt?
Some chemicals mimic a natural hormone, fooling the body into over-responding to the stimulus (e.g., a growth hormone that results in increased muscle mass), or responding at inappropriate times (e.g., producing insulin when it is not needed). Other endocrine disruptors block the effects of a hormone from certain receptors (e.g. growth hormones required for normal development). Still others directly stimulate or inhibit the endocrine system and cause overproduction or underproduction of hormones (e.g. an over or underactive thyroid).
What are the effects of chemicals on wildlife?
increased cancer risk; and. disturbances in the immune and nervous system function. Clear evidence exists that some chemicals cause these effects in wildlife, but limited evidence exists for the potential of chemicals to cause these effects in humans at environmental exposure levels. Very few chemicals have been tested for their potential ...
Why was DES banned in 1970?
Prior to its ban in the early 1970's, doctors mistakenly prescribed DES to as many as five million pregnant women to block spontaneous abortion and promote fetal growth. It was discovered after the children went through puberty that DES affected the development of the reproductive system and caused vaginal cancer.
Can chemicals affect the endocrine system?
In recent years, some scientists have proposed that chemicals might inadvertently be disrupting the endocrine system of humans and wildlife. A variety of chemicals have been found to disrupt the endocrine systems of animals in laboratory studies, and there is strong evidence that chemical exposure has been associated with adverse developmental and reproductive effects on fish and wildlife in particular locations. The relationship of human diseases of the endocrine system and exposure to environmental contaminants, however, is poorly understood and scientifically controversial (Kavlock et al., 1996, EPA, 1997).
Is endocrine disruptor screening a requirement?
The statutory requirement to establish an endocrine disruptor screening program is a highly significant step. Growing scientific evidence shows that humans, domestic animals, and fish and wildlife species have exhibited adverse health consequences from exposure to environmental chemicals that interact with the endocrine system.
What is an endocrine disrupting chemical?
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines an endocrine disrupting chemical as “an exogenous substance or mixture that alters function (s) of the endocrine system and consequently causes adverse health effects in an intact organism, or its progeny, or (sub)populations.”
What are regulatory decisions about chemicals that may affect the endocrine system?
Regulatory decisions about chemicals that may affect the endocrine system need to be based on a combination of factors – whether a chemical causes endocrine-related activity; what is the chemical’s potency and levels and means of exposure; whether it produces adverse effects and if so, at what dose levels; and what is the life-stage and susceptibility of an individual.
What is the interaction between the endocrine system and substances that are endocrine-active?
In some cases, the interaction between the endocrine system and substances that are endocrine-active is neutral: the substances lack sufficient potency, or exposures may be so low that no effects occur at all.
What is the OECD?
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have developed scientifically-validated screens and tests for identifying chemicals with endocrine active properties to enable science-based examinations of the endocrine disruptor issue. Due to these efforts, regulatory agencies today have access to toxicological screening test guidelines that are relevant, reliable, sensitive, and specific for evaluating the potential for substances to interact with the estrogen, androgen, and thyroid pathways.
When screening substances for endocrine-related activities, especially when using emerging technologies, must regulatory agencies use?
When screening substances for endocrine-related activities, especially when using emerging technologies, regulatory agencies must use validated methods so the results can be relied upon and trusted by all stakeholders.
Is an endocrine disruptor harmful?
The likelihood that an endocrine disruptor will cause harmful effects is based on its potency (how active it is) and potential for exposure (dosage, frequency, and duration). The definition is important so as not to confuse neutral “endocrine effects” with negative “endocrine disruption,” with the latter term being linked to adverse/negative health ...
Can natural substances interact with the endocrine system?
Certain natural substances, in addition to some synthetic chemicals, can be shown to have the potential to interact with components of the endocrine system while not causing any changes in function of the organism whatsoever; or they may cause transient effects which are readily reversible and do not result in adverse health effects.
What is NIEHS Doing?
For more than three decades, NIEHS has been a pioneer in conducting research on the health effects of endocrine disruptors. NIEHS-supported research leads to a greater understanding of how endocrine-disrupting chemicals may harm our health and cause disease.
How do you get endocrine disruptors?
People may be exposed to endocrine disruptors through food and beverages consumed, pesticides applied, and cosmetics used . In essence, your contact with these chemicals may occur through diet, air, skin, and water.
What is the purpose of conducting animal and human health research?
Conducting animal and human health research to define linkages between exposure to endocrine disrupters and health effects
What is the NTP?
In 2000, an independent panel of experts convened by NIEHS and the National Toxicology Program (NTP), which is housed at NIEHS, concluded there was credible evidence that very low doses of some hormone-like chemicals can adversely affect bodily functions in test animals.
How does DES affect reproduction?
Reproduction. DES can cause epigenetic changes, altering the way genes are turned on and off, in reproductive organs of mice. The findings provide a possible explanation for how endocrine disruptors affect fertility and reproduction.
