
What is epithelialization and why is it important?
What is Epithelialization? Epithelialization is the process of covering open wounds with new epithelial surfaces. Hence, it is an essential process in wound healing. Moreover, this process involves both molecular and cellular processes. They are responsible for the initiation, maintenance, and completion of epithelialization.
Which process covers a wound with epithelial tissue?
epithelialization (Noun) the process that covers a wound with epithelial tissue. epithelialization (Noun) the process of assembling an epithelium from non-epithelial cells, such as in the process of mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition.
What is epithelialisation of incisional wound?
Epithelialisation of an incisional wound involves the migration of cells at the wound edges over a distance of less than 1 mm, from one side of the incision to the other. Incisional wounds are epithelialised within 24–48 h after injury. This epithelial layer provides a seal between the underlying wound and the environment.
Why is epithelialisation postponed for a while?
Epithelialisation is postponed for a while to allow the granulation tissue to be filled into the wound defect. Epithelialisation is the formation of epithelium over a denuded surface.
What is the epithelial layer?
Can epithelial cells migrate?
About this website
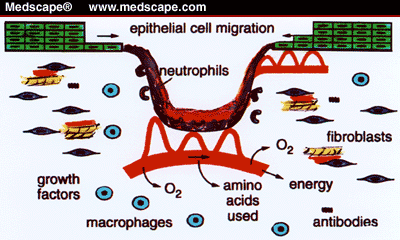
What stage of healing is epithelialization?
Epithelialization is a process where epithelial cells migrate upwards and repair the wounded area. This process is the most essential part in wound healing and occurs in proliferative phase of wound healing.
What does Epithelialize mean?
verb (used with or without object), ep·i·the·li·al·ized, ep·i·the·li·al·iz·ing. to form a covering of epithelial cells over, as a wound.
How long does it take a wound to Epithelialized?
Some sources report that well-approximated wounds can re-epithelialize within 48 hours; others report the process of epithelialization generally takes 2 to 3 weeks. [10] The faster this process occurs, the less scarring there is.
What is granulation and epithelialization?
Epithelialization is the process by which the keratinocytes covers the granulation tissue of the wound.
Does Epithelialized mean healed?
Epithelialization is an essential component of wound healing used as a defining parameter of its success. In the absence of re-epithelialization, a wound cannot be considered healed. Barrier breach provides a portal for wound infection. This process is impaired in all types of chronic wounds.
What does an Epithelialized wound look like?
Wound Tissue Types. The process of epidermis regenerating over a partial-thickness wound surface or in scar tissue forming on a full-thickness wound is called epithelialization. The epithelium manifests as light pink with a shiny pearl appearance.
What happens during epithelialization?
Epithelialization is defined as a process of covering denuded epithelial surface. The cellular and molecular processes involved in initiation, maintenance, and completion of epithelialization are essential for successful wound closure.
How long does the epithelialization phase last?
In acute wounds that are primarily closed, epithelization is normally completed in 1 to 3 days. In open wounds, including chronic wounds, healing by secondary intention cannot progress until the wound bed is fully granulated. Like immunity and granulation, epithelization depends on growth factors and oxygen.
What does Newly Epithelialized mean?
Response “0 – Newly epithelialized”: Enter Response 0 when the wound bed has completely covered with new epithelium; no exudate; no avascular tissue (eschar and/or slough); no signs or symptoms or infection.
What are the 3 stages of wound healing in order?
Three Stages of Wound HealingInflammatory phase – This phase begins at the time of injury and lasts up to four days. ... Proliferative phase – This phase begins about three days after injury and overlaps with the inflammatory phase. ... Remodeling phase – This phase can continue for six months to one year after injury.
What are the 4 stages of wound healing?
Wound healing is classically divided into 4 stages: (A) hemostasis, (B) inflammation, (C) proliferation, and (D) remodeling. Each stage is characterized by key molecular and cellular events and is coordinated by a host of secreted factors that are recognized and released by the cells of the wounding response.
What is Sluff in a wound?
Slough refers to the yellow/white material in the wound bed; it is usually wet, but can be dry. It generally has a soft texture. It can be thick and adhered to the wound bed, present as a thin coating, or patchy over the surface of the wound (Figure 3). It consists of dead cells that accumulate in the wound exudate.
What does it mean when a wound is granulating?
What Does The Presence of Granulation Tissue Mean? In short, observing granulation tissue in the bed of the wound means that the wound is progressing from the inflammatory phase of healing to the proliferative phase of healing. Several important cellular developments are occurring.
What is meant by granulation?
Definition of granulation 1 : the act or process of granulating : the condition of being granulated. 2 : one of the minute red granules of new capillaries formed on the surface of a wound in healing.
What does Eschar mean in medical terms?
Eschar is dead tissue that falls off (sheds) from healthy skin. It is caused by a burn or cauterization (destroying tissue with heat or cold, or another method). An escharotic is a substance (such as acids, alkalis, carbon dioxide, or metallic salts) that causes the tissue to die and fall off.
