Haematoxylin
Haematoxylin or hematoxylin, also called natural black 1 or C.I. 75290, is a compound extracted from heartwood of the logwood tree with a chemical formula of C₁₆H₁₄O₆. This naturally derived dye has been used as a histologic stain, ink and as a dye in the textile and leather industry…
Eosin
Eosin is the name of several fluorescent acidic compounds which bind to and form salts with basic, or eosinophilic, compounds like proteins containing amino acid residues such as arginine and lysine, and stains them dark red or pink as a result of the actions of bromine on fluorescein. I…
What is the difference between hematoxylin and eosin?
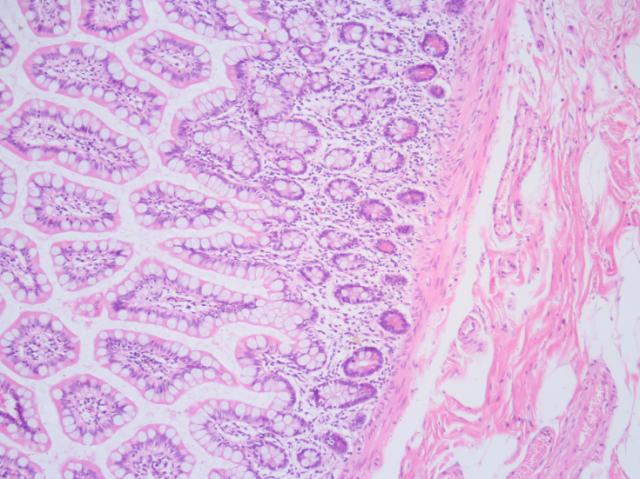
Principle of Hematoxylin & Eosin Stain Haematoxylin is a basic dye which stain acidic components of the cell, such as nuclei in purple- black colour. Eosin is a acidic dye which stain basic components such as cytoplasm, connective tissues in pink- orange colour.
What are haematoxylin stains?
Haematoxylin stains can be categorized based on the types of mordants used. What are the uses of Hematoxylin & Eosin Stain ? Hematoxylin & Eosin is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard.
What is the color of eosin staining?
Eosin is pink and stains proteins nonspecifically. In a typical tissue, nuclei are stained blue, whereas the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix have varying degrees of pink staining. Well-fixed cells show considerable intranuclear detail.
Why is hematein used in tissue staining?
To demonstrate the morphologies of tissues and cells. Hematoxylin is extracted from Hematoxylon campechianum tree upon which on oxidation, hematein is produced from hematoxylin, the dye used in the hematoxylin and Eosin staining technique. Adding a mordant enables hematein to bind to the anionic elements of the tissues.

What is the purpose of hematoxylin and eosin staining?
H and E staining helps identify different types of cells and tissues and provides important information about the pattern, shape, and structure of cells in a tissue sample. It is used to help diagnose diseases, such as cancer. Also called hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Does hematoxylin stain acidic or basic?
Haemotoxylin is actually a dye called hematein (obtained from the log-wood tree) used in combination with aluminium ions (Al3+). It is used to stain acidic (or basophilic) structures a purplish blue. (Haematoxylin is not strictly a basic dye, but it is used with a 'mordant' that makes this stain act as a basic dye.
What two stains are used in an H&E stain?
As its name suggests, H&E stain makes use of a combination of two dyes – haematoxylin and eosin.
Why does hematoxylin stain the nucleus?
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) is the most widely used stain in histology and allows localization of nuclei and extracellular proteins. Hematoxylin, not a dye itself, produces the blue Hematin via an oxidation reaction with nuclear histones causing nuclei to show blue.
What is hematoxylin used to stain?
Hematoxylin precisely stains nuclear components, including heterochromatin and nucleoli, while eosin stains cytoplasmic components including collagen and elastic fibers, muscle fibers and red blood cells.
What color does eosin stain?
pinkEosin is pink and stains proteins nonspecifically. In a typical tissue, nuclei are stained blue, whereas the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix have varying degrees of pink staining.
What does H and E staining mean?
hematoxylin and eosin stainingListen to pronunciation. (hee-muh-TOK-suh-lin … EE-oh-sin STAY-ning) A common laboratory method that uses two dyes called hematoxylin and eosin that make it easier to see different parts of the cell under a microscope.