What are phthalates used for?
Phthalates — used to make plastics more flexible, they are also found in some food packaging, cosmetics, children’s toys, and medical devices
What is PBDE used for?
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) — used to make flame retardants for household products such as furniture foam and carpets. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) — used to make electrical equipment like transformers, and in hydraulic fluids, heat transfer fluids, lubricants, and plasticizers.
What is an endocrine disruptor?
Definition. Endocrine disruptors are defined as "exogenous" chemicals that may interfere with the actions of hormones in our bodies. The term exogenous means that they come from outside of the body.
What are the roles of endocrine disruptors in cancer?
Role in Cancer. Reducing Exposure. Endocrine disruptors or endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are substances in the environment that can interfere with the actions of hormones in our bodies. Through a number of mechanisms, endocrine disruptors have been linked to several cancers, including those of the thyroid, breast, and prostate.
What are the effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on ovarian cancer?
Similarly, studies evaluating ovarian cancer cells have found that exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals causes changes in the way that DNA is read (epigenetic changes) that are associated with progression, spread, and resistance to treatment. 7
What cancers are endocrine disrupting?
Intuition tells us that cancers such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, testicular cancer, and thyroid cancer could be influenced by chemicals that mimic the effects of hormones in the body.
How do chemicals affect the body?
A chemical may act by interfering with or disrupting a wide variety of signaling pathways in the body involving hormones. Epigenetic alterations: Non-genetic changes that affect the way that DNA is "read" may result, and this has been seen with ovarian cancer cells in the lab.
What cancers mimic hormones?
Intuition tells us that cancers such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, testicular cancer, and thyroid cancer could be influenced by chemicals that mimic the effects of hormones in the body.
Is low exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals bad for you?
The true effect of low dose exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals on the development and progression of cancer is unknown, but there is evidence showing a cause for concern. Fortunately, there are many simple changes people can make to reduce their exposure daily, and there may even be additional benefits to these changes with regard to the environment and your general sense of wellbeing.
What are the human impacts of EDCs?
Attention has focused on health problems arising when EDCs interfere with estrogens, androgens, and other sex hormones and the thyroid hormones.
How do endocrine disrupting chemicals affect the human body?
Our understanding of how endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) interfere with hormones and other chemical signalers is growing rapidly. Once thought to primarily interfere with hormone receptors, we now know the culprits impact a wide range of signaling processes. They can interfere with hormone binding, transport, and production; gene expression; and a host of other cell regulatory mechanisms. These disruptions may affect the endocrine, immune and neural systems and may lead to developmental, reproductive, metabolic, brain, and behavior problems.
What is IPCS in science?
IPCS (International Programme on Chemical Safety). 2002. Global Assessment of the State-of-the-Science of Endocrine Disruptors. WHO/PCS/EDC/02.2. Eds. Damstra T, Barlow S, Bergman A, Kavlock R, and Van Der Kraak G. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. Available: http://www.who.int/ipcs/publications/new_issues/endocrine_disruptors/en/
What is E. Hormone?
E.Hormone is sponsored and designed by the Center for Bioenvironmental Research at Tulane and Xavier Universities as a gateway to the environment and hormones by informing on such diverse issues as environmental research, environmental hormones, endocrine research, endocrine disrupter, endocrine disrupters, endocrine disruptor, endocrine disruptors, endocrine disrupting chemicals, estrogens, hormones, and environmental signaling.
Why are cause and effect data elusive?
Cause and effect data are elusive with issues like EDCs because they involve complex biological systems, unclear exposure facts, and diverse health responses. In these cases, we use scientific, political, and public debate to weigh the evidence and decide how to deal with the potential effects.
What are some examples of consensus statements?
Many consensus statements issued and endorsed by scientists and scientific organizations echo this. The Wingspread statements, the Weybridge Report, and the Prague Declaration on Endocrine Disruption are examples.
Why is DES banned?
DES, a strong synthetic estrogen banned since the 1970s, was given to pregnant women to prevent miscarriages. Years later, the grown daughters and sons of women who took the drug were having more reproductive problems and higher cancer rates than those not exposed to DES in the womb.
What is the EPA's proposed Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program?
EPA's proposed Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program substantially reflects the EDSTAC recommendations. (114) Particularly, EPA agreed to expand the scope of the testing program beyond the FQPA and SDWA provisions to include a wide range of chemicals to which Americans are exposed. (115) After initial screening and priority setting, EPA plans to promulgate its first test orders under its FQPA and SWDA authority in late 2001. (116) Additionally, "EPA may propose a TSCA test rule to require screening of chemicals that may not be covered by the FFDCA/SDWA.
What is EDSP in pesticides?
At issue is EPA's Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program (EDSP) which requires pesticide and other chemical manufacturers to test their products for adverse effects on the human endocrine system.
