Enteral feeding refers to the delivery of a nutritionally complete feed, containing protein, carbohydrate, fat, water, minerals and vitamins, directly into the stomach, duodenum or jejunum.
Full Answer
What are the problems with feeding tube?
Use and Care
- Clean your hands. Use alcohol-based hand sanitizer or soap and water before you work with the tube. Make sure your hands are dry.
- Prevent clogs. This is one of the biggest problems with feeding tubes. ...
- Watch for infections. It’s important to keep the spot on your skin where the tube goes into your stomach -- the stoma -- clean and dry.
What are the side effects of tube feeding?
What are the side effects of a feeding tube in the stomach?
- Constipation.
- Dehydration.
- Diarrhea.
- Skin Issues (around the site of your tube)
- Unintentional tears in your intestines (perforation)
- Infection in your abdomen (peritonitis)
- Problems with the feeding tube such as blockages (obstruction) and involuntary movement (displacement)
What can you eat on a feeding tube?
Choose soft, moist foods that are easier to swallow. o Moist scrambled eggs with cheese o Whipped yogurts or Greek yogurt o Pudding (make with whole milk) o Mashed potatoes with or without gravy o Cream of wheat or moist oatmeal o Macaroni and cheese o Pureed squash or sweet potato o Applesauce o Diced fruit in syrup o Cottage Cheese
What are the different types of tube feeding?
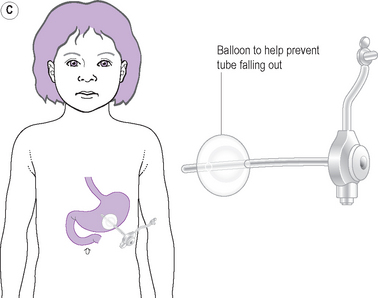
Different types of feeding tubes may be used to provide enteral nutrition: Nasogastric tube (NG-tube) — a tube placed through the nose to the stomach or small intestine (for short-term feeding needs) Gastrostomy (G-tube) — a tube placed through the skin into the stomach (for long-term feeding needs)

Is enteral feeding the same as tube feeding?
Enteral nutrition, also known as tube feeding, is a way of delivering nutrition directly to your stomach or small intestine. Your doctor might recommend tube feeding if you can't eat enough to get the nutrients you need. When tube feeding occurs outside the hospital, doctors refer to it as home enteral nutrition (HEN).
What are the 4 main routes of enteral feeding?
Enteral Nutrition (EN), tube feeding, is given via different types of tubes.Nasoenteric Feeding Tubes (NG & NJ) ... Gastrostomy Feeding. ... Jejunostomy Feeding. ... Gastrostomy with Jejunal Adapter.
What do you mean by enteral feeding?
Enteral feeding is a method of supplying nutrients directly into the gastrointestinal tract. This guideline will use this term describe Orogastric, Nasogastric and Gastrostomy tube feeding.
What are enteral feeding tubes used for?
A person on enteral feeds usually has a condition or injury that prevents eating a regular diet by mouth, but their GI tract is still able to function. Being fed through a tube allows them to receive nutrition and keep their GI tract working.
What are the disadvantages of enteral tube feedings?
There are disadvantages with enteral feedings. If the child has gastroesophageal reflux, aggressive enteral feeding may increase his risk of aspiration or vomiting. Other physical disadvantages are diarrhea, skin breakdown or anatomic disruption. Mechanical disadvantages include a dislodged or occluded feeding tube.
What can you eat with a feeding tube?
Foods that are popular for blending include sweet potatoes, bananas, quinoa, avocado, oats, nut and seed butters, chicken, yogurt, kefir, various grains, and milk (cow's, soy, almond, coconut, etc). Other liquids include water, broths, and juices.
Can you eat food with a feeding tube?
If an individual can eat by mouth safely, then he/she can eat food and supplement with tube feeding if necessary. Eating food will not cause damage to the tube, nor does having a feeding tube make it unsafe to eat.
What are the 3 types of feeding?