Why does hematoxylin stain blue?
The process of bluing is to convert the soluble red component of haematoxylin into an insoluble blue. It is a pH dependent reaction occurring in an alkaline solution. As haematoxylin is responsible for nuclear staining, the nucleus is therefore stained blue (or blue-purple) in standard haematoxylin and eosin staining.
What structures does hematoxylin stain?
Hematoxylin precisely stains nuclear components, including heterochromatin and nucleoli, while eosin stains cytoplasmic components including collagen and elastic fibers, muscle fibers and red blood cells.
What organelle is stained by the hematoxylin?
Mitochondria can be distinguished as darkly stained, thread-like structures in the apical cytoplasm of some cells.
Does hematoxylin stain red blood cells?
Tissue stained with haematoxylin and eosin shows cytoplasm stained pink-orange and nuclei stained darkly, either blue or purple. Eosin also stains red blood cells intensely red.
What makes a stain basic or acidic?
Basic - Contains basic groups that have an affinity for acidic tissue elements. Acidic - Contains acidic groups that have an affinity for basic tissue elements. Basic stains are used to stain nuclei and other basophilic (base-loving) cellular structures in tissues.
Which stain contains acidic and basic dye?
Amphophilic - It is a term used to indicate that the tissue stains with both the basic and the acidic dyes.
What is the pH of hematoxylin?
pH 2.4- 2.9The correct pH for hematoxylin solution is pH 2.4- 2.9. Check manufacturer's SDS for pH for commercially prepared stains. i) Check the pH of the hematoxylin solution. If necessary, adjust the pH using the acid used in the original formulation.
How can you tell if a stain is acidic or basic?
According to nature of stain, it can be classified into:Acidic Dyes: It is dye which has negative charge so they bind to positively charged cell structures like some proteins. ... Basic Dyes: This dye have positive charge & bind to negatively charged molecules(nucleic acid, -COOH -OH).More items...•
What is the purpose of adding mordant to hematein?
Adding a mordant enables hematein to bind to the anionic elements of the tissues. Hematoxylin without eosin acts a counterstain in immunohistochemical and hybridization protocols that use colorimetric substrates (such as alkaline phosphatase or peroxidase) Eosin dye is acidic dye hence it as a negative charge (eosinophilic). ...
Why are hematoxylin and eosin inefficient?
Hematoxylin and Eosin are inefficient in that not all features of a substance can be received and special stains must be used.
What color does eosin stain?
Therefore it stains the basic structures of a cell (acidophils), giving them a red or pink color, for example, the cytoplasm is positively charged, and therefore it will take up the eosin dye, and appear pink. Hematoxylin dyes are basic dyes, hence they are positively charged. Therefore it will stain the acidic structures fo tissues ...
What is the purpose of hematoxylin and eosin stain?
Hematoxylin and Eosin stain is the primary diagnostic stain used in histology and Histopathology including application in the Fine-needle Aspiration Biopsies, Paraffin Fixed embedded tissue. Hematoxylin is used to demonstrate the nuclear of the cell and its content , by observing the depth of the color of dye and the time ...
What color is hematoxylin?
Hematoxylin has a deep blue-purple color and stains nucleic acids by a complex, incompletely understood reaction. Eosin is pink and stains proteins nonspecifically. In a typical tissue, nuclei are stained blue, whereas the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix have varying degrees of pink staining. Hematoxylin and Eosin stain is ...
What is progressive staining?
Progressive staining takes place without a differentiator for removing any excess dye after adding hematoxylin. This cause background staining to occur in charged slides. Its mainly used to stain Mucin. While the Modified progressive and regressive, use a differentiator in removing excessive dyes.
How long does it take to fix a hematoxylin stain?
Clean the sections to distilled water. Then stain nuclei with the alum hematoxylin (Mayer’s) to fix the tissue, for about 5 minutes.
What is the color of the retina?
Retina (part of the eye) stained with hematoxylin and eosin, cell nuclei stained blue-purple and extracellular material stained pink. Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology.
What is the H&E method?
The H&E staining method involves application of haematoxylin mixed with a metallic salt, or mordant, often followed by a rinse in a weak acid solution to remove excess staining ( differentiation ), followed by bluing in mildly alkaline water. After the application of haematoxylin, the tissue is counterstained with eosin (most commonly eosin Y ).
