What causes uranium to undergo fission?
When a free neutron hits the nucleus of a fissile atom like uranium-235 ( 235 U), the uranium splits into two smaller atoms called fission fragments, plus more neutrons. Fission can be self-sustaining because it produces more neutrons with the speed required to cause new fissions. This creates the chain reaction.
What are the two products formed by the fission of uranium?
The fission creates radioactive isotopes of lighter elements such as cesium-137 and strontium-90. These isotopes, called "fission products," account for most of the heat and penetrating radiation in high-level waste. Second, some uranium atoms capture neutrons produced during fission. Does fission produce waste?
What is the specific fission reaction that occurs in uranium?
The energy from the neutrons can cause the uranium nucleus to break in several different ways. A common fission reaction produces barium- 141 and krypton- 92. In this particular reaction, one uranium nucleus breaks into a barium nucleus, a krypton nucleus, and two neutrons.
Who really discovered nuclear fission?
Nuclear fission was discovered in December 1938 by chemists Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann and physicists Lise Meitner and Otto Robert Frisch.Fission is a nuclear reaction or radioactive decay process in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller, lighter nuclei and often other particles. The fission process often produces gamma rays and releases a very large amount of energy ...
How many neutrons does a fission produce?
It will produce 2 or more fission fragments, 2–3 neutrons, some alpha, beta , and gamma particles which will all add up to be about 208 MEV of energy released mostly in the kinetic energy of the fission fragments. The fission fragments themselves will also be radioactive releasing energy depending on their half life and isotope. There is something called the fission yield curve which plots the probability of the various fission products.
What is the process of diffusion of uranium hexafluoride?
Gaseous diffusion process: It involves forcing uranium hexafluoride gas under pressure through a series of porous membranes or diaphragms. As U-235 molecules are lighter than the U-238 molecules they move faster and have a slightly better chance of passing through the pores in the membrane. The UF6 which diffuses through the membrane is thus slightly enriched, while the gas which did not pass through is depleted in U-235.
How is UF6 used in centrifuge?
Centrifuge process: the centrifuge process uses UF6 gas as its feed and makes use of the slight difference in mass between U-235 and U-238. The gas is fed into a series of vacuum tubes, each containing a rotor 3 to 5 metres tall and 20 cm diameter. When the rotors are spun rapidly, at 50,000 to 70,000 rpm, the heavier molecules with U-238 increase in concentration towards the cylinder's outer edge. There is a corresponding increase in concentration of U-235 molecules near the centre. The counter current flow set up by a thermal gradient enables enriched product to be drawn off axially, heavier molecules at one end and lighter ones at the other.
What is the probability of spontaneous fission in a reactor?
Heavy elements have a small probability of undergoing spontaneous fission. In a reactor, the sponateous fission rate of 238U is about 5, 4 10 − 5 % of the decay which gives about 13,6 neutrons/kg of 238U per second. The contribution of 235U in this respect is smaller. Here the spontaneous fission probability is 2, 0 10 − 7 % corresponding to 0.3 neutrons/kg per second.
Why is Uranium 235 used in nuclear reactors?
Uranium 235, which is an isotope of uranium, is used in nuclear reactors mainly because of how unstable it is. In a nuclear reactor it would be physically possible to create energy by splitting hydrogen atoms, but the amount of energy used to fire protons at that atom would far outweigh the energy given. Thus, radioactive atoms were used, but they figured that they could still get more energy from a more unstable atom. With uranium 235, there are so many more neutrons, that at the slightest touch the atom splits. But that isn’t the only reason it is used, it is also used because it is the best
Why are uranium 238 and 235 separated?
Electromagnetic process: Ions of uranium-238 and uranium-235 are separated because they describe arcs of different radii when they move through a magnetic field.
How does UF6 work?