Feeding MethodsEnteral. The term, enteral, refers to nutrition administered via the gastrointestinal tract. ... Oral. ... Tube Feeding. ... Parenteral.
How long can you have a feeding tube in your stomach?
A feeding tube can remain in place as long as you need it. Some people stay on one for life.
Who needs enteral feeding?
There are many reasons for enteral and parenteral nutrition including GI disorders such as bowel obstruction, short bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis; as well as certain cancers or in comatose patients.
How is enteral feeding done?
A flexible tube is inserted through the nose or belly area to provide nutrients by delivering liquid nutrition directly into the stomach or small intestine. Doctors usually insert the tube while you are in the hospital, but you may continue to use it outside the hospital, at home, or in a nursing facility.
What are the different types of enteral feeding?
Several types of tubes are used for enteral feeding:Nasogastric tubes. ... Nasojejunal tube (NJT) ... Jejunostomy tubes (JEJ, PEJ or RIJ tubes) ... Radiologically inserted gastrostomy tube (RIG) ... Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tubes (PEG tube)
What are the different types of enteral feeding?
Several types of tubes are used for enteral feeding:Nasogastric tubes. ... Nasojejunal tube (NJT) ... Jejunostomy tubes (JEJ, PEJ or RIJ tubes) ... Radiologically inserted gastrostomy tube (RIG) ... Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tubes (PEG tube)
What are the 3 types of feeding?
Feeding MethodsEnteral. The term, enteral, refers to nutrition administered via the gastrointestinal tract. ... Oral. ... Tube Feeding. ... Parenteral.
How many types of feedings are there?
Types of feeding tubes Nasogastric feeding tube (NG) Nasojejunal feeding tube (NJ) Gastrostomy tubes, e.g. percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG), radiologically inserted gastrostomy (RIG) Jejunostomy tubes, e.g. surgical jejunostomy (JEJ), jejunal extension of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG-J).
What are the three methods of delivering a bolus feed?
Bolus feeds can be delivered with an enteral syringe or bolus set using a plunger, gravity or a feeding pump.
What is tube feeding?
Tube feeding is a therapy where a feeding tube supplies nutrients to people who cannot get enough nutrition through eating. A flexible tube is inserted through the nose or belly area to provide nutrients by delivering liquid nutrition directly into the stomach or small intestine. Doctors usually insert the tube while you are in the hospital, ...
When is tube feeding needed?
Tube feeding is needed when a person can't eat through their mouth, for whatever reason. Nutrition is delivered using a flexible tube inserted through the nose, or directly into the stomach or small intestine.
How long does a feeding tube last?
Depending on the reason for the tube, people may use a feeding tube for a few weeks, several months, or years. In some cases, people use a feeding tube for the rest of their lives after surgery or an injury impairs their ability to receive enough nutrition through eating.
What are the risks of home tube feeding?
The risks of home tube feeding are small, but complications can occur. These complications may include: Clogged, damaged or displaced tube. Infection at the tube insertion site. Gastrointestinal problems including constipation, nausea and diarrhea. Leaking of stomach contents at the tube site. Pain at the tube site.
How long does it take for a feeding tube to be inserted?
Doctors usually recommend this tube for people who need feeding tube/enteral access longer than 4-6 weeks. After your doctor inserts the tube, you will receive instructions on how to care for it. Your doctor will also tell you what kind of tube feeding formula to use to receive proper nutrition.
Why do people need tube feeding?
Tube feeding can help people who have trouble eating get the nutrition they need. Doctors often use it at the end of life to help people stay more comfortable, though some patients choose to opt out of tube feeding.
Can you use a tube in the hospital?
Doctors usually insert the tube while you are in the hospital, but you may continue to use it outside the hospital, at home, or in a nursing facility. Tube feeding is also known as enteral nutrition and if provided at home, is termed home enteral nutrition (HEN). Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is tube feeding?
Tube feeding is a process of obtaining food and nutrition through a tube, instead of a traditional diet. Enteral feeding is always doctor-prescribed and should never be attempted without a medical professional. This kind of tube is inserted through the nose and ends up in the stomach. The term “nasogastric” literally means nose (“naso”) ...
