What are the most common causes of small intestine inflammation?
The most common are:
- viral or bacterial infection
- radiation induced
- medication induced
- alcohol or drug induced
- enteritis related to poor blood flow
- enteritis related to inflammatory conditions, such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis
What diseases are in the small intestine?
There are many common causes and risk factors, including:
- Adhesions: These are bands of scar tissue that may form after abdominal or pelvic surgery. ...
- Hernias: Segments of the intestine may break through a weakened section of the abdominal wall. ...
- Inflammatory disease: Inflammatory bowel disorders such as Crohn’s disease or diverticulitis can damage parts of the small intestine. ...
What causes an inflammed intestine?
What causes inflammatory bowel disease?
- Family history and genetics. People who have a parent, sibling, or child with IBD are at a much higher risk for developing it themselves.
- The immune system. The immune system may also play a role in IBD. ...
- Smoking. Smoking is one of the main risk factors for developing Crohn’s disease. ...
- Ethnicity. ...
- Age. ...
- Environmental factors. ...
- Gender. ...
What is natural remedy for inflammation?
It is loaded with anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, carminative and anti-flatulent properties that helps prevent cold and flu. According to Dr. Ashutosh Gautam from Baidyanath, “Clove (and clove oil) is one of the richest sources of antioxidants.

What happens if the small intestine becomes inflamed?
People with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis have chronic intestinal inflammation. Symptoms include stomach cramps, diarrhea and gas. Medications and surgery can help manage IBD flares, putting the condition into remission.
Can inflammation in intestine be cured?
No, IBD cannot be cured. There will be periods of remission when the disease is not active. Medicines can reduce inflammation and increase the number and length of periods of remission, but there is no cure.
How do you fix inflammation of the small intestine?
Here are tips that can help reduce inflammation and set you on the path to improving your overall gut health.Eat an anti-inflammatory diet. ... Try an elimination diet. ... Reduce your stress levels. ... Take probiotics. ... Ensure you're getting the right amount of nutrients. ... 5 of the Most Anti-Inflammatory Foods You Can Eat.
Is intestinal inflammation serious?
Although inflammatory bowel disease usually isn't fatal, it's a serious disease that, in some cases, may cause life-threatening complications.
What causes inflammation of the intestines?
Colitis is a general term for the inflammation of the colon's inner lining, which is your large intestine. There are different types of colitis categorized by cause. Infections, poor blood supply, and parasites can all cause an inflamed colon.
What are the 5 classic signs of inflammation?
Based on visual observation, the ancients characterised inflammation by five cardinal signs, namely redness (rubor), swelling (tumour), heat (calor; only applicable to the body' extremities), pain (dolor) and loss of function (functio laesa).
How long does it take for inflamed intestines to heal?
Treatment often involves intravenous nutrition to allow the bowel to rest, which typically resolves the disease within one or two weeks.
What foods soothe inflamed intestines?
Cooked vegetables: Well-cooked vegetables such as green beans, carrots, mashed potatoes without skin, steamed asparagus tips and pureed squash. Use fresh or frozen. Canned or soft fruits: Peeled apples, ripe bananas, cantaloupe, honeydew, watermelon, and canned fruit in fruit juice or light syrup.
What causes inflammation in stomach and small intestines?
The most common cause of gastritis and duodenitis is a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. Large amounts of the bacteria invading your stomach or small intestine can cause inflammation.
What causes small intestine problems?
What conditions can affect the small intestine? The common conditions that can affect the small intestine include Crohn's disease, celiac disease, bowel obstructions, small bacterial overgrowth, and irritable bowel syndrome. Other, more rare conditions can also affect the small bowel, such as cancer.
What are four symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease?
What are the symptoms of IBD?Diarrhea (often loose and watery with Crohn's disease or bloody with ulcerative colitis)Severe or chronic cramping pain in the abdomen.Loss of appetite, leading to weight loss.Fatigue.Fever.Rectal bleeding.Joint pain.Skin problems, such as rashes.
Does colitis always show up on colonoscopy?
Gastroenterologists almost always recommend a colonoscopy to diagnose Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. This test provides live video images of the colon and rectum and enables the doctor to examine the intestinal lining for inflammation, ulcers, and other signs of IBD.
How long does it take for inflamed intestines to heal?
Treatment often involves intravenous nutrition to allow the bowel to rest, which typically resolves the disease within one or two weeks.
What is inflammation of the intestine called?
Inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD, is a condition in which there is chronic or recurring inflammation of the gastrointestinal, or GI, tract. In a type of IBD called ulcerative colitis, the condition is limited to the colon, also known as the large intestine.
What are four symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease?
What are the common symptoms of IBD?Persistent diarrhea.Abdominal pain.Rectal bleeding/bloody stools.Weight loss.Fatigue.
What is intestinal inflammation?
Inflammation is the body's reaction to harmful stimuli. The blood circulation is stimulated and messenger substances are released, which then attract immune cells. This is how the body prepares to ward off and repair the damage.
Where can inflammation occur in the intestine?
Theoretically, the entire intestine (i.e. small and large intestine) can be affected by inflammation. But it rarely happens that the full length of the intestine is affected. Depending on the cause of the inflammation, certain sections of the intestine are mostly affected.
How is inflammation in the intestine diagnosed?
There are several diagnostic tools to diagnose intestinal inflammation. Viral gastroenteritis, which accounts for a large part of the intestinal inflammation, can already be recognized from the patient's descriptions. Examination of a stool sample is not necessary with common viral gastroenteritis.
What is yeast candida?
The yeast candida albicans plays an important role in inflammation of the intestine caused by fungi. Although it also occurs in healthy people on the intestinal mucosa (colonisation), it can also multiply drastically and break the mucosal barrier. Then an infection occurs. However, this rarely happens and generally occurs in people with impaired immune systems.
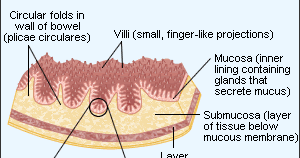
What is the layer of the intestinal wall that is exposed to external stimuli?
When inflammation occurs in the intestine, it usually affects the mucous membrane (this is the layer that lines the inside of the intestinal wall). The cells of the mucous membrane are constantly exposed to external stimuli, for example from food components, bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other intruders.
What is the most common symptom of inflammation in the intestine?
Abdominal pain and indigestion are the most common intestinal inflammation symptoms. About 1 in 10 people regularly suffers from these, and in many cases an inflammation in the intestine is the cause.
Why do we need ultrasound for intestinal inflammation?
However, ultrasound examinations are only of limited use for the diagnosis of intestinal inflammation. The reason is that they may reveal gross signs of inflammation, but it is difficult to determine the exact extent of the inflammation and its cause.
What is the umbrella term for inflammation of the digestive system?
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an umbrella term used to describe disorders that involve chronic inflammation of your digestive tract. Types of IBD include:
Why is inflammation bowel disease not a cause of IBD?
One possible cause is an immune system malfunction.
What is the perianal fistula?
It's often associated with painful bowel movements and may lead to a perianal fistula. Complications of ulcerative colitis may include: Toxic megacolon. Ulcerative colitis may cause the colon to rapidly widen and swell, a serious condition known as toxic megacolon. A hole in the colon (perforated colon).
Why does my immune system attack my digestive system?
When your immune system tries to fight off an invading virus or bacterium, an abnormal immune response causes the immune system to attack the cells in the digestive tract , too. Heredity also seems to play a role in that IBD is more common in people who have family members with the disease.
Which system is affected by Crohn's disease?
Digestive system. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are both forms of inflammatory bowel disease. Crohn's disease most commonly affects the colon and the last part of the small intestine (ileum). Ulcerative colitis affects only the colon.
What causes a scar in the bile ducts?
Primary sclerosing cholangitis. In this condition, inflammation causes scarring within the bile ducts, eventually making them narrow and gradually causing liver damage. Blood clots. IBD increases the risk of blood clots in veins and arteries. Complications of Crohn's disease may include: Bowel obstruction.
When to see a doctor for inflammatory bowel disease?
When to see a doctor. See your doctor if you experience a persistent change in your bowel habits or if you have any of the signs and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease. Although inflammatory bowel disease usually isn't fatal, it's a serious disease that, in some cases, may cause life-threatening complications.
What causes bacterial enteritis?
Infectious enteritis. The most common type of bacterial enteritis is caused by food poisoning. You can get it after ingesting food or water that is contaminated with bacteria. The bacteria can enter the food supply in a number of ways, including: improper food handling. poor hygiene.
What are the symptoms of enteritis?
medication induced. alcohol or drug induced. enteritis related to poor blood flow. enteritis related to inflammatory conditions, such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. Symptoms of enteritis can include fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
How long does it take for enteritis to show symptoms?
