What does interstitial mean in biology? 1. Relating to, occurring in, or affecting interstices. 2. Anatomy Relating to or situated in the small, narrow spaces between tissues or parts of an organ: interstitial cells; interstitial fluid. in′ter·sti′tial·ly adv.
What does interstitial means?
in•ter•sti•tial (ˌɪn tərˈstɪʃ əl) adj. 1. pertaining to, situated in, or forming interstices. 2. situated in the interstices of a tissue or organ. n. 3. an imperfection in a crystal caused by the presence of an extra atom in an otherwise complete lattice. [1640–50] in`ter•sti′tial•ly, adv.
What is interstitial space?
Interstitial sites are empty spaces in a crystal lattice. Depending on the number of atoms surrounding that empty space, the interstitial site can be designated as triangular (3), tetrahedral (4), octahedral (6), or cubic (8).
What is the definition of interstitial space?
Interstitial Space. The area of load bearing surfaces located above or below occupied building floors that is not available for general occupancy often due to inadequate clear headroom or lack of provisions for egress, and containing building structure or services predominantly serving adjacent floors or to provide access to such systems.
Is interstitial fluid found inside or outside of the cell?
Interstitial fluid is the intracellular fluid of the blood cells. Interstitial fluid is the intracellular fluid found in all cell types. Interstitial fluid is the extracellular fluid inside the circulatory system. Interstitial fluid is extracellular fluid outside the circulatory system and the cells.

What is interstitial biology?
Interstitial fluid is a biological fluid present between the cells and tissues, comprising a similar composition to that of the plasma [79].
What's interstitial mean?
in·ter·sti·tial ˌint-ər-ˈstish-əl. : situated within but not restricted to or characteristic of a particular organ or tissue. used especially of fibrous tissue. : affecting the interstitial tissues of an organ or part.
What is interstitial space in the body?
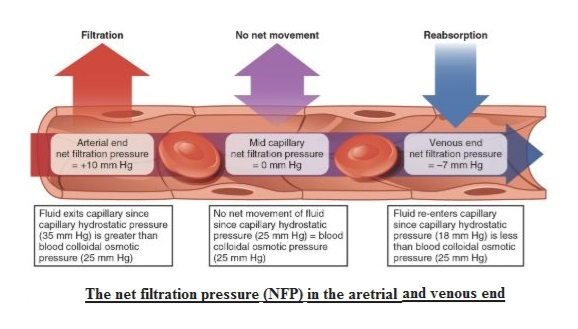
The Interstitium. The interstitial space that lies between blood vessels and cells provides the fluid and structural environment surrounding those cells. Under most conditions in most tissues, fluid from the vascular space continually filters from the microvessels into the interstitial space and is not reabsorbed (1).
What is an interstitial tissue?
Interstitial tissue is composed of cells, water and electrolytes, ground substance, and fibrillary elements (Figure 2-1). The pH and the electrolyte composition of interstitial tissue are maintained in equilibrium both with those of plasma in capillaries and with those of the intracellular fluid compartment.
What is interstitial in cells?
Interstitial cell refers to any cell that lies in the spaces between the functional cells of a tissue. Examples include: Interstitial cell of Cajal (ICC) Leydig cells, cells present in the male testes responsible for the production of androgen (male sex hormone) A portion of the stroma of ovary.
What is an interstitial example?
Interstitial ads are full-screen placements between standard interactions in the user experience of a site, app, or game. For example, navigation between two articles on a news media website or the transition between levels of a hyper-casual game can warrant one of these ads.
What is the function of interstitial?
A hormone made in the pituitary gland. In females, it acts on the ovaries to make follicles release their eggs and to make hormones that get the uterus ready for a fertilized egg to be implanted. In males, it acts on the testes to cause cells to grow and make testosterone.
What organ has interstitial cells?
The testesThe testes contain germ cells that differentiate into mature spermatozoa, supporting cells called Sertoli cells, and testosterone-producing cells called Leydig (interstitial) cells.