What is the term for feeding through a tube?
Enteral feeding refers to methods of feeding that use the gastrointestinal route (either through the mouth or through a tube). Most often, when people talk about “enteral feeding,” they actually mean “tube feeding.”. Tube feeding is a process of obtaining food and nutrition through a tube, instead of a traditional diet.
What is an enteral feeding formula?
The term “enteral feeding formulas” refers to the nutritional liquids that are put through enteral feeding tubes. Enteral feeding formulas need to support an entire diet, so they’re packed with all the vitamins, minerals, calories, and protein that people need to survive and thrive.
How long does it take to feed a bolus?
Formula is poured into a bag, and held by hand (instead of left on a pole). It takes around 15-20 minutes to consume 8 ounces this way, so this kind of feeding typically happens twice at breakfast, twice at lunch, and twice at dinner.
How long does it take to pump feed?
This kind of feeding usually takes 16-24 hours, and is typically used on bedridden patients.
Can you use enteral formula without a doctor's consent?
There are many kinds of enteral feeding formulas, to support many different nutritional needs, but you should never decide which enteral feeding formula to use without a doctor’ s suggestion or consent.
Can you add nutritional drinks to enteral feeding?
When you’re using enteral feeding formulas make sure that you: Are following the maintenance instructions laid out by your doctor. Don’t add nutritional drinks and shakes in the long-term, as the added sugar can lead to discomfort. Use the formula recommended by your doctor.
Why flush enteral tubes?
Flushing enteral tubes to keep them free from build-up is essential, because unclogging a tube wastes time, effort, and resources. The best method of tube flushing is a matter of active research; local protocols apply. Tubes that cannot be unclogged must be replaced.
What is intravenous feeding?
intravenous feeding administration of nutrient fluids through a vein; see also intravenous infusion and parenteral nutrition.
How is bolus delivered?
In bolus administration the formula is delivered in four to six daily feedings by a large syringe attached to the feeding tube in the stomach. This type of delivery is the least well tolerated. In intermittent infusion the formula is delivered four to six times daily over 30 to 60 minutes using a pump or gravity flow. In cyclic infusion an infusion pump delivers the nutrient solution for specified hours of the day and is turned off during other hours. In continuous drip an infusion pump delivers nutrition all day long.
What is nutritional formula?
The patient is fed an appropriate nutritional formula through a tube passed into the stomach or duodenum from the nasal passage (nasogastric or nasoduodenal tube) or by a gastrostomy tube, gastrostomy button, or gastrojejunostomy tube. Synonym: total enteral nutrition
What is enteral feeding?
Enteral feeding: Indications, complications, and nursing care. Enteral feedings deliver nourishment through a tube directly into the GI tract. They’re ordered for patients with a functioning GI tract who can’t ingest enough nutrition orally to meet their needs.
What are the complications of enteral feeding?
Patients with feeding tubes are at risk for such complications as aspiration, tube malpositioning or dislodgment, refeeding syndrome, medication-related complications, fluid imbalance, insertion-site infection, and agitation. To identify these problems, thoroughly assess the patient before tube feeding begins ...
Why do enteral feedings cause diarrhea?
Until recently, clinicians assumed diarrhea in patients receiving enteral feedings stemmed from malabsorption and feeding intolerance. But more recent research points to medications, especially those high in sorbitol, as the main culprit.
What is the role of nursing assistant in a patient's nutritional needs?
Caloric requirements calculated by a dietitian must be ordered by a healthcare provider and delivered and monitored by a nurse. (However, some states permit dietitians to initiate nutritional interventions.) Nursing assistants can help with patient positioning and comfort care as well as behavioral monitoring. Consult additional specialists, such as a wound ostomy nurse, about the risk of pressure injuries compounded by malnutrition or dehydration.
Where do the prepyloric tubes end?
The two main types of feeding tubes are prepyloric and postpyloric. • Prepyloric tubes end in the stomach above the pyloric sphincter. They’re preferred for intermittent feeding and to allow gastric absorption. • Postpyloric tubes end beyond the pyloric sphincter in the jejunum.