How long does the epithelialization phase last?
In acute wounds that are primarily closed, epithelization is normally completed in 1 to 3 days. In open wounds, including chronic wounds, healing by secondary intention cannot progress until the wound bed is fully granulated. Like immunity and granulation, epithelization depends on growth factors and oxygen.
Epithelialization in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review
Significance: Keratinocytes, a major cellular component of the epidermis, are responsible for restoring the epidermis after injury through a process termed epithelialization. This review will focus on the pivotal role of keratinocytes in epithelialization, including cellular processes and mechanisms of their regulation during re-epithelialization, and their cross talk with other cell types ...
Epithelialization Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster
The meaning of EPITHELIALIZATION is the process of becoming covered with or converted to epithelium. How to use epithelialization in a sentence.
Epithelization | definition of epithelization by Medical dictionary
The nutritional condition is another decisive factor in the evolution of the scarring process due to the specificity of action as the proteins favor the inflammatory response and the synthesis of collagen with the remodeling of the ulcer; carbohydrates and fats by providing energy; vitamin K by acting in the coagulation process, B complex in collagen metabolism, zinc in cell proliferation and ...
Epithelization - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Harriet W. Hopf MD, ... Dag Shapshak MD, in Physiology and Medicine of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy, 2008. Epithelization. Epithelization is characterized by replication and migration of epithelial cells across the skin edges in response to growth factors. Cell migration may begin from any site that contains living keratinocytes, including remnants of hair follicles, sebaceous glands, islands of ...
Epithelialized | definition of epithelialized by Medical dictionary
v. epithelial·ized, epithelial·izing, epithelial·izes or epithe·lized or epithe·lizing or epithe·lizes
Are we missing a good definition for epithelialization? Don't keep it to yourself..
The ASL fingerspelling provided here is most commonly used for proper names of people and places; it is also used in some languages for concepts for which no sign is available at that moment.
Definitions & Translations
Get instant definitions for any word that hits you anywhere on the web!
What is the epithelial layer?
This epithelial layer provides a seal between the underlying wound and the environment. The process begins within hours of tissue injury. Epidermal cells at the wound edges undergo structural changes, allowing them to detach from their connections to other epidermal cells and to their basement membrane.
Can epithelial cells migrate?
Epithelial cells can only migrate over a moist, vascular wound surface, and are hampered by a dry or necrotic wound surface [7]. Lateral migration continues until the defect is renovated, before the cells carry on upward migration and differentiation and the epidermis regains its normal thickness and stratification.
Why is epithelialization important?
Hence, it creates a barrier to cover the wound and prevents the entering of microorganisms and other pathogenic substances. On the other hand, granulation forms new connective tissue and blood vessels to fill the wound completely. Thus, both epithelialization and granulation are important ...
What is epithelialization in wound healing?
Epithelialization is the process of covering open wounds with new epithelial surfaces. Hence, it is an essential process in wound healing. Moreover, this process involves both molecular and cellular processes. They are responsible for the initiation, maintenance, and completion of epithelialization. Thus, this results in successful closure of ...
What are the two processes of wound healing?
Both epithelialization and granulation are two processes of wound healing. Both processes use different types of cells for wound healing. Moreover, they prevent the occurrence of chronic wounds and other clinical problems associating wounds. Also, they occur immediately after rupturing of epithelia and other tissues during a wound.
What is granulation tissue?
Granulation or granulation tissue is a new connective tissue that forms during the wound healing. The connective tissue contains microscopic blood vessels. Hence, granulation is a process of forming new connective tissue, covering the wound surface. Granulation occurs from the base of the wound.
What is the difference between granulation and epithelialization?
The key difference between epithelialization and granulation is that epithelialization is a part of wound healing which forms a new epithelial surface on the open wound while granulation is the process of forming new connective tissue and blood vessels during wound healing. Epithelialization and granulation are two processes linked to wound healing.
What are the cells that make up the granulation tissue?
These cells help in the formation of extracellular matrix or in immunity and vascularization. The tissue matrix of granulation tissue consists of fibroblasts. The major immune cells present in the granulation tissue include macrophages and neutrophils.
Does re-epithelialization take place in wounds?
Also, in chronic wounds, re-epithelialization doesn ’t take place. In summarizing the difference between epithelialization and granulation, granulation involves many cells, including immune cells and fibroblasts, while epithelialization involves only one major type of cell – keratinocytes.
What is the epithelial layer?
This epithelial layer provides a seal between the underlying wound and the environment. The process begins within hours of tissue injury. Epidermal cells at the wound edges undergo structural changes, allowing them to detach from their connections to other epidermal cells and to their basement membrane.
Can epithelial cells migrate?
Epithelial cells can only migrate over a moist, vascular wound surface, and are hampered by a dry or necrotic wound surface [7]. Lateral migration continues until the defect is renovated, before the cells carry on upward migration and differentiation and the epidermis regains its normal thickness and stratification.
