
What kind of bone marrow is considered hematopoietic?
hematopoietic to fatty bone marrow starts in the periphery and the distal part of the long bones. By the age of 20 years most of the appendicular skeleton contains fatty bone marrow, while the central skeleton including proximal femur and humerus contain largely hematopoietic bone marrow. In the 6th decade of life a substantial amount of fatty bone
How are RBCs produced in bone marrow?
Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow (the spongy tissue inside the bone). In order to make red blood cells, the body maintains an adequate supply of erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone that is produced by the kidney. EPO helps make red blood cells.
What is the normal bone marrow plasma cell percentage?
Up to 5% is normal as long as they are not "monoclonal" meaning derived from a cell. If monoclonal then a bone cancer called myeloma needs to be rule... Read More Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers — it's anonymous and free! Doctors typically provide answers within 24 hours.
What is bone marrow responsible for?
Bone marrow, a component of the lymphatic system, is the soft and flexible tissue in the cavities of bone. In the body, the major function of bone marrow is to produce blood cells. Bone marrow also helps to remove old cells from the circulation.
What does Hypocellular bone marrow indicate?
Pancytopenia with hypocellular bone marrow most often is caused by idiopathic aplastic anemia, but can be caused by inherited bone marrow failure syndromes, drugs, infections, nutritional deficiencies, and rheumatologic disease.
When the bone marrow is Hypercellular?
Hypocellular AML is currently defined as AML with a bone marrow cellularity less than 20%, although in some earlier reports, cellularity less than 40% or 50% was considered to be hypocellular.
What does Hypercellular mean in medical terms?
an abnormal excess of cellsMedical Definition of hypercellularity : the presence of an abnormal excess of cells (as in bone marrow)
What does Hypercellular marrow with Trilineage hematopoiesis mean?
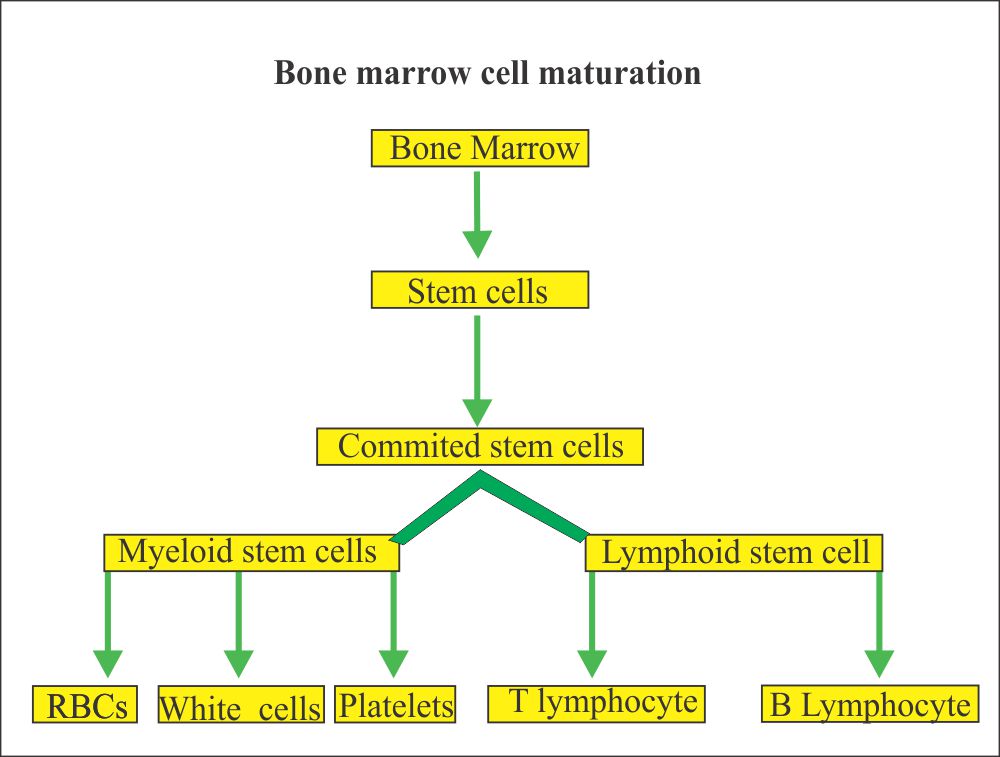
Myeloid cells are involved in trilineage hematopoiesis. This term refers to the normal production by your bone marrow of three blood cell lines: red blood cells, certain white blood cells, and platelets. Lymphoid cells create a separate white blood cell line leading to T cells and B cells.
What does Hypocellular mean in medical terms?
Medical Definition of hypocellular : containing less than the normal number of cells hypocellular bone marrow in chronic lead poisoning.
How does bone marrow change with age?
Like every organ system, the bone marrow undergoes changes with age. The most readily apparent change is a decline in marrow cellularity. The percentage of marrow space occupied by hematopoietic tissue goes from 40–60% in young adults to 20–40% in older people, with the remaining space being taken up by fat.
What is the normal me ratio in the bone marrow?
There is a normal ratio of myeloid to erythroid precursors (approximately 4:1) with normal maturation of both cell lines.
What does decreased cellularity mean?
