Gouging is the term to define a type of corrosion which occurs on a metallic surface in which a hole, groove or indentation is created. In welding, gouging has been a requirement for many years in several industries and applications – and is one method to scrutinise.
What is back gouging in welding?
Back gouging is a material removal process that is used to remove material from the back side of a weld. This is done to remove any welding defects that may have been created during the welding process and to ensure that the weld is smooth and free of any imperfections.
What is “gouging”?
Gouging correctly termed as “Air Arc Gouging” is an arc process for removal of material from steel plate/ pipe. Arc is formed between carbon electrode and workpiece.
What are the applications of metal arc gouging?
Typical applications include back gouging, removal of surface and internal defects, removal of excess weld metal and preparation of bevel edges for welding. The main advantage of manual metal arc (MMA) gouging is that the same power source can be used for welding, gouging or cutting, simply by changing the type of electrode.
What is gouging in boilers?
- Definition from Corrosionpedia What Does Gouging Mean? Gouging is a type of corrosion that occurs on a metallic surface in which a hole, groove or indentation is created. Gouging happens in boiler tubes because of caustic corrosion that occurs as a result of excessive use of alkalines such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH).

What is gouging in welding?
Gouging is the term to define a type of corrosion which occurs on a metallic surface in which a hole, groove or indentation is created. In welding, gouging has been a requirement for many years in several industries and applications – and is one method to scrutinise.
Why is gouging important in welding?
Thermal gouging is an essential part of welding fabrication. Used for rapid removal of unwanted metal, the material is locally heated and molten metal ejected - usually by blowing it away. Normal oxyfuel gas or arc processes can be used to produce rapid melting and metal removal.
What is the purpose of arc gouging?
The main goal of air arc gouging is to remove defective or old welds to repair or dismantle equipment. Unlike oxy-fuel cutting, air arc gouging avoids the need for oxidation of the metal to cut. The rate of metal removal depends on the efficiency of air jet in removing molten metal and the melting rate.
What is gouging technique?
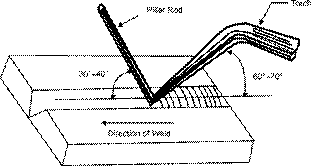
Gouging is commenced by striking the electrode tip on to the workpiece surface to initiate the arc. Unlike manual metal arc (MMA) welding the electrode tip is not withdrawn to establish arc length. Molten metal directly under the electrode tip (arc) is immediately blown away by the air stream.
Can you arc gouge without air?
having to invest big bucks in an air-arc cutting equipment (or worrying about starting fires when using it out doors). ZENA NO-Gas arc cutting/gouging rods let you gouge, bevel, and cut metal without needing a 300+ Amp air-arc gouging/cutting rig or an acetylene cutting torch and bulky gas bottles.
What do you need for arc gouging?
Required equipment includes an air compressor, welding power source, carbon electrode and a gouging torch.
Can you arc gouge stainless steel?
The air carbon-arc gouging process does not require oxidation to maintain the cut, so it can gouge or cut metals that the oxyfuel process cannot. In fact, most common metals (carbon steel, stainless steel, high-alloy wear plate, copper alloys and cast irons) can be cut using air carbon-arc gouging.
Can you arc gouge aluminum?
This process is useful for cutting a variety of materials, but it is most often used for cutting and gouging aluminum, copper, iron, magnesium, and carbon and stainless steel. Because the metal is blown away by the air jet, it does not need to be oxidized.
Can you arc gouge cast iron?
1:372:41Gouging on a cast iron manifold - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn in a cast iron. It also allows you to um to a trim uh trim other things on it too like as anMoreIn in a cast iron. It also allows you to um to a trim uh trim other things on it too like as an example we have this big uh this big piece right here that's cast in that may be in the way if we're
Is arc gouging welding?
Carbon arc gouging is an important part of many welding applications — from structural steel construction to field repairs. Understanding the gouging process and how to choose the right equipment and electrodes for the job can help improve efficiency and optimize results with this process.
What are the types of gouging?
Common methods of gouging are mechanical techniques such as grinding, hand milling, routing, and chipping; oxyfuel gouging, which can be used only on carbon steels; and air carbon-arc gouging. The plasma cutting process was invented in 1954 at the Tonawanda Laboratory of the Linde Division of Union Carbide.
What is a gouging electrode?
Gouging electrodes are made of carbon and have a copper coating. Gouging carbon rods are used for metal removal at fast rates with low power consumption. It is generally used to remove welding defects, excess welds and foundry risers from cast products.
How do you use the gouging technique to cut?
0:208:06Arc Gouging Basics (Part 2): Proper Torch Angle - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThat can be used for procedures where we're getting full penetration. We do a partial penetrationMoreThat can be used for procedures where we're getting full penetration. We do a partial penetration weld on one side we turn it over we back gouge down to clean metal grind. Clean complete the weld.