Molecular processes works on a principle of photo-dissociation of UF6 to solid UF5+, using tuned laser radiation to break the molecular bond holding one of the six fluorine atoms to a U-235 atom. This then enables the ionized UF5 to be separated from the unaffected UF6 molecules containing U-238 atoms, hence achieving a separation of isotopes. Any process using UF6 fits more readily within the conventional fuel cycle than the atomic process.
What happens when uranium 235 is fissioned?
When uranium 235 undergoes fission, the nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei, along with a few neutrons. Uranium 235 is a fissile isotope and its fission cross-section for thermal neutrons is about 585 barns (for 0.0253 eV neutron). Skip to content.
What causes a fission fragment to ionize?
The fission fragments interact stronglywith the surrounding atoms or molecules traveling at high speed, causing them to ionize. Creation of ion pairs requires energy, which is lost from the kinetic energy of the charged fission fragment causing it to decelerate.
How does a fission fragment work?
Most of the fission fragments are highly unstable (radio active) nuclei and undergo further radioactive decays to stabilize itself. Therefore part of the released energy is radiated away from the reactor (See also: Reactor antineutrinos ). On the other hand most of the energy released by one fission (~170MeV of total ~200MeV) appears as kinetic energy of these fission fragments. The fission fragments interact strongly with the surrounding atoms or molecules traveling at high speed, causing them to ionize. Creation of ion pairs requires energy, which is lost from the kinetic energy of the charged fission fragment causing it to decelerate. The positive ions and free electrons created by the passage of the charged fission fragment will then reunite, releasing energy in the form of heat (e.g. vibrational energy or rotational energy of atoms). This is the principle how fission fragments heat up fuel in the reactor core.
How many neutrons does uranium 235 have?
Typically, when uranium 235nucleus undergoes fission, the nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei (triple fission can also rarely occur), along with a few neutrons(the average is 2.43 neutrons per fission by thermal neutron) and release of energy in the form of heat and gamma rays.
Is Uranium 235 a fissile isotope?
Uranium 235 is a fissile isotopeand its fission cross-sectionfor thermal neutrons is about 585 barns(for 0.0253 eV neutron). For fast neutrons its fission cross-section is on the order of barns. Most of absorption reactions result in fission reaction, but a minority results in radiative capture forming 236U.
How did Uranium form?
Uranium was apparently formed in supernovae about 6.6 billion years ago. While it is not common in the solar system, today its slow radioactive decay provides the main source of heat inside the Earth, causing convection and continental drift.
Where does uranium come from?
Uranium occurs in seawater, and can be recovered from the oceans.
Who has and who mines uranium?
However, like other metals, it is seldom sufficiently concentrated to be economically recoverable. Where it is, we speak of an orebody. In defining what is ore, assumptions are made about the cost of mining and the market price of the metal. Uranium reserves are therefore calculated as tonnes recoverable up to a certain cost.
What are the features of nuclear power stations?
Both require heat to produce steam to drive turbines and generators. In a nuclear power station, however, the fissioning of uranium atoms replaces the burning of coal or gas .
What is the melting point of uranium?
Uranium has a melting point of 1132°C. The chemical symbol for uranium is U.
What happens when U-235 atoms split?
When this happens over and over again, many millions of times, a very large amount of heat is produced from a relatively small amount of uranium.
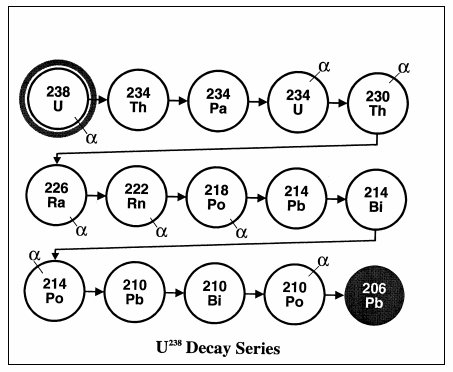
How long does U-238 decay?
U-238 decays very slowly, its half-life being about the same as the age of the Earth (4500 million years). This means that it is barely radioactive, less so than many other isotopes in rocks and sand. Nevertheless it generates 0.1 watts/tonne as decay heat and this is enough to warm the Earth's core.
How does nuclear fission work?
Nuclear fission produces energy for nuclear power and drives the explosion of nuclear weapons. Both uses are possible because certain substances called nuclear fuels undergo fission when struck by fission neutrons, and in turn emit neutrons when they break apart.
What is nuclear fission?
e. Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay . Nuclear fission of heavy elements was discovered on December 17, 1938, ...
Why are neutrons important in a nucleus?
Also because of the short range of the strong binding force, large stable nuclei must contain proportionally more neutrons than do the lightest elements, which are most stable with a 1 to 1 ratio of protons and neutrons. Nuclei which have more than 20 protons cannot be stable unless they have more than an equal number of neutrons. Extra neutrons stabilize heavy elements because they add to strong-force binding (which acts between all nucleons) without adding to proton–proton repulsion. Fission products have, on average, about the same ratio of neutrons and protons as their parent nucleus, and are therefore usually unstable to beta decay (which changes neutrons to protons) because they have proportionally too many neutrons compared to stable isotopes of similar mass.
Why is fission a form of nuclear transmutation?
Fission is a form of nuclear transmutation because the resulting fragments (or daughter atoms) are not the same element as the original parent atom.
How many charged fragments are produced in a fission?
Most fissions are binary fissions (producing two charged fragments), but occasionally (2 to 4 times per 1000 events), three positively charged fragments are produced, in a ternary fission. The smallest of these fragments in ternary processes ranges in size from a proton to an argon nucleus.
When was nuclear fission discovered?
The discovery of nuclear fission occurred in 1938 in the buildings of Kaiser Wilhelm Society for Chemistry, today part of the Free University of Berlin, following over four decades of work on the science of radioactivity and the elaboration of new nuclear physics that described the components of atoms. In 1911, Ernest Rutherford proposed a model of the atom in which a very small, dense and positively charged nucleus of protons was surrounded by orbiting, negatively charged electrons (the Rutherford model ). Niels Bohr improved upon this in 1913 by reconciling the quantum behavior of electrons (the Bohr model ). Work by Henri Becquerel, Marie Curie, Pierre Curie, and Rutherford further elaborated that the nucleus, though tightly bound, could undergo different forms of radioactive decay, and thereby transmute into other elements. (For example, by alpha decay: the emission of an alpha particle —two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus.)
What is the name of the process that produces large amounts of energy?
Frisch named the process by analogy with biological fission of living cells. For heavy nuclides, it is an exothermic reaction which can release large amounts of energy both as electromagnetic radiation and as kinetic energy of the fragments ( heating the bulk material where fission takes place).
What are the main elements in the mixture of fission products produced by nuclear fission?
This page discusses each of the main elements in the mixture of fission products produced by nuclear fission of the common nuclear fuels uranium and plutonium. The isotopes are listed by element, in order by atomic number .
What is in a fission product?
The fission product mixture contains significant amounts of molybdenum .
How much of the fission products of mass 85 become 85 Kr?
Only 20% of the fission products of mass 85 become 85 Kr itself; the rest passes through a short-lived nuclear isomer and then to stable 85 Rb. If irradiated reactor fuel is reprocessed, this radioactive krypton may be released into the air.
Why is fission gas measurement important?
Increase of fission gases above a certain limit can lead to fuel pin swelling and even puncture, so that fission gas measurement after discharging the fuel from the reactor is most important to make burn-up calculations, to study the nature of fuel inside the reactor, behaviour with pin materials, for effective utilization of fuel and also reactor safety.
What is the most significant radioisotope left in the area around Chernobyl?
137 Cs. Caesium-137, with a half-life of 30 years, is the main medium-lived fission product, along with Sr-90. Cs-137 is the primary source of penetrating gamma radiation from spent fuel until 300 years or more after discharge. It is the most significant radioisotope left in the area around Chernobyl.