Low cellularity was defined as 10 or fewer cell clusters, moderate cellularity was defined as 11-30 clusters, and high cellularity was defined as more than 30 clusters. A cell cluster was defined as five or more cells.
How is bone marrow cellularity calculated?
Cellularity was calculated from T1 signal intensity measurements=100 - {[(marrow - CSF)/(subcutaneous fat - CSF)] X 100}.
What triggers hematopoiesis?
The cells of the hematopoietic (blood-forming) system in the bone marrow do so upon receipt of a signal by a hormone called erythropoietin, or Epo for short. This hormone is produced mainly by the kidney that increases the Epo level by up to a thousand-fold as a response to falling oxygen saturation of the blood.
What is Trilineage?
Trilineage hematopoiesis refers to the production of three types of blood cells: platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells. Each of these cells begins with the transformation of HSC into cells called common myeloid progenitors (CMP).
What are the stages of hematopoiesis?
Hematopoiesis is the process by which the cellular elements of blood are formed. In the developing human embryo and fetus, hematopoiesis has 3 developmental waves and is conceptually divided into 3 anatomic stages: mesoblastic, hepatic, and myeloid.
What is Hypercellular marrow with erythroid hyperplasia?
Erythroid hyperplasia is a condition of excessive count of erythroid precursor cells (in layman words, immature red blood cells) in the bone marrow.
What are the stages of Granulopoiesis?
These granulocytic precursors are conceptually divided into those stages that can divide, including myeloblasts, promyelocytes, and myelocytes (proliferation pool), and those that cannot, including metamyelocytes, and band and segmented forms (maturation pool).
What are two conditions that cause polycythemia?
Apparent polycythaemia is often caused by being overweight, smoking, drinking too much alcohol or taking certain medicines – including diuretics (tablets for high blood pressure that make you pee more). Apparent polycythaemia may improve if the underlying cause is identified and managed.
How is bone marrow cellularity calculated?
Cellularity was calculated from T1 signal intensity measurements=100 - {[(marrow - CSF)/(subcutaneous fat - CSF)] X 100}.
Why is my marrow hypercellular?
Many reasons: Marrow can be hypercellular because any of the cell lines, red cells , white cells or platelets or intercellular matrix may start to grow due to beni ... Read More
What is bone marrow?
Bone marrow is: tissue in the center or hollow part of the bones. It makes red blood cells. Eventually white blood cells are manufactured. All of this is helps our ... Read More
Why is bone marrow painful?
It can be: If bone marrow is collected the standard way by retrieving it directly from a bone, it can be painful due to pressure when the needle is inserted into ... Read More
What is cellularity in medicine?
The cellularity is the percentage of blood cell production as compared to fat. As a rule of thumb the cellularity as a percent is 1 ... Read More. 90,000 U.S. doctors in 147 specialties are here to answer your questions or offer you advice, prescriptions, and more.
How much cellular marrow should a 60 year old have?
Cellularity: Cellularity is typically calculated by 100-the age of the person. So a 60 year old should have a 40% cellular marrow. If it is considerably more, th ... Read More
Where are blood cells born?
Home of blood cells: The cells in your blood are born and reach maturity in the bone marrow. This is the very protected space in the middle of your large bones like your a ... Read More
What is bone marrow?
Bone marrow is: tissue in the center or hollow part of the bones. It makes red blood cells. Eventually white blood cells are manufactured. All of this is helps our immune system protect us from infection.
What is cellularity in blood?
The cellularity is the percentage of blood cell production as compared to fat. As a rule of thumb the cellularity as a percent is 100 - your age. Hypercellularity means that number is higher than expected. 4.9k views Reviewed >2 years ago.
Where are blood cells born?
Home of blood cells: The cells in your blood are born and reach maturity in the bone marrow. This is the very protected space in the middle of your large bones like your arms, legs, hips and back.
Can you tell me about hypercellular bone marrow?
Many reasons: Marrow can be hypercellular because any of the cell lines, red cells , white cells or platelets or intercellular matrix may start to grow due to benign or malignant causes. Bottom line is we have to look for clones or abnormal cells and/ or poor Cytogenetics or molecular markers
What does MCH mean on CBC?
MCH~ Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin/ MCHC are testing to evaluate presence of anemia. The results on your CBC show these numbers are low~but just below the norm.
What does it mean when your hematocrit is elevated?
Hematocrit number is elevated but most often is a sign of dehydration. How’s your liquid intake? Have you also been checked for Magnesium, calcium, sodium and potassium levels?
Is RBC/Hg elevated?
RBC/Hg are only slightly elevated but not significantly. Usually fatigue is caused by these numbers being low.
What is markedly hypocellular marrow with no morphologic or flow cytometric evidence of malignancy?
Markedly hypocellular marrow with no morphologic or flow cytometric evidence of malignancy Most consistent with acquired aplastic anemia
Which mutations are associated with higher rates of malignant transformation?
Mutated ASXL1, DNMT3A, and RUNX1are associated with higher rates of malignant transformation Mutated BCOR or BCORL1 are associated with better response to IST
What mutation is associated with myeloid neoplasms?
Myeloid neoplasms with germline GATA2 mutation: other clues