Symptoms of enteritis can start anywhere from a few hours to a few days after infection. Symptoms may include: diarrhea. nausea and vomiting. loss of appetite. abdominal cramps and pain. pain, bleeding, or mucus-like discharge from the rectum. fever.
How long does it take for enteritis to clear up?
Viral enteritis usually clears up without treatment in a few days. However, if you have symptoms of enteritis for more than three or four days, or you suspect that you have bacterial enteritis, seek medical attention.
What is the most common type of enteritis?
There are various types of enteritis. The most common are: viral or bacterial infection. radiation induced. medication induced.
What to do if you have enteritis?
Additional precautions. Use caution with medications such as NSAIDs, Aspirin, and oral steroids. Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol use. If you have a condition that is associated with an increased risk of enteritis, talk with your doctor and take your medications as directed by your doctor.
How to reduce the risk of developing enteritis?
Practicing good personal hygiene and safe food handling can help lower your chances of developing infectious enteritis.
Conditions That Affect the Small Intestine
When food is chewed and swallowed, it goes down the esophagus (food tube) into the stomach, and then into the small intestine. It travels through the three parts of the small intestine—the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The muscles in the walls of the small bowel move the food along while it is digested and vitamins and minerals are absorbed.
What Are the Symptoms of Small Intestine Problems?
In some cases, a problem with the small intestine might not cause any symptoms at all. Signs and symptoms will depend on which disorder is causing the problem, but there are some that may be more common across conditions.
What Causes Small Intestine Problems?
The causes of small intestine problems are different based on the condition. In some cases, the causes might not be well understood and include:
How Are Small Intestine Problems Diagnosed?
When problems in the small intestine start, the signs and symptoms might not seem related to digestion. In some cases, it might take time and a healthcare provider who is good at diagnosing to get to the heart of the matter.
How Are Small Intestine Problems Treated?
The treatment for small bowel conditions will be different based on what’s causing them. However, part of treatment might include lifestyle changes such as nutrition and diet, stress reduction, or working with a mental health professional.
Summary
Diseases and disorders of the small intestine are common. They include Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, and irritable bowel syndrome. These may cause digestive symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, or vomiting. They may also lead to vitamin deficiencies or anemia.
A Word From Verywell
Small intestinal problems can be tricky to diagnose and treat. It may help to get a referral to a gastroenterologist (a doctor who specializes in the digestive system). Sometimes small intestine problems cause signs and symptoms outside the digestive system so it can take time to find the problem.
Why does the digestive system get inflamed?
The digestive tract becomes inflamed as the body tries to create an immune response against the invaders. In a healthy immune response, the inflammation goes away when the infection is gone. In people with IBD, however, digestive tract inflammation can occur even when there’s no infection.
What is the function of the large intestine?
large intestine. It’s responsible for breaking down food, extracting the nutrients, and removing any unusable material and waste products. Inflammation anywhere along the digestive tract interferes with this normal process. IBD can be very painful and disruptive.
What is the first step in IBD treatment?
Anti-inflammatory drugs are the first step in IBD treatment. These drugs help decrease inflammation of the digestive tract. However, they have many side effects.
What is the purpose of antibiotics in Crohn's disease?
Antibiotics are used to kill bacteria in the small intestine that may trigger or aggravate the symptoms of Crohn’s.
What is an IBD?
If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) represents a group of intestinal disorders that cause prolonged inflammation of the digestive tract. The digestive tract comprises the: mouth. esophagus. stomach. small intestine. large intestine.
What are the two most common diseases that are included in the umbrella term IBD?
Many diseases are included under the umbrella term IBD. The two most common ones are ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease.
Why does Crohn's disease cause bloating?
stomach pain, cramping, and bloating due to bowel obstruction. weight loss and anemia, which can cause delayed physical growth or development in children. People with Crohn’s disease may also get canker sores in their mouths. Sometimes ulcers and fissures also appear around the genital area or anus.
How to reduce inflammation in the gut?
Chronic stress can really wreck your gut health, so managing your stress is crucial for reducing gut inflammation. Meditation regulates the stress response, helping to maintain healthy gut barrier function and inflammatory balance. ( 106) A consistent exercise routine and healthy sleep habits are also crucial for managing stress and supporting gut health.
How to limit gut inflammation?
To limit gut inflammation, be judicious about your use of antibiotics and non-antibiotic drugs. While our understanding of the effects of non-antibiotic drugs on gut health is in its infancy, the available information is worrisome. Conversely, the evidence of the harmful effects of antibiotics on the gut is robust.
What is the role of dysbiosis in the gut?