When to turn off tube feeding?
During patient transport or when placing the head of the bed flat for patient repositioning, turn the tube feeding off, especially if the patient has a high aspiration risk. However, be aware that no conclusive evidence shows that pausing tube feeding during repositioning reduces aspiration risk for patients with high GRVs.
Can enteral formulas be administered?
Enteral formulas can be administered using either an open or a closed (ready-to-use) system and can be delivered through several methods. (See Understanding enteral feeding systems and methods.)
What is a small bowel feeding tube?
They are called Small Bowel Feeding Tubes. When a feeding tube is inserted through the nose or mouth, the nurse or physician will attempt to manipulate the tube in a way that encourages it to pass from the stomach and into the bowel.
What is a feeding tube called?
A feeding tube inserted through a puncture wound is called a Percutaneous feeding tube . Tubes that end in the stomach are called " gastric " tubes or G tubes. The stomach empties toward the right side and into the small bowel. The initial segment of the small bowel (or small intestine) is called the duodenum.
What is an OJ tube?
An OJ is a small bowel feeding tube (ending in the Jejunum) that was inserted through the mouth. Finally, a tube inserted through a puncture site can be identified by the end of the word. A puncture hole is called a "stoma" or "ostomy". A stomach tube that is inserted through a puncture is called as gastrostomy.
What is the name of the tube that is inserted through the nose?
A stomach tube that is inserted through the nose is called a nasogastric tube or NG. Tubes inserted through the mouth are called "oral" tubes. An orogastric tube or OG is a stomach tube that is inserted through the mouth. An OJ is a small bowel feeding tube (ending in the Jejunum) that was inserted through the mouth.
What is the name of the tube that ends in the duodenum?
A tube that ends in the duodenum is called a duodenal tube. The next section of the small bowel is the jejunum. A tube inserted into the jejunum is called a " J " tube or jejunal tube. If a tube is inserted through the nose, it is called a " nasal" tube.
What is a feeding tube inserted through a puncture wound called?
A feeding tube inserted through a puncture wound is called a Percutaneous feeding tube.
Why do you need a gastric drain tube?
This is called gastric drainage. This is done to promote patient comfort and prevent vomiting or aspiration. These can be connected to low suction (or low vacuum), to help keep the stomach empty.
What is enteral feeding?
Enteral feeding refers to liquid nutrition processed by the gastrointestinal tract. Individuals who are prescribed enteral feeding consume their meals through a tube that connects to their stomach or small intestine. Sometimes, enteral feeding provides supplemental nutrition; other times, it accounts for a patient’s entire caloric intake.
Why is enteral feeding important?
That’s because it’s less costly, easier on the body, and presents fewer complications. In addition, enteral feeding allows for more efficient nutrient consumption and encourages the body’s natural healing process by stimulating intestinal blood flow.
What are the types of enteral vs parenteral feeding?
Enteral and parenteral feeding fall into several sub-categories. Your loved one’s primary care physician makes a recommendation based on their age, current health, medical history, and nutritional needs.
What is the outlook for someone using enteral vs. parenteral feeding?
Both enteral feeding and parenteral feeding require significant lifestyle changes. It’s normal to feel stressed out or overwhelmed, especially during the first few days or weeks. If you have questions or concerns at any point, contact your loved one’s doctor, nutritionist, or home health providers. They can correct any mistakes, provide key insights, and help you establish a feeding routine.
What are the benefits of parenteral nutrition?
Parenteral nutrition is like enteral nutrition in that it helps prevent malnourishment. However, it’s designed to assist individuals who have gastrointestinal issues that prevent them from properly digesting food. Common conditions that may benefit from parenteral nutrition include: Crohn’s disease. Cancer.
What does enteral nutrition do?
Enteral nutrition reduces the risk of malnourishment, or a lack of vitamins, minerals, and nutrients. If your loved one isn’t able to eat enough calories throughout the day, they’re more likely to lose weight and experience serious health problems.
How many types of enteral feeding are there?
There are six main types of enteral feeding, including: