
Geophysical survey
Geophysical survey is the systematic collection of geophysical data for spatial studies. Detection and analysis of the geophysical signals forms the core of Geophysical signal processing. The magnetic and gravitational fields emanating from the Earth's interior hold essential information concerning seismic activities and the internal structure.
Full Answer
What are the methods of geophysical survey?
These methods are used to determine the layout, thickness and properties of individual layers below the terrain surface, on which the construction of a specific structure is planned. Geophysical surveys are performed from the soil surface, through boreholes, excavations or in a combination of placing sources and detectors.
What is geophysics in archaeology?
Geophysical surveys are archaeological methods that use ground-based physical sensing techniques to produce a detail image or map of an area. These methods are neither invasive nor destructive, an important goal when surveying culturally sensitive sites such as cemeteries. GPR visual representation of a cemetery.
Is geophysical survey invasive or destructive?
Unlike other archaeological methods, geophysical survey is neither invasive nor destructive. For this reason, it is often used where preservation (rather than excavation) is the goal, and to avoid disturbance of culturally sensitive sites such as cemeteries.
What is offshore geophysics?
Offshore areas are now covered using data available from airborne and shipborne geophysical surveys, although the quality of the coverage is variable. In a geophysical context this can be considered a study of the response of a continuously stratified ocean to wind-stress forcing at the surface.
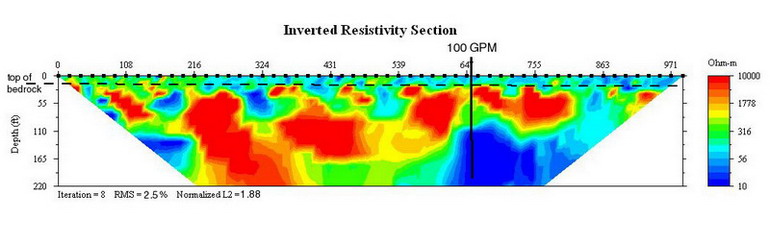
What do geophysical surveys do?
Geophysical surveys are archaeological methods that use ground-based physical sensing techniques to produce a detail image or map of an area. These methods are neither invasive nor destructive, an important goal when surveying culturally sensitive sites such as cemeteries.
What does geophysical survey mean in history?
Geophysical survey means any investigation carried out on the surface of the ground to determine the nature and structure of the subsurface; « levé géophysique »
What type of data do geophysical surveys collect?
Such geophysical surveys help to identify buried rock types and geologic structures associated with mineral, energy, and groundwater resources and buried geohazards such as seismogenic faults. New Earth MRI-funded data are currently being collected.
How do you conduct a geophysical survey?
0:512:09Introducing geophysical surveying - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipComputers are used to analyze these timings and translate them into a cross-section. Image of theMoreComputers are used to analyze these timings and translate them into a cross-section. Image of the rocks below the survey. Area seismic surveys will be a key technology in our WM.
What does the word geophysical mean?
: a branch of earth science dealing with the physical processes and phenomena occurring especially in the earth and in its vicinity.
What are the types of geophysical data?
The primary types of data held by the GSQ include:2D and 3D seismic data.airborne geophysical data.gravity data.deep seismic reflection surveys.magnetotellurics (MT) surveys.
What is geophysical used for?
Geophysical data is used to provide information on the physical properties of the Earth's surface and subsurface. As a result, geophysical data can help locate hydrocarbons, minerals, aggregate, and other natural resources.
What are the limitations of geophysical surveys?
Some of the general disadvantages of geophysical methods include: Most methods work best for situations in which there is a large difference in stiffness between adjacent subsurface units. It is difficult to develop good stratigraphic profiling if the general stratigraphy consists of hard material over soft material.
How are geological surveys performed?
Geological surveying employs techniques from the traditional walk-over survey, studying outcrops and landforms, to intrusive methods, such as hand augering and machine-driven boreholes, to the use of geophysical techniques and remote sensing methods, such as aerial photography and satellite imagery.