Dysbiosis is a disruption of the gut microbial community by various stressors, such as an unhealthy diet and antibiotics. Dysbiosis promotes gut inflammation , and, if left unchecked, contributes to the development of chronic diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), colon cancer, obesity, and asthma.
What are the effects of maltodextrin on the gut?
Maltodextrin, a synthetic carbohydrate used as a thickener and preservative in processed foods, enhances the adhesion of harmful bacteria to intestinal cells, and promotes biofilm formation. ( 17) The artificial sweetener Splenda stimulates the growth of inflammatory gut bacteria. ( 18) Carrageenan, a seaweed-based polysaccharide used for its thickening and emulsifying properties, exacerbates IBD. Carboxymethylcellulose and polysorbate-80, two more ubiquitous food emulsifiers, increase intestinal permeability. ( 19, 20 ) Titanium dioxide, a whitening and brightening agent, provokes an inflammatory cytokine response in the gut. ( 21 ) To keep gut inflammation at bay, avoidance of these ubiquitous food additives should be a top priority.
What are the two factors that affect gut health?
Gut health is influenced by two related variables: the intestinal barrier and the gut microbiota. Disturbances in either one of these factors can induce gut inflammation, inciting a chain reaction of damage that begins locally and may spread systemically throughout the body.
Can industrial seed oil cause gut inflammation?
The high omega-6 fatty acid content of industrial seed oils makes them susceptible to damage from heat and light. Processing and cooking with industrial seed oils create oxidized, inflammatory byproducts that, when consumed, induce gut inflammation. Indeed, a diet rich in industrial seed oils has been found to provoke gut inflammation, while also enhancing the growth of intestinal pathogens. ( 12, 13, 14)
Is gut inflammation a determinant of health?
However, gut inflammation is also a crucial determinant of intestinal and whole-body health. Read on to learn how various diet and lifestyle factors cause gut inflammation, the health consequences of a chronically inflamed gut, and practical strategies for alleviating inflammation and restoring gut health. Gut inflammation can contribute ...
What is the name of the inflammation of the duodenum?
Duodenitis is inflammation occurring in the duodenum, the beginning of the small intestine. Inflammation in the lining of the duodenum may result in abdominal pain, bleeding, and other gastrointestinal symptoms.
What is the most common cause of duodenitis?
The most common cause of duodenitis is a stomach infection associated with a type of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori (H pylori). This organism disrupts the mucus barrier that normally protects the delicate duodenal lining from acidic stomach contents.
What are the symptoms of duodenitis?
Duodenitis causes inflammation of the stomach lining that may result in a number of symptoms. The symptoms can vary in intensity among individuals.
How is duodenitis treated?
Treatment for duodenitis begins with seeking medical care from your health care provider. To determine if you have duodenitis, your health care provider may ask you to provide blood, urine, and stool samples for laboratory tests. Upper endoscopy permits visualization of the duodenum and the collection of small mucosal biopsies. Biopsies are studied under the microscope to confirm H pylori infection.
What are the potential complications of duodenitis?
You can help minimize your risk of serious complications by following the treatment plan you and your health care professional design specifically for you. Complications of duodenitis include:
What causes a duodenal infection?
The most common cause of duodenitis is H pylori infection. Other causes of duodenitis include prolonged use of medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can cause inflammation of the lining of the duodenum. Severe illness, radiation therapy, and Crohn’s disease are also associated with duodenitis.
How to treat H pylori?
In the case of H pylori-related duodenitis, the infection can be treated successfully with antibiotics. For duodenitis not related to H pylori, medications that reduce stomach acid can be an effective treatment. You can reduce your risk of H pylori infection by following commonsense hygiene practices such as washing your hands with soap and water. Lifestyle changes, such as limiting alcohol consumption and limiting your use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce your risk of duodenitis that is not related to H pylori.
Why is the small intestine called the small intestine?
Although being longest portion of GI tract, small intestine is called small because it is narrow or it has small diameter as compared to large intestine which is also called colon. The average length of small intestine is 14 feet. Chances of small intestine bleeding are only 5% as compared to more frequent upper gastric bleeding or lower large ...
What Causes Bleeding In Small Intestine?
Ulcer anywhere in the small intestine can be a reason for bleeding. Among this most common is duodenal ulcer bleeding. The ulcer can perforate and cause bleeding together with other characteristic symptoms. It can result from excessive use of NSAID (non steroid anti inflammatory drugs) or prolonged use of steroid medicines.
Why does my bowel bleed?