Where is interstitial tissue found?
An interstitial space is found in the dermis and submucosae and other fibroconnective tissues throughout the body.
What does interstitial mean medically?
Interstitial (in-tur-STISH-ul) lung disease describes a large group of disorders, most of which cause progressive scarring of lung tissue. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease eventually affects your ability to breathe and get enough oxygen into your bloodstream.
What does interstitial inflammation mean?
Interstitial lung disease refers to a group of about 100 chronic lung disorders characterized by inflammation and scarring that make it hard for the lungs to get enough oxygen. The scarring is called pulmonary fibrosis. The symptoms and course of these diseases may vary from person to person.
What is interstitial inflammation?
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a term for a group of conditions that cause inflammation and scarring in your lungs. Symptoms of ILD include shortness of breath and a dry cough. ILD can be caused by medication, radiation therapy, connective tissue diseases or inhaling harmful substances.
What does interstitial fluid mean in medical terms?
Interstitial fluid, or simply tissue fluid, is a mixture of water, ions, and small solutes that are forced out of the blood plasma by the systolic pressure created when the heart pumps.
What is the interstitial space between two concrete surfaces?
The interstitial spacebetween the two concrete surfaces provides an area for the mechanical, electric, plumbing, and fire protection subsystems.
What is the blue space between the cells and the vascular space?
Around and between the cells and vascular space is the blue interstitial space.
How many colors did Richter paint in 1966?
192 Farben (192 Colors), 1966, though arbitrary in selection and allocation of colors, still looks strikingly handpainted, and therefore subjective, including even the white interstitial space; Richter subsequently switched from using oil to enamel.
How long after radiation does the epithelial cell vacuolize?
At 2 weeks to 8 weeks after radiation, electron microscopy revealed vacuolization of Type II epithelial cells, total emptying of lamellar bodies, massive shedding of microvilli, partial necrosis and exfoliation of Type II epithelium, increased vacuolization of capillary endothelial cells, large amount of nondecomposed collagen fibers exudation from the capillaries into the interstitial spaceand into the alveolar lumen.
What is contamination analysis?
The contamination analysis en tailed culturing microbial samples from the coil surfaces with sterile swabs (Healthlink, Inc.) and collection of a hard black material coming from within the interstitial spaceof the cooling coil fins.
What is the Zapatista movement?
The Zapatista movement, which since 1994 has struggled to wrest control over local resources from the central government in favor of local (mostly indigenous) people in Chiapas, Mexico, is an example of the operation of interstitial space. Alexander Reid Ross (Ed.). Grabbing Back: Essays against the Global Land Grab.
What is tissue space?
The fluid filled areas that surround the cells of a given tissue; also known as tissue space.
What is extracellular fluid?
Extracellular Fluid – Fluids that surround cells within the body. Blood Plasma – The extracellular fluid that surrounds blood molecules in the vessels of the circulatory system. Transcellular Fluid – Fluids contained within spaces that are “external” to the body, such as the urine, joint fluid, and ocular fluid.
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
Once in the lymph vessels, the fluid contains many other cells and substances which aid in the immune response, by allowing white blood cells to find and digest harmful bacteria and virus infected cells. Many cells also remove their metabolic wastes into the interstitial fluid, and the wastes are cleaned through the lymphatic system.
What is the fluid between cells called?
Between the cells of the body, this fluid is known collectively as interstitial fluid. If there were no mechanism to remove it, parts of the body would swell up with pressure. Luckily, the lymphatic system is a network of vessels and tissues that actively removes the tissue fluid from tissues, and returns it to the blood plasma.
What is the fluid that is forced out of the blood?
Interstitial fluid, or simply tissue fluid, is a mixture of water, ions, and small solutes that are forced out of the blood plasma by the systolic pressure created when the heart pumps. Plasma is a mixture of water and many other constituents, which carry blood cells and oxygen to various parts of the body. Interstitial fluid makes up the large ...
