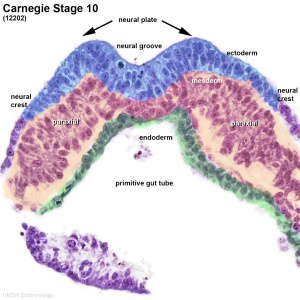
What is the mesoderm of the embryo?
Mesoderm. Gastrulation is an early stage of development during which an embryo, then a single-layered ball of cells called a blastula, reorganizes itself into a three-layered ball of cells, called a gastrula. During this process, the primary germ layers, endoderm and ectoderm, interact to form the third, called mesoderm.
What is the difference between lateral and extraembryonic mesoderm?
During human development, the intraembryonic mesoderm on each side of the neural groove differentiates into paraxial, intermediate and lateral mesoderm. The lateral mesoderm is continuous with the extraembryonic mesoderm covering the yolk sac and amnion.
What is the function of the mesoderm?
Mesoderm. The process that gives rise to the mesoderm also creates a dorso-ventral pattern within the mesoderm. This patterning of the mesoderm organizes cells in specific locations along the dorso-ventral axis, and a cell's location determines what kinds of cell it and its daughter cells can become (cell fate).
What are the two layers of the lateral mesoderm?
The lateral mesoderm is continuous with the extraembryonic mesoderm covering the yolk sac and amnion. At the end of the third week, small spaces appear in the lateral mesoderm that fuse, dividing the mesoderm into two layers: the intraembryonic somatic or parietal layer and the intraembryonic splanchnic or visceral layer (Batra and Antony, 2014 ).

What happens to the Extraembryonic mesoderm?
The extraembryonic mesoderm proliferates to line both Heuser's membrane (forming the primary yolk sac) and cytotrophoblast (forming the chorion). The extraembryonic reticulum then breaks down and is replaced by a fluid-filled cavity, the chorionic cavity.
What is an Extraembryonic mesoderm?
The extraembryonic mesoderm supports the epithelium of the amnion and yolk sac as well as the villi, which arise from the trophoblastic tissue. It also is involved in the development of the fetal blood.
What does mesoderm develop into?
By the process of gastrulation, the embryo differentiates into three types of tissue: the ectoderm, producing the skin and nervous system; the mesoderm, from which develop connective tissues, the circulatory system, muscles, and bones; and the endoderm, which forms the digestive system, lungs, and urinary system.
What happens to the extraembryonic coelom?
The intraembryonic coelom, which will form the body cavities of the embryo, is still continuous with the extraembryonic coelom via a space within the umbilical cord. Again, it should be emphasized that all of these continuities are located at the umbilical ring, and still exist in the developing embryo, even at term.
What are the two layers of Extraembryonic mesoderm?
The extra-embryonic mesoderm is subdivided into two layers: the extra-embryonic splanchnopleuric mesoderm, which is outside the primitive yolk sac; and the extra-embryonic somatopleuric mesoderm, which is adjacent to the cytotrophoblast.
What does Extraembryonic mean?
situated outside the embryoDefinition of extraembryonic : situated outside the embryo especially : developed from the zygote but not part of the embryo extraembryonic membranes.
Which of the following is formed from mesoderm?
The mesoderm is responsible for the formation of a number of critical structures and organs within the developing embryo including the skeletal system, the muscular system, the excretory system, the circulatory system, the lymphatic system, and the reproductive system.
Which tissue type is formed from mesoderm?
As organs form, a process called organogenesis, mesoderm interacts with endoderm and ectoderm to give rise to the digestive tract, the heart and skeletal muscles, red blood cells, and the tubules of the kidneys, as well as a type of connective tissue called mesenchyme.
What body part develops from the mesoderm quizlet?
The mesoderm gives rise to all muscle, bone, connective tissue, cardiovascular system, lymphatic system, urogenital organs, and the dermis.
What is the function of extraembryonic coelom?
The exocoelomic cavity forms inside the extraembryonic mesoderm alongside the placental chorionic plate and is now believed to be an important transfer interface and a reservoir of nutrients for the embryo.
Which body cavity is formed from the embryonic Coelom?
The primitive intraembryonic coelom forms in the lateral and cardiogenic mesoderm about the fourth week of development. The embryo undergoes two foldings and this cavity is eventually divided into the pericardial, pleural, and peritoneal embryonic body cavities.
What does intraembryonic coelom become?
The resulting cavity between the somatopleure and splanchnopleure is called the intraembryonic coelom. This space will give rise to the thoracic and abdominal cavities....Intraembryonic coelomDetailsPrecursorlateral plate mesodermGives rise topericardial cavity, pleural cavity, peritoneal cavityIdentifiers4 more rows
What are the 4 extraembryonic membranes?
There are four extra-embryonic membranes commonly found in VERTEBRATES, such as REPTILES; BIRDS; and MAMMALS. They are the YOLK SAC, the ALLANTOIS, the AMNION, and the CHORION.
What is Extraembryonic ectoderm?
The extraembryonic ectoderm (ExE) is formed following implantation as cells from the polar trophectoderm proliferate.
What is extra embryonic endoderm?
The extraembryonic endoderm is a derivative of the hypoblast cells that migrate into the blastocyst cavity (beginning on day 8 of human embryonic development), and line the cavity, giving rise to the primary and definitive yolk sacs. The extraembryonic endoderm fills the remaining cavity of the blastocyst.
What are the four extraembryonic membranes that are formed from the three germ layers?
Summary. The extraembryonic membranes consist of the chorion (the combination of trophoblast plus underlying extraembryonic mesoderm), amnion, yolk sac, and allantois.
What is the process of mesoderm and endoderm?
As organs form, a process called organogenesis, mesoderm interacts with endoderm and ectoderm to give rise to the digestive tract, the heart and skeletal muscles, red blood cells, and the tubules of the kidneys, as well as a type of connective tissue called mesenchyme. All animals that have only one plane of symmetry through the body, ...
Where is mesoderm found?
Mesendoderm has been found in species from Echinoderms, such as sea urchins, to mice, Mus musculus. The process that gives rise to the mesoderm also creates a dorso-ventral pattern within the mesoderm.
What are the three germ layers of symmetry?
All animals that have only one plane of symmetry through the body, called bilateral symmetry, form three germ layers. Animals that have only two germ layers develop open digestive cavities. In contrast, the evolutionary development of the mesoderm allowed in animals the formation of internal organs such as stomachs and intestines (viscera). ...
What is the term for the three germ layers of cells that form organs and tissues?
Published: 2013-11-26. Keywords: embryos. Mesoderm. Mesoderm is one of the three germ layers, groups of cells that interact early during the embryonic life of animals and from which organs and tissues form. As organs form, a process called organogenesis, mesoderm interacts with endoderm and ectoderm to give rise to the digestive tract, ...
When was mesoderm discovered?
Mesoderm, along with the other two germ layers, was discovered in the early nineteenth century. In 1817 Christian Pander received an MD from the University of Würzburg, in Würzburg, Germany, after completing his dissertation. " Beiträge zur Entwickelungsgeschichte des Hühnchens im Eie " ( Contributions to the Developmental History ...
What is the first stage of embryonic development?
Gastrulation is an early stage of development during which an embryo, then a single-layered ball of cells called a blastula, reorganizes itself into a three-layered ball of cells, called a gastrula. During this process, the primary germ layers, endoderm and ectoderm, interact to form the third, called mesoderm.
Which process establishes polarity in the mesoderm?
Using those experiments, Nieuwkoop also demonstrated that the induction process establishes a polarity in the mesoderm, such that dorsal endoderm induces dorsal mesoderm, ...