What is gouging with a plasma cutter?
Plasma arc gouging is a variation of PAC in which material from the surface of a plate, casting, welded assembly, or other metal workpiece is melted and removed to form a gouge or groove. The plasma gouging arc is less constricted than the cutting arc.
How do you use a gouging tip?
7:519:10Flame Grooving - Oxy-fuel Gouging Instructions - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipStart preheat with the end of the nozzle at an angle of about 30 degrees to the plate surface. AsMoreStart preheat with the end of the nozzle at an angle of about 30 degrees to the plate surface. As cutting starts turn the blowpipe in a smooth downward arc until the nozzle angle is about 7 degrees.
What does gouge to sound metal mean?
Good to know Welding gouging is a process in which an arc is used to melt and remove metal from the base material. Gouging can be done with either an electrode or a carbide-tipped tool.
What is a gouge in welding?
Gouging is the term to define a type of corrosion which occurs on a metallic surface in which a hole, groove or indentation is created. In welding, gouging has been a requirement for many years in several industries and applications – and is one method to scrutinise. Particularly in maintenance and repair, the ability to gouge or groove metal is critical and deserves full consideration.
What is gouging used for?
This type of gouging is used for localised gouging operations such as the removal of defects. It is also used where it is more convenient to switch from a welding electrode to a gouging electrode, rather than using specialised equipment.
What is MMA gouge?
The MMA gouging process is characterised by the large amount of gas which is generated to eject the molten metal. However, because the arc/gas stream is not as powerful as a gas or a separate air jet, the surface of the gouge is not as smooth as an oxyfuel gouge or air carbon arc gouge.
How is arc formed in MMA welding?
The arc is formed between the tip of the electrode and the workpiece in conventional MMA welding. MMA gouging differs due to requiring special purpose electrodes with thick flux coatings in order to generate a strong arc force and gas stream. Unlike MMA welding where a stable weld pool must be maintained, this process can force the molten metal away from the arc zone to leave a clean-cut surface.
How does a metal gouge work?
The metal becomes molten and a high velocity air streams down the electrode to blow it away and thus leaves a clean groove. It is a simply process to apply, has a high metal removal rate and gouge profile can be closely controlled.
What is DC gouging?
This type of gouging can be applied to a wide range of metals. DC (electrode positive) is normally preferred for steel and stainless steel, but AC is more effective for cast iron, copper and nickel alloys. Typical applications include back gouging, removal of surface and internal defects, removal of excess weld metal and preparation of bevel edges for welding.
Why is air jet gouging so noisy?
However, there are disadvantages: the air jet causes the molten metal to be ejected over quite a large distance and, because of high currents (up to 2000A) and high air pressures (80 to 100 psi), it can be very noisy. This type of gouging can be applied to a wide range of metals.
What are the two methods of gouging metal?
Two of the most common methods of gouging metal are plasma gouging and air carbon-arc gouging.
What is air arc gouging?
Gouging correctly termed as “Air Arc Gouging” is an arc process for removal of material from steel plate/ pipe. Arc is formed between carbon electrode and workpiece. This arc melts the workpice in arc area. Compressed air is blown over the molten pool to dislodge the material.
How does carbon arc gouge work?
The metal becomes molten and a high velocity air streams down the electrode to blow it away and thus leaves a clean groove. It is a simply process to apply, has a high metal removal rate and gouge profile can be closely controlled. However, there are disadvantages: the air jet causes the molten metal to be ejected over quite a large distance and, because of high currents (u
What is a weld in metal?
Welding is when you use a like metal to attach two pieces. That like metal can be the pieces themselves (like in the case of fusing, or a solid state diffusion well) or it can be in the filler wire in a MIG or TIG weld. In general this is done at the melting temperature of those alloys because you are using that alloy to attach the two pieces together.
How to remove metal from a carbon arc?
This process uses carbon electrodes, compressed air and a suitable power source. The strong arc used between the tip of the carbon electrode and the metal workpiece will dissolve the workpiece. Start the arc by hitting the electrode tip on the surface of the workpiece. Start the arc by hitting the electrode tip on the surface of the workpiece. Compressed air is then used to blow the molten metal out of the metal surface.
What is the advantage of MMA welding?
The main advantage of manual metal arc (MMA) gouging is that the same power source can be used for welding, gouging or cutting, simply by changing the type of electrode.
What is MMA gouge?
The MMA gouging process is characterised by the large amount of gas which is generated to eject the molten metal. However, because the arc/gas stream is not as powerful as a gas or a separate air jet, the surface of the gouge is not as smooth as an oxyfuel gouge or air carbon arc gouge.
What is a gouging torch?