Bleeding from small bowel can be either profuse as a result of hemorrhage or it can be slow with burst on tiny blood vessels in the internal lining of the intestine. Occult blood in stool and anemia are two crucial symptoms that can aid in diagnosis of small intestine bleeding.
How to diagnose small intestine bleeding?
Several methods are used for this purpose. X- Ray of abdomen, Barium meal and follow through, CT scan, deep small bowel enteroscopy, as well as pathological stool and blood test may aid in diagnosing the condition. Angiographies of intestinal peripheral arteries are also valuable in diagnosing the condition and to find the bleeder. Once the cause is detected, it becomes easier to treat small bowel bleeding.
What causes a peyer's patch in the ileum?
Peyer’s patches are present in ileum. If there is heavy infestation of intestinal worms, it may cause microscopic bleeding from the lining of small intestine. Zollinger Ellison syndrome is a rare disorder which is characterized by severe ulceration in stomach and jejunum with hyper secretion of gastric acid.
What is the longest part of the gastrointestinal tract?
This is because small intestine is the longest part of gastrointestinal tract. Anatomically small intestine is divided in three portions, the first is called duodenum, followed by jejunum, and the last part is ileum. All three parts of the small intestine play an active role in absorption of nutrients from the food we eat.
What causes a person to bleed in the small bowel?
Atreiovenous malformation in the walls of small bowel is another common cause for bleeding. They are more common in people after the age of 50 and it is often associated with diseases of heart and kidney.
Why is gastroenteritis a problem?
Bacterial gastroenteritis is frequently a result of poor sanitation, the lack of safe drinking water, or contaminated food-conditions common in developing nations. Natural or man-made disasters can make underlying problems in sanitation and food safety worse. In developed nations, the modern food production system potentially exposes millions of people to disease-causing bacteria through its intensive production and distribution methods. Common types of bacterial gastroenteritis can be linked to Salmonellaand Campylobacterbacteria; however, Escherichia coli0157 and Listeria monocytogenesare creating increased concern in developed nations. Choleraand Shigella remain two diseases of great concern in developing countries, and research to develop long-term vaccines against them is underway.
What are the symptoms of gastroenteritis?
Symptoms of great concern include a high fever (102 ° F [38.9 °C] or above), blood or mucus in the diarrhea, blood in the vomit, and severe abdominal pain or swelling. These symptoms require prompt medical attention.
How long does it take for gastroenteritis to heal?
Gastroenteritis is usually resolved within two to three days and there are no long-term effects. If dehydration occurs, recovery is extended by a few days.
What is the term for a virus that causes diarrhea and vomiting?
Gastroenteritis is a catchall term for infection or irritation of the digestive tract, particularly the stomach and intestine. It is frequently referred to as the stomach or intestinal flu, although the influenza virus is not associated with this illness. Major symptoms include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. These symptoms are sometimes also accompanied by fever and overall weakness. Gastroenteritis typically lasts about three days. Adults usually recover without problem, but children, the elderly, and anyone with an underlying disease are more vulnerable to complications such as dehydration.
What is the greatest danger of gastroenteritis?
The greatest danger presented by gastroenteritis is dehydration. The loss of fluids through diarrhea and vomiting can upset the body's electrolyte balance, leading to potentially life-threatening problems such as heart beat abnormalities (arrhythmia). The risk of dehydration increases as symptoms are prolonged. Dehydration should be suspected if a dry mouth, increased or excessive thirst, or scanty urination is experienced.
How to treat uncomplicated gastroenteritis?
Symptoms of uncomplicated gastroenteritis can be relieved with adjustments in diet, herbal remedies, and homeopathy. An infusion of meadowsweet (Filipendula ulmaria) may be effective in reducing nausea and stomach acidity. Once the worst symptoms are relieved, slippery elm (Ulmus fulva) can help calm the digestive tract. Of the homeopathic remedies available, Arsenicum album, ipecac, or Nux vomicaare three said to relieve the symptoms of gastroenteritis.
What is the best medicine for gastroenteritis?
Probiotics, bacteria that are beneficial to a person's health, are recommended during the recovery phase of gastroenteritis. Specifically, live cultures of Lactobacillus acidophilusare said to be effective in soothing the digestive tract and returning the intestinal flora to normal. L. acidophilusis found in live-culture yogurt, as well as in capsule or powder form at health food stores. The use of probiotics is found in folk remedies and has some support in the medical literature. Castor oil packs to the abdomen can reduce inflammation and also reduce spasms or discomfort.