What elements are produced by nuclear fuel?
Neutron capture by the nuclear fuel in nuclear reactors and atomic bombs also produces actinides and transuranium elements (not listed here). These are found mixed with fission products in spent nuclear fuel and nuclear fallout . Neutron capture by materials of the nuclear reactor (shielding, cladding, etc.) or the environment (seawater, soil, ...
Is 107 PD a radioactive isotope?
107 Pd is the only long-living radioactive isotope among the fission products and its beta decay has a long half life and low energy, this allows industrial use of extracted palladium without isotope separation.
What are the byproducts of nuclear fission?
Some of these fission products are neutron poisons, and therefore, must be compensated for byremoving some of the controllable poisons (such as the control rods for boiling water reactors or control rods orboron for pressurized water reactors) as they are produced. The fission products are usually very highlyradioactive. They emit a large amount of radiation, and therefore, must be contained within the plant. A systemof “barriers” has been developed to prevent these atoms from escaping into the environment. These barriers arethe fuel pellet and cladding, the reactor coolant system pressure boundary, and the containment.
Why are neutrons needed for fission?
Since neutrons are necessary to cause the fission event, and since each fission releases neutrons, there is thepotential to set up a self-sustaining chain reaction. For this to occur, there must be sufficient material capableof fissioning, and the material must be arranged such that the neutrons will reach other fuel atoms beforeescaping.
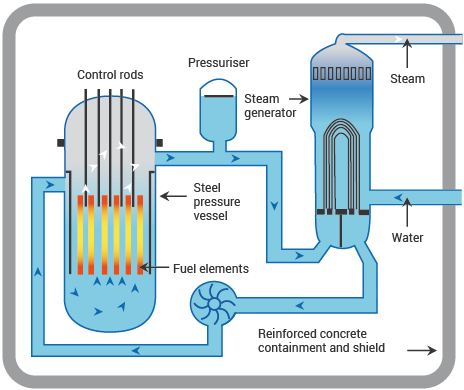
How does water help the reactor?
The use of water as a neutron moderator helps produce a steady rate of reactor power by slowing the neutronsdown that will be absorbed by the U-235 and by reflecting many of the neutrons that try to leak out of the reactorback into the core. The water can also remove neutrons from the fission chain.
How many fissions per second are needed to produce high temperature, high pressure steam for the production of electricity?
Every fission releases a tiny amount of heat. Trillions of fissions per second are necessary to produce the hightemperature, high pressure steam for the production of electricity. The rate at which the uranium atoms arefissioned determines the rate at which heat (and power) are produced.
How does U-235 absorb neutrons?
U-235 does have a high probability of absorbing a neutron. However, the probability increases even more if theneutron is moving slower. Therefore, in the reactor, it is desired to slow the neutrons down and then let the U-235 absorb them. This slowing down process is accomplished by the same water that is used to remove the heatfrom the fuel. Therefore, the water circulating through the reactor (called the reactor coolant system) has twoimportant functions. First, the water carries the heat from the reactor core to produce the steam used in theturbine. This prevents the fuel from becoming too hot, which could lead to fuel damage. Second, the water isused to control the fission process by slowing the neutrons down and by acting as a reflector to bounce back anyhigh energy neutrons that try to escape. This conserves the neutrons so that even more fissions may occur. The“slowing down” process is called “thermalization” or “moderation.”
What happens to the neutrons in a nuclear reactor?
Some of the neutrons released by fission will “leak” out of the reactor core area to be absorbed by the denseconcrete shielding around the reactor vessel. All the neutrons that remain in the core area will be absorbed bythe materials from which the various core components are constructed (U-235, U-238, steel, control rods, etc.).
How does nuclear energy work?
A nuclear power plant converts the energy contained within the nuclei of atoms into electrical energy. Thissection discusses the release of nuclear energy by the fission of uranium atoms and the methods used to controlthe rate at which energy is released and power is produced.