A manual gouging torch and cable assembly includes connections for the welding lead and compressed air line. Be sure to size the torch and ground cable appropriately based on amperage and length of the cable. An insulated connection boot and hookup kit simplifies torch hookup and eliminates the possibility of arcing when contacting electrically hot parts.
How does a torch work?
The manual torch holds the carbon electrode in a swiveling head so that the air jets stay aligned with the electrode regardless of angle. Most torches have one set of air jets, but some have air jets on two sides of the electrode, which are better for some uses, such as removing pads and risers from large castings (padwashing).
What type of electrode is used for AC power?
1. Choose an electrode. There are three types of carbon electrodes: AC coated electrodes (for use with AC power sources), DC plain electrodes and DC copper-coated electrodes. The latter is most widely used because of their comparatively long electrode life, stable arc characteristics and groove uniformity.
How does carbon arc gouging work?
Air carbon-arc gouging removes metal through the intense heat of an arc created between a carbon electrode and the workpiece. As the material melts, compressed air, which is directed through outlets in the lower jaws of the torch holding the electrode, lifts the molten metal clear of the arc before the metal solidifies.
How to prevent carbon from going through a gouge?
When using copper-coated carbon electrodes, position the electrode in the torch so that the uncoated end points toward the workpiece. Set the air pressure to 80 to 100 psi, which is a flow sufficient enough to prevent trapping carbon in the gouge.
How much pressure does an Arcair torch need to open?
Traditional manual torch models require a fair amount of grip pressure to open, about 27 lbs. or more. Arcair’s newest torch, the AirPro X4000, uses the compressed air already flowing through the torch to pneumatically open the torch jaws. The operator pushes a rocker switch, the jaws open and the operator can insert, adjust and remove carbon electrodes without effort. As an added benefit, elimination of a lever assembly creates a lower profile torch for improved access.
What are the sizes of copper electrodes?
Copper-coated carbon electrodes come in three shapes and multiple sizes: round electrodes in diameters ranging from 1/8 in. to 1 in., half-round electrodes in 5/8-in. diameters and flat (rectangular) electrodes measuring 5/32 in. by 3/8 in. or 3/16 in. by 5/8 in. Recta ngular electrodes are used to make rectangular grooves and remove weld reinforcements, while half-round electrodes provide the versatility of creating a round or flat gouge depending on their orientation.
Q1: When is gouging used?
A: Gouging is necessary for many tasks related to welding when the operator is trying to remove material to get to clean metal. The most obvious use of gouging is to remove large amounts of metal or welds that need to be repaired.
Q2: Can I gouge in CV mode?
A: You can gouge in constant voltage (CV) mode, but it will result in a shallower penetration profile that is wider and flatter than gouging in constant current (CC) mode.
Q3: How do I know what size of electrode to use for gouging?
A: Gouging electrodes are available in a range of sizes, so understanding your machine’s capabilities is key to avoid using too large of an electrode. The spec sheet or owner’s manual for some machines will specify the electrode diameter ranges that can be run and list the maximum electrode size that can be used for carbon arc gouging.
Q4: What are the advantages of using electrodes of different geometries for gouging?
A: Typical cylindrical electrodes, also known as pointed electrodes, are best for all-purpose gouging. Flat electrodes are good for achieving a flush surface, as in removing weld reinforcement or creating rectangular grooves.
Q6: Why should I use a machine with a dedicated gouging process?
A: Gouging is a process just like stick or MIG welding. Just as with those welding processes, technology in Miller engine-driven welder/generators and plug-in welding power sources that include a gouging mode has resulted in optimized gouging performance. Reference the owner’s manual for your power source to find the gouging setup, if applicable.
Q7: Are inverter-based welding power sources bad for gouging?
A: While this used to pose a problem with older inverter machines, today’s inverter-based power sources from Miller have been engineered, designed and tested for the gouging process, providing exceptional reliability and operation.
Understanding carbon arc gouging
Carbon arc gouging is an important part of many welding applications — from structural steel construction to field repairs. Understanding the gouging process and how to choose the right equipment and electrodes for the job can help improve efficiency and optimize results with this process.
What Does Gouging Mean?
Gouging is a type of corrosion that occurs on a metallic surface in which a hole, groove or indentation is created. Gouging happens in boiler tubes because of caustic corrosion that occurs as a result of excessive use of alkalines such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH). This can lead to caustic gouging and stress corrosion cracking.
How to repair corrosion from caustic gouging?
Corrosion due to caustic gouging can be repaired or maintained by performing mechanical techniques such as grinding of the damaged surface, then milling, routing and chipping. Once this is done, either of the two common methods of gouging metal can be used for repair works
Why do carbon steel tubes fail?
Similarly, stainless steel tubes are failed because of caustic induced stress corrosion cracking.