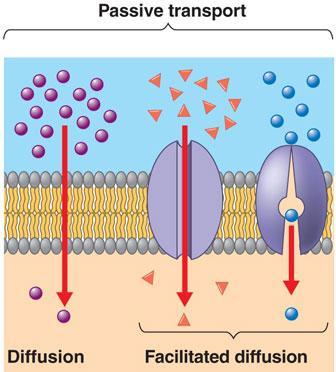
Facilitated diffusion
- the transport relies on molecular binding between the cargo and the membrane-embedded channel or carrier protein.
- the rate of facilitated diffusion is saturable with respect to the concentration difference between the two phases; unlike free diffusion which is linear in the concentration difference.
What are three facts about Facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion is the passive movement of molecules along the concentration gradient. It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. The electric charge and pH helps in the diffusion across the membrane.
What are what are facts about Facilitated diffusion?
The different factors that affect diffusion either individually or collectively are:
- Temperature: Warmer the temperature, higher is the rate of diffusion.
- Area of Interaction: More the surface area of interacting molecules, higher is the rate of diffusion.
- The Extent of the Concentration Gradient : Greater the difference in concentration between the regions, higher is the rate of diffusion.
What biomolecule is responsible for facilitated diffusion?
Carrier proteins involved in facilitated diffusion often have two conformations. The binding of a molecule on one side of the membrane induces a change in the three-dimensional structure of the protein, which allows the passage of the molecule through to the other side.
Does facilitated diffusion require energy from ATP hydrolysis?
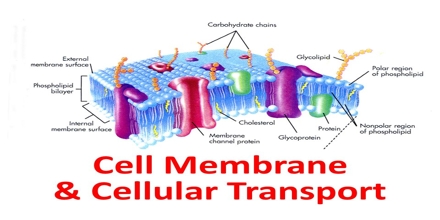
Water soluble molecules/charged molecules move through the membrane via channel proteins or carrier proteins. Channel and carrier proteins are specific (due to their tertiary structure); they only transport specific molecules. Facilitated diffusion is a passive process, it does not require extra energy from the hydrolysis of ATP.
What Does facilitated diffusion require quizlet?
Facilitated diffusion requires. carrier proteins. Facilitated diffusion occurs. in either direction depending on the concentration gradient of the molecule. Facilitated diffusion is used to transport.
What Does facilitated diffusion depend on?
The main factors affecting the process of facilitated diffusion are: Temperature- As the temperature increases, the movement of the molecules increases due to an increase in energy. Concentration- The movement of the molecules takes place from the region of higher concentration to lower concentration.
What is facilitated diffusion does it require energy?
Facilitated diffusion is movement of ions and small, polar molecules along their concentration gradient. This passive movement of molecules or ions from regions of high concentration to low, does not require the use of cellular energy (ATP).
What facilitates facilitated diffusion in the cell?
Facilitated diffusion is a form of passive transport across a biological membrane in which a transporter protein facilitates (or mediates or catalyzes) the movement of an otherwise membrane-impermeant molecule or ion across the plasma membrane down its concentration or electrochemical gradient.
Do you need ATP for facilitated transport?
Facilitated diffusion does not require high energy molecules such as ATP. This type of diffusion uses channel proteins and carrier proteins to transport molecules across the plasma membrane. Facilitated diffusion involves the movement of molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
Does diffusion require energy or protein?
Diffusion is the movement from a high concentration of molecules to a low concentration of molecules. Molecules can diffuse across membranes through the phospholipid bilayer or using a special protein. Either kind of diffusion does not need energy from the cell.
Does facilitated diffusion require active transport?
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport. Even though facilitated diffusion involves transport proteins, it is still passive transport because the solute is moving down the concentration gradient. Small nonpolar molecules can easily diffuse across the cell membrane.
What is facilitated diffusion in biology?
Facilitated diffusion is the passive movement of molecules across the cell membrane via the aid of a membrane protein. It is utilised by molecules that are unable to freely cross the phospholipid bilayer (e.g. large, polar molecules and ions)
Does facilitated diffusion require energy quizlet?
Unlike simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion requires energy expenditure by the cell. Facilitated diffusion requires a specific transporter for a specific molecule. sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell.
Why doesnt facilitated diffusion need energy?
In active transport, like exocytosis or endocytosis, energy is required to move substances. The transport proteins involved in facilitated diffusion don't need energy. This is because the molecules are spontaneously going down their concentration gradient.
What is facilitated diffusion give an example?
Facilitated diffusion can also be seen in the movement of oxygen through the blood and muscles. The carrier protein in blood is haemoglobin, whereas the carrier protein in muscles is myoglobin. Blood diffusion is caused by higher pressure on one side of the membrane and lower pressure on the other.
What is facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion is a form of facilitated transport involving the passive movement of molecules along their concentration gradient, guided by the presence of another molecule – usually an integral membrane protein forming a pore or channel. Facilitated diffusion does not directly involve high-energy molecules like adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ...
How does perfume affect the senses?