How do endocrine disruptors affect the nervous system?
Endocrine disruptors can also affect the nervous system via receptors expressed on neuroendocrine cells.
What is an endocrine disruptor?
endocrine disruptor. (dĭs-rŭp′tĕr) A chemical that may imitate or block the function of natural hormones if it is absorbed by the body. Many pesticides and plasticizing compounds, e.g., phthalates, are thought to disrupt endocrine pathways, esp. if they are absorbed by pregnant women during embryonic and fetal development.
What percentage of Americans have BPA in their urine?
Endocrine disruptor. According to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) figures, 93 percent of Americans have traces of BPA in their urine.
Does BPA affect animals?
Washington, Nov 08 ( ANI ): While traditional toxicology studies have indicated that only very high doses of Bisphenol A (BPA)- known endocrine disruptor that hijacks the normal responses of hormones- affect exposed animals, a new study has revealed that the lower doses of the chemical may also affect humans.
Can BPA be reduced?
But a recent study from Silent Spring Institute in Massachusetts (silentspring.org) shows we can drastically reduce our consumption of the endocrine disruptors bisphenol A (BPA) and di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) by making a few basic changes in our dietary practices.
Are we missing a good definition for endocrine disruptor? Don't keep it to yourself..
The ASL fingerspelling provided here is most commonly used for proper names of people and places; it is also used in some languages for concepts for which no sign is available at that moment.
Definitions & Translations
Get instant definitions for any word that hits you anywhere on the web!
How Can Chemicals Affect the Endocrine System?
Scientific research on human epidemiology, laboratory animals, and fish and wildlife suggests that environmental contaminants can disrupt the endocrine system leading to adverse-health consequences. It is important to gain a better understanding of what concentrations of chemicals found in the environment may cause an adverse effect. Various types of scientific studies (epidemiology, mammalian toxicology, and ecological toxicology) are necessary to resolve many of the scientific questions and uncertainty surrounding the endocrine disruptor issue. Many such studies are currently underway by government agencies, industry, and academia.
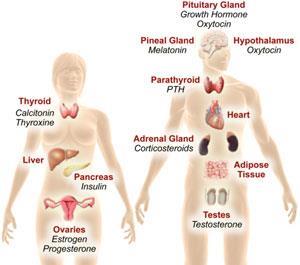
Why are Hormones Important?
Hormones act as chemical messengers that are released into the blood stream to act on an organ in another part of the body. Although hormones reach all parts of the body, only target cells with compatible receptors are equipped to respond. Over 50 hormones have been identified in humans and other vertebrates.
What are the two hormones that the thyroid gland secretes?
The thyroid gland secretes two main hormones, thyroxine and triiodothyronine, into the bloodstream. These thyroid hormones stimulate all the cells in the body and control biological processes such as growth, reproduction, development, and metabolism. The endocrine system, made up of all the body's different hormones, ...
What hormones are involved in body growth?
body growth and energy production (growth hormone and thyroid hormone).
What are the types of studies that are needed to solve the endocrine disruptor issue?
Various types of scientific studies (epidemiology, mammalian toxicology, and ecological toxicology) are necessary to resolve many of the scientific questions and uncertainty surrounding the endocrine disruptor issue. Many such studies are currently underway by government agencies, industry, and academia. Learn more with EDSP about concerns and ...
Which hormones are responsible for sexual development?
Estrogens are the group of hormones responsible for female sexual development. They are produced primarily by the ovaries and in small amounts by the adrenal glands.
How many hormones are there in the human body?
Over 50 hormones have been identified in humans and other vertebrates. Hormones control or regulate many biological processes and are often produced in exceptionally low amounts within the body. Examples of such processes include: blood sugar control (insulin);

What Are Concerns Regarding Endocrine Disruptors?
- In the last two decades there has been a growing awareness of the possible adverse effects in humans and wildlife from exposure to chemicals that can interfere with the endocrine system. These effects can include: 1. developmental malformations, 2. interference with reproduction, 3. increased cancer risk; and 4. disturbances in the immune and nervous system function. Clear evi…
How Can Chemicals Disrupt The Endocrine System?
- Disruption of the endocrine system can occur in various ways. Some chemicals mimic a natural hormone, fooling the body into over-responding to the stimulus (e.g., a growth hormone that results in increased muscle mass), or responding at inappropriate times (e.g., producing insulin when it is not needed). Other endocrine disruptors block the effects of a hormone from certain r…
What Are Examples of Endocrine Disruption?
- One example of the devastating consequences of the exposure of developing animals, including humans, to endocrine disruptors is the case of the potent drug diethylstilbestrol (DES), a synthetic estrogen. Prior to its ban in the early 1970's, doctors mistakenly prescribed DES to as many as five million pregnant women to block spontaneous abortion an...