What is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis?
H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin.
What is the color of H&E?
H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue , and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern recognition, both by expert humans themselves and by software that aids those experts (in digital pathology ), provides histologic information.
Why is H&E used in histology?
The H&E staining procedure is the principal stain in histology in part because it can be done quickly, is not expensive, and stains tissues in such a way that a considerable amount of microscopic anatomy is revealed, and can be used to diagnose a wide range of histopathologic conditions.
What color is hematoxylin?
Hematoxylin principally colors the nuclei of cells blue or dark-purple, along with a few other tissues, such as keratohyalin granules and calcified material. Eosin stains the cytoplasm and some other structures including extracellular matrix such as collagen in up to five shades of pink.
What is the most used stain in Mohs surgery?
Alternatively, H&E stain is the most used stain in Mohs surgery in which tissues are typically frozen, cut on a cryostat (a microtome that cuts frozen tissue), fixed in alcohol, and then stained.
What is hematoxylin and eosin staining?
Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. INTRODUCTIONHematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stains have been used for at least a century and are still essential for recognizing various tissue types and the morphologic changes that form the basis of contemporary cancer diagnosis. The stain has been unchanged for many years ...
What is the limitation of hematoxylin staining?
A limitation of hematoxylin staining is that it is incompatible with immunofluorescence.
Why is hematoxylin blue?
Hematoxylin has a deep blue-purple color and stains nucleic acids by a complex, incompletely understood reaction.
Why is H&E stain unchanged?
The stain has been unchanged for many years because it works well wi …. INTRODUCTIONHematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stains have been used for at least a century and are still essential for recognizing various tissue types and the morphologic changes that form the basis of contemporary cancer diagnosis. The stain has been unchanged for many years ...
What type of stain is used for nuclei?
Nuclei show varying cell-type- and cancer-type-specific patterns of condensation of heterochromatin (hematoxylin staining) that are diagnostically very important. Nucleoli stain with eosin. If abundant polyribosomes are present, the cytoplasm will have a distinct blue cast.
Is hematoxylin a counterstain?
Hematoxylin, generally without eosin, is useful as a counterstain for many immunohistochemical or hybridization procedures that use colorimetric substrates (such as alkaline phosphatase or peroxidase). This protocol describes H&E staining of tissue and cell sections.

Principle
Reagents
- Distilled water
- Alum hematoxylin
- Acid alcohol
- Scott’s tap water
Procedure
- The procedure is simplified into various processes: Dewaxing, Dehydration, Hematoxylin, Differentiation, Bluing, Eosin, Dehydration, Clearing, Cover-slipping. The steps include: 1. Clean the sections to distilled water. 2. Then stain nuclei with the alum hematoxylin (Mayer’s) to fix the tissue, for about 5 minutes. 3. Rinse the stain with smoothly running tap water 4. Using the differ…
Results and Interpretation
- Nuclei are stained blue, whereas the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix have varying degrees of pink staining. Well-fixed cells show considerable intranuclear detail. Nuclei show varying cell-type- and cancer-type-specific patterns of condensation of heterochromatin (hematoxylin staining) that are diagnostically very important. Nucleoli stain with eosin. If abundant polyribosomes are prese…
Applications
- It is widely used in Histopathology, Immunochemistry, and Immunopathology to analyze and demonstrate morphologies of tissues, and cells.
Overview
Uses
Method of application
Results
Mode of action
Hematoxylin and eosin stain (or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained …
Further reading
The H&E staining procedure is the principal stain in histology in part because it can be done quickly, is not expensive, and stains tissues in such a way that a considerable amount of microscopic anatomy is revealed, and can be used to diagnose a wide range of histopathologic conditions. The results from H&E staining are not overly dependent on the chemical used to fix the tissue or slight inconsistencies in laboratory protocol, and these factors contribute to its routine …
External links
There are many ways to prepare the hematoxylin solutions (formulation) used in the H&E procedure, in addition, there are many laboratory protocols for producing H&E stained slides, some of which may be specific to a certain laboratory. Although there is no standard procedure, the results by convention are reasonably consistent in that cell nuclei are stained blue and the cytoplasm and extracellular …