For instance, when someone walks into a room wearing a strong perfume, the odorous molecules diffuse outwards, from the skin or clothes. The people in the room perceive some of these randomly moving molecules when they trigger the sensory receptors in the nose. When there is a high density of scented molecules in a region, there is a chance that a few will move away due to the innate kinetic energy of these molecules. However, the likelihood that these few stray molecules will move in a directed manner, back towards the sleeve or cuff of the person wearing the perfume is relatively small. The end result is a cloud of progressively decreasing concentration away from the person wearing the perfume.
How does diffusion affect the biosphere?
Diffusion is ubiquitous across the biosphere. It is seen in the movement of air and water, and is a necessary force driving global weather patterns. Within living systems, the presence of lipid -based membranes creates compartments that allow the selective concentration of water-soluble substances. For instance, mitochondrial membranes can create 2 distinct regions within the organelle – the inner matrix and the inter-membrane space. Each of these sub-compartments has a specific composition and function, distinct from the adjoining spaces. The generation of order in this manner is one of the hallmarks of nearly every unit of the living world – from organelles within a cell to entire organ systems and organisms.
Why is independent diffusion important?
Though this could be an unpleasant experience, independent diffusion is an important property of molecules that allows cells to take in nutrients (diffusing in one direction), while at the same time, expelling metabolic waste products (diffusing outwards in the opposite direction).
What is the driving force behind diffusion?
The driving force behind diffusion of fluids is simply the probability behind Brownian motion. All molecules have some degree of erratic, random movement, largely dependent on temperature. As temperature increases, the energy of these molecules increases.
Why is it so difficult to study integral membrane proteins?
The study of integral membrane proteins is always difficult, since they are made of long hydrophobic stretches interspersed with hydrophilic regions. Crystallizing these proteins in order to understand their structure is fraught with difficulty.
Which type of protein is involved in facilitated diffusion?
Carrier proteins involved in facilitated diffusion often have two conformations. The binding of a molecule on one side of the membrane induces a change in the three-dimensional structure of the protein, which allows the passage of the molecule through to the other side.
Why does facilitated diffusion not require energy?
The facilitated diffusion does not require energy while transporting the molecules or ions through the cell membrane.
Why does facilitated diffusion via glut proteins require no metabolic energy?
The transportation of glucose molecule needs GLUT proteins and does not need metabolic energy in the form of ATP molecules.
Why does active transport require energy when facilitated diffusion does not?
The energy is required in active transport because the molecules are transported against their concentration gradient whereas energy is not required in facilitated diffusion as the molecules are transported from high concentration gradient.
Is facilitated diffusion active or passive transport?
The facilitated diffusion is said to be passive transport as it does not require energy during transportation.
What are the factors involve in facilitated diffusion?
In facilitated diffusion process factors involved are namely temperature, concentration, diffusion, distance, size of the molecules, selectivity and saturation.
How does facilitated diffusion channel proteins?
In facilitated diffusion the molecules flow freely through plasma membrane With help of proteins which are present in the membrane.
Is channel protein diffusion active or passive?
Channel protein diffusion is always a passive diffusion as in this process energy is not required.
Does facilitated diffusion require a carrier protein?
In facilitated diffusion process the carrier proteins play a pivotal role in the transportation of molecules.
What is the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion?
Diffusion is the process of transfer of molecules and ions from high concentration gradient to low concentration gradient.
What is meant by an active transport?
Active transport is the process of movement of molecules from low concentration gradient to high concentration gradient. This process require ATP molecules.
How does the carrier protein change shape?
The carrier protein then changes shape again. The ions from the extracellular fluid are then transported across the cell membrane to the inside of the cell. The ions in the extracellular fluid bind to the carrier protein, and the potassium attached to the carrier protein is released.
How does water diffuse through a membrane?
the water will diffuse through the membrane until there is an equal concentration of solute on both sides. the water will diffuse through the membrane until there is an equal concentration of solute and water on both sides.
How does a solute pass through a membrane?
the solute will pass through the membrane in both directions until equilibrium is reached on both sides of the membrane for the solute. both the water and the solute will pass through the membrane in both directions until equilibrium is reached on both sides of the membrane for both water and the solute.
What is simple diffusion?
Simple diffusion is defined as the movement of. molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. molecules from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration. water molecules across a membrane. gas molecules across a membrane. gas or water molecules across a membrane.
When does the motion of the molecules of both the solute and water cease?
the motion of the molecules of both the solute and water will cease when equilibrium is reached. both the water and the solute will pass through the membrane in both directions until equilibrium is reached on both sides of the membrane for both water and the solute. When a membrane that is only permeable to water separates water with ...
What is diffusion in biology?
Diffusion is one of the processes whereby materials are exchanged between a cell and its environment. True.
When a membrane that is permeable to both a solute and water separates water with a answer?
When a membrane that is permeable to both a solute and water separates water with a high osmolarity from water with a low osmolarity. the water will only move through the membrane in one direction while the solute will move through the membrane in the other. the solute will pass through the membrane in both directions until equilibrium is reached ...