What types of equipment might be used for a geophysical survey?
Electromagnetic geophysical surveys often use the following equipment. Geonics' EM31 normal, EM31 short, EM38, EM34, EM61, G-Tem system, Protem Receiver with TEM47, TEM57, and TEM67 Transmitters, magnetic susceptibility meters from Geonics or TerraPlus' KT 10.
What is the difference between geology and geophysics?
Geologists focus on the materialistic surface of the Earth and its evolution. Geophysicists are mainly concerned about the Earth's physical processes, including its internal composition and atmosphere.
What are the geophysical methods?
These methods are:Gravity method.Seismic method.Electromagnetic method.Geothermal method.Magnetic method.Electrical method.Radiometric method.
What are geophysical surveys quizlet?
Geophysical Survey is a term that covers techniques and methods that detect archaeological remains through physical differences in soil.
How are geological surveys performed?
Geological surveying employs techniques from the traditional walk-over survey, studying outcrops and landforms, to intrusive methods, such as hand augering and machine-driven boreholes, to the use of geophysical techniques and remote sensing methods, such as aerial photography and satellite imagery.
What are the geophysical methods?
These methods are:Gravity method.Seismic method.Electromagnetic method.Geothermal method.Magnetic method.Electrical method.Radiometric method.
What are the geophysical activities?
Some geophysical processes in biosphere run very slowly (e.g. tide deformations, surface subsidence, etc.), and some of them have the character of sudden catastrophic events (e.g. earthquakes, landslips, floods, volcanic eruptions, atmospheric storms, etc.).
What is geophysical survey?
Geophysical survey is the systematic collection of geophysical data for spatial studies. Detection and analysis of the geophysical signals forms the core of Geophysical signal processing. The magnetic and gravitational fields emanating from the Earth's interior hold essential information concerning seismic activities and the internal structure.
What are the technologies used in geophysical surveys?
Technologies used for geophysical surveys include: Seismic methods, such as reflection seismology, seismic refraction, and seismic tomography. This type of survey is carried out to discover the detailed structure of the rock formations beneath the surface of the Earth. Seismoelectrical method.
What instruments detect the gravitational wave?
The sensing instruments such as gravimeter, gravitational wave sensor and magnetometers detect fluctuations in the gravitational and magnetic field. The data collected from a geophysical survey is analysed to draw meaningful conclusions out of that. Analysing the spectral density and the time-frequency localisation of any signal is important in applications such as oil exploration and seismography.
What are the components of geophysical signals?
This section deals with the principles behind measurement of geophysical waves. The magnetic and gravitational fields are important components of geophysical signals.
How can a gravitational wave sensor detect a change in the gravitational field?
Gravitational wave sensors can detect even a minute change in the gravitational fields due to the influence of heavier bodies. Large seismic waves can interfere with the gravitational waves and may cause shifts in the atoms. Hence, the magnitude of seismic waves can be detected by a relative shift in the gravitational waves.
What is used to measure changes in magnetic field?
To measure the changes in magnetic field the magnetometer is used. There are two types of magnetometers, one that measures only vertical component of the magnetic field and the other measures total magnetic field.
What is the purpose of gravity and geodesy?
This type of survey is carried out to discover the structure of rock formations beneath the surface of the Earth.
What is a geophysical survey?
Geophysical surveys include the implementation of geophysical methods to indirectly determine the geological and structural as well as the physical and mechanical characteristics of the foundation soil.
Why are geophysical surveys important?
Proper selection of geophysical survey accelerates and improves exploration, which reduces the exploratory drilling scope as an expensive and demanding research method.
What is the method of determining the electrical resistance of different types of rocks and materials?
Geoelectric tomography is a method based on the determination of different electrical resistance of different types of rocks and materials that indicate differences in the geological terrain structure.
How is the potential field measured in soil?
The generated field is measured by the second pair of electrodes. Changing the electrode depth and their distance, horizontal and vertical distribution of potentials or apparent resistance of the foundation soil is obtained.
When is seismic reflection used?
Seismic reflection is used when greater depths of soil foundation are analyzed and for determining faults and caverns.
Where are geophysical surveys performed?
Geophysical surveys are performed from the soil surface, through boreholes, excavations or in a combination of placing sources and detectors. The survey scope, the method types and work techniques depend on the survey purpose, the available funds, the geological and topographic conditions.
How does seismic refraction work?
Seismic refraction measures the wave time traveling from a source to a layer of varying density, along with the layer and back to the geophone. Placing the geophone along the direction gives a 2D profile of the wave propagation velocities. For 3D velocity profiles, multiple lines of geophones are placed on predefined grids on the terrain.
What is geophysical survey?
Geophysical survey is a broad term covering the suite of detection methods used to map contrasts between the physical properties of buried archaeological remains and the surrounding soil.
Why is geophysical survey important?
Geophysical techniques play a vital role in discovering new archaeological sites as well as helping to define and interpret remains that are not completely understood. They allow us to “see beneath the soil” without disturbing the ground and can examine large areas rapidly.
Why are geophysical techniques used?
Different geophysical techniques have unique and often complementary roles to play in the location and interpretation of archaeological sites. They are therefore generally best employed in combination to maximise the information obtained.
What are the factors that determine geophysical techniques?
Choice of the best geophysical technique to use depends on several factors including the type of site, the expected nature and burial depth of the archaeological targets and the area to be covered given the time available. Local site conditions such as vegetation, geology, soils and terrain also influence the decision.
What are some examples of archaeological sites?
Understanding of a wide range of archaeological sites is significantly enhanced through geophysical investigation and examples of monuments that can benefit include stone circles, barrows, hillforts, Roman camps and villas, industrial sites, deserted villages and historic gardens amongst others.
Can surveys cover large areas?
Surveys can now cover very large areas quickly, for example encompassing an entire Roman town. The results can rapidly transform our knowledge of such settlements leading to improved management at a landscape scale.
Why is geophysical survey used?
For this reason, it is often used where preservation (rather than excavation) is the goal, and to avoid disturbance of culturally sensitive sites such as cemeteries. Although geophysical survey has been used in the past with intermittent success, good results are very likely when it is applied appropriately.
What is the purpose of geophysical instruments?
Data processing and imaging convert raw numeric data into interpretable maps. Data processing usually involves the removal of statistical outliers and noise, and interpolation of data points.
How to measure electrical resistance?
Electrical resistance meters can be thought of as similar to the Ohmmeters used to test electrical circuits. In most systems, metal probes are inserted into the ground to obtain a reading of the local electrical resistance. A variety of probe configurations are used, most having four probes, often mounted on a rigid frame. Capacitively coupled systems that do not require direct physical contact with the soil have also been developed. Archaeological features can be mapped when they are of higher or lower resistivity than their surroundings. A stone foundation might impede the flow of electricity, while the organic deposits within a midden might conduct electricity more easily than surrounding soils. Although generally used in archaeology for planview mapping, resistance methods also have a limited ability to discriminate depth and create vertical profiles (see Electrical resistivity tomography ).
What are the geophysical methods used in archaeology?
Geophysical methods used in archaeology are largely adapted from those used in mineral exploration, engineering, and geology. Archaeological mapping presents unique challenges, however, which have spurred a separate development of methods and equipment.
How do conductivity meters detect underground features?
Underground archaeological features are detected by creating a magnetic field underground by applying an electric current that has a known frequency and magnitude through a sending coil. The currents spur a secondary current in underground conductors that is picked up by a receiving coil. Changes in the underground conductivity can indicate buried features. Although EM conductivity instruments are generally less sensitive than resistance meters to the same phenomena, they do have a number of unique properties. One advantage is that they do not require direct contact with the ground, and can be used in conditions unfavorable to resistance meters. Another advantage is relatively greater speed than resistance instruments. Unlike resistance instruments, conductivity meters respond strongly to metal. This can be a disadvantage when the metal is extraneous to the archaeological record, but can be useful when the metal is of archaeological interest. Some EM conductivity instruments are also capable of measuring magnetic susceptibility, a property that is becoming increasingly important in archaeological studies.
What are the limitations of magnetometer survey?
The chief limitation of magnetometer survey is that subtle features of interest may be obscured by highly magnetic geologic or modern materials. GPR survey. Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is perhaps the best known of these methods (although it is not the most widely applied in archaeology).
Who carried out magnetic survey at Pembroke Castle?
A magnetic survey at Pembroke Castle carried out by Andile Cele. The use of geophysical survey is well established in European archaeology, especially in Great Britain, where it was pioneered in the 1940s and 1950s.
What is geophysics used for?
Many of these technologies are traditionally used for exploration of economic materials such as groundwater, metals, and hydrocarbons. Geophysics is: The non-invasive investigation of subsurface conditions in the Earth through measuring, analyzing and interpreting physical fields at the surface.
How are Geophysical Methods Applied in Practice?
The implementation of geophysical methods is a structured process that consists of a number of key steps, including:
What are the commonly used Near Surface Geophysics terms and their definitions?
Click here to open a MS Word file to view a Near Surface Geophysics Glossary. If you have corrections, additions, or suggestions regarding the glossary, please contact Paul Wolfe at Wright State University.
How Do Environmental and Engineering Geophysics Relate to Each Other?
Magnetometers and gradiometers are used to acquire high resolution data for non-invasive archaeological investigation. In looking at the previous topic, it may not be immediately apparent that there are distinct components of environmental and engineering sub-disciplines within each "problem" or application area.
What are the Benefits of Geophysics?
Environmental and Engineering Geophysics offers a unique window into the earth as a means of detecting sub-surface conditions, and its relevancy lies in the concrete and cost-effective benefits it delivers. These include:
What is non-invasive geophysics?
Both of these definitions have a common component, namely that geophysics represents a class of subsurface investigations that are non-invasive (i.e. that do not require excavation or direct access to the sub-surface). The exceptions are borehole geophysical methods that expand the use of holes already drilled to access the subsurface on a very localized basis.
What is a near surface geophysics glossary?
This web page provides a Near Surface Geophysics Glossary (MS Word document), some fundamental definitions, and descriptions of many of the ways in which geophysics is used - ways in which specific methods or techniques are employed to address environmental and engineering problems. It is also a resource for finding answers to the questions listed below.
What are geophysical methods used for?
Many geophysical methods commonly used in exploration have potential application to geoenvironmentalinvestigations. Although these methods have mainly been used to identify pollutants and record their dispersion frommine areas, their application is not limited to studies of this sort. For instance, geophysical monitoring of pollutantactivity, which requires significantly greater study, is another aspect of geoenvironmental investigations. Monitoringdiffers from detection chiefly in recurrent use of geophysical techniques. The effort required to extend applicationof geophysical techniques to naturally occurring pollutants related to mineralized, but unmined, rock or to othercultural concentrations of toxic or potentially toxic substances is minimal and could be of considerable assistancein meeting national needs for healthy environmental conditions (Henderson, 1992).
How do gravity measurements work?
Gravity measurements define anomalous density within the Earth; in most cases, ground-based gravimeters are usedto precisely measure variations in the gravity field at different points. Gravity anomalies are computed by subtractinga regional field from the measured field, which result in gravitational anomalies that correlate with source bodydensity variations. Positive gravity anomalies are associated with shallow high density bodies, whereas gravity lowsare associated with shallow low density bodies. Thus, deposits of high-density chromite, hematite, and barite yieldgravity highs, whereas deposits of low-density halite, weathered kimberlite, and diatomaceous earth yield gravitylows. The gravity method also enables a prediction of the total anomalous mass (ore tonnage) responsible for ananomaly. Gravity and magnetic (discussed below) methods detect only lateral contrasts in density or magnetization,respectively. In contrast, electrical and seismic methods can detect vertical, as well as lateral, contrasts of resistivityand velocity or reflectivity.
What is electromagnetic measurement?
Electromagnetic measurements use alternating magnetic fields to induce measurable current in the Earth. Thetraditional application of electromagnetic methods in mineral exploration has been in the search for low-resistivity(high-conductivity) massive sulfide deposits. Airborne methods may be used to screen large areas and provide amultitude of targets for ground surveys. Electromagnetic methods, including airborne, are widely used to maplithologic and structural features (Palacky, 1986; Hoover and others, 1991) from which various mineral explorationand geoenvironmental inferences are possible.
Which topography is more relevant to geophysical problems?
A topography with similar scales in both the downstream and the cross-stream directions is potentially more relevant to geophysical problems.
What is turbulence in stratified media?
Turbulence in stratified media is a phenomenon common t o a variety of geophysical and engineering situations.
Is geophysical characteristics correlated with tectonic structures?
The geophysical characteristics of the area may be correlated with main tectonic structures.
What is the common feature of potential field geophysical methods?
Another feature common to all potential field geophysical methods is that a particular distribution of potential at the ground surface does not generally have a unique interpretation.
How does resistivity affect soil?
In coarse, granular soils, the groundwater surface is generally marked by an abrupt change in water saturation and thus by a change of resistivity. In fine-grained soils, however, there may be no such resistivity change coinciding with a piezometric surface. Generally, since the resistivity of a soil or rock is controlled primarily by the pore water conditions , there are wide ranges in resistivity for any particular soil or rock type, and resistivity values cannot be directly interpreted in terms of soil type or lithology. Commonly, however, zones of distinctive resistivity can be associated with specific soil or rock units on the basis of local field or drill hole information, and resistivity surveys can be used profitably to extend field investigations into areas with very limited or nonexistent data. Also, resistivity surveys may be used as a reconnaissance method, to detect anomalies that can be further investigated by complementary geophysical methods and/or drill holes.
Is resistivity a rock?
Generally, since the resistivity of a soil or rock is controlled primarily by the pore water conditions, there are wide ranges in resistivity for any particular soil or rock type, and resistivity values cannot be directly interpreted in terms of soil type or lithology.
Why do we need geophysical surveys?
Geophysical surveys provide the opportunities to locate and identify variations in the subsurface through non-inva sive methodologies. Identification of natural and man-made features such as cavities, buried obstructions, utilities and other geological variations can help to reduce the risk of unforeseen ground conditions for designers and developers.
What are the opportunities for geophysical investigations?
Different sites offer wide-ranging opportunities for applying geophysical investigation techniques. From large-scale geological site characterisation for critical infrastructure projects to identifying the presence of a chimney flue for a redevelopment project, our team of geophysical experts can provide advice on when to safely apply geophysical techniques. Thanks to our team’s extensive experience, we can design surveys appropriate to site conditions and apply innovative techniques to locate subsurface voids, from identifying unrecorded historical mine entries to mapping badger sets. We have the skillset to apply a range of geophysical techniques to detect and map discontinuities in subsurface or structure properties and can apply this to a wide range of projects, from locating large-scale faults to identifying cracks in concrete.
What is RSK surveying?
RSK offers comprehensive geophysical surveying services for the construction industry. Expert knowledge of a wide range of geophysical techniques including ground-penetrating radar, microgravity, electrical resistivity tomography, electromagnetics, seismic and magnetics allow us to offer bespoke survey solutions for a broad range of applications. Our team of highly experienced and skilled professional geophysicists deliver expert advice, design, execution and reporting services.
What is ground penetrating radar?
Ground penetrating radar. Applications of ground-penetrating radar (GPR) are broad and varied owing to the versatility of use in urban environments. GPR is most commonly used to confirm the position of buried utilities, with specific benefits to locate non-metallic utilities that electromagnetic locators cannot detect.

Overview
Geophysical survey is the systematic collection of geophysical data for spatial studies. Detection and analysis of the geophysical signals forms the core of Geophysical signal processing. The magnetic and gravitational fields emanating from the Earth's interior hold essential information concerning seismic activities and the internal structure. Hence, detection and analysis of the electric and Magnetic fields is very crucial. As the Electromagnetic and gravitational waves are …
Types of geophysical survey
There are many methods and types of instruments used in geophysical surveys. Technologies used for geophysical surveys include:
1. Seismic methods, such as reflection seismology, seismic refraction, and seismic tomography. This type of survey is carried out to discover the detailed structure of the rock formations beneath the surface of the Earth.
Geophysical signal detection
This section deals with the principles behind measurement of geophysical waves. The magnetic and gravitational fields are important components of geophysical signals.
The instrument used to measure the change in gravitational field is the gravimeter. This meter measures the variation in the gravity due to the subsurf…
Existing approaches in geophysical signal recognition
This section addresses the methods and mathematical techniques behind signal recognition and signal analysis. It considers the time domain and frequency domain analysis of signals. This section also discusses various transforms and their usefulness in the analysis of multi-dimensional waves.
The first step in any signal processing approach is analog to digital conversion…
Applications
The method being discussed here assumes that the mass distribution of the underground objects of interest is already known and hence the problem of estimating their location boils down to parametric localisation. Say underground objects with center of masses (CM1, CM2...CMn) are located under the surface and at positions p1, p2...pn. The gravity gradient (components of the gravity field) is measured using a spinning wheel with accelerometers also called as the gravity …
Summary
In archaeology, geophysical survey is ground-based physical sensing techniques used for archaeological imaging or mapping. Remote sensing and marine surveys are also used in archaeology, but are generally considered separate disciplines. Other terms, such as "geophysical prospection" and "archaeological geophysics" are generally synonymous.
Overview
Geophysical survey is used to create maps of subsurface archaeological features. Features are the non-portable part of the archaeological record, whether standing structures or traces of human activities left in the soil. Geophysical instruments can detect buried features when their physical properties contrast measurably with their surroundings. In some cases individual artifacts, especially metal, may be detected as well. Readings taken in a systematic pattern become a dat…
Methods
Geophysical methods used in archaeology are largely adapted from those used in mineral exploration, engineering, and geology. Archaeological mapping presents unique challenges, however, which have spurred a separate development of methods and equipment. In general, geological applications are concerned with detecting relatively large structures, often as deeply as possibl…
Development
The use of geophysical survey is well established in European archaeology, especially in Great Britain, where it was pioneered in the 1940s and 1950s. It is increasingly employed in other parts of the world, and with increasing success as techniques are adapted to unique regional conditions.
In early surveys, measurements were recorded individually and plotted by hand. Although useful …
See also
• Archaeological field survey
• Magnetic survey (archaeology)
• Ground penetrating radar survey (archaeology)
• Electrical resistance survey (archaeology)
Further reading
A general overview of geophysical methods in archaeology can be found in the following works:
• Clark, Anthony J. (1996). Seeing Beneath the Soil. Prospecting Methods in Archaeology. London, United Kingdom: B.T. Batsford Ltd.
• Gaffney, Chris; John Gater (2003). Revealing the Buried Past: Geophysics for Archaeologists. Stroud, United Kingdom: Tempus.
External links
• International Society for Archaeological Prospection
• "The North American Database of Archaeological Geophysics (NADAG)".
• "Geophysical Data in Archaeology: A Guide to Good Practice".