Why do arteries swell with pressure?
These arteries, all the way down to the smallest capillaries, swell with pressure. Because the vessels are created by a series of cells, there exist small gaps between the many cells that make up a vessel, and some water and solutes can leak out.
Where is lymph fluid located?
Lymph is in the lymph vessels, plasma in the blood vessels, and interstitial fluid between the cells. Extracellular fluid refers to all of the above, as any fluid that exists within an organism and outside of the cytoplasm.
Which system collects and redistributes interstitial fluid to the blood?
Lymphatic System – A series of vessels that collects and redistributes interstitial fluid to the blood.
Definition of interstitial
1 : occurring in or being an interval or intervening space or segment : of, relating to, or forming an interstice an interstitial space … the site has been running interstitial ads, which consist of a full page of advertising between editorial pages, for a little more than a year. — Carl Sullivan
Examples of interstitial in a Sentence
Recent Examples on the Web The moves, volume, and interstitial corrective stretches included in the program are informed by all of the data Tonal collects across its user base. — Wes Siler, Outside Online, 12 Feb. 2022 When work is squeezed into four days, the human interactions that fill the interstitial time can suffer.
Medical Definition of interstitial
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
What does "interstitial cells" mean?
n. (Chemistry) chem an atom or ion situated in the interstices of a crystal lattice.
What does "incomplete" mean?
2. situated in the interstices of a tissue or organ. n. 3. an imperfection in a crystal caused by the presence of an extra atom in an otherwise complete lattice. [1640–50]
What is the definition of interstitial?
1. of or relating to an interstice or interstices. 2. (Chemistry) physics forming or occurring in an interstice: an interstitial atom. 3. (Chemistry) chem containing interstitial atoms or ions: an interstitial compound. 4. (Biology) anatomy zoology occurring in the spaces between organs, tissues, etc: interstitial cells. n.
What is interstitial fluid?
1. Relating to, occurring in, or affecting interstices. 2. Anatomy Relating to or situated in the small, narrow spaces between tissues or parts of an organ: interstitial cells; interstitial fluid.
What is the end stage of interstitial lung disease?
This is often a consequence of pulmonary hypertension. Respiratory failure. In the end stage of chronic interstitial lung disease, respiratory failure occurs when severely low blood oxygen levels along with rising pressures in the pulmonary arteries and the right ventricle cause heart failure. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What happens if you have acid reflux?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease. If you have uncontrolled acid reflux or indigestion, you may be at increased risk of interstitial lung disease.
What are the factors that make you more susceptible to interstitial lung disease?
Factors that may make you more susceptible to interstitial lung disease include: Age. Interstitial lung disease is much more likely to affect adults, although infants and children sometimes develop the disorder. Exposure to occupational and environmental toxins.
How does interstitial lung disease happen?
Interstitial lung disease seems to occur when an injury to your lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, your body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage. But in interstitial lung disease, the repair process goes awry and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into your bloodstream.
Why do I have tiny air sacs?
Causes. In your lungs, the main airways (bronchi) branch off into smaller and smaller passageways — the smallest, called bronchioles, lead to tiny air sacs (alveoli). Interstitial lung disease seems to occur when an injury to your lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, your body generates just the right amount ...
What happens if you work in mining?
If you work in mining, farming or construction or for any reason are exposed to pollutants known to damage your lungs, your risk of interstitial lung disease is increased. Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
What drugs can damage your lungs?
Many drugs can damage your lungs, especially: Chemotherapy drugs. Drugs designed to kill cancer cells, such as methotrexate (Otrexup, Trexall, others) and cyclophosphamide, can also damage lung tissue. Heart medications.
What is the newfound network of interconnected spaces filled with moving fluid called?
The study says the newfound network is where lymph comes from. Lymph is the fluid that your immune cells need to work well.
What is the role of the interstitium in the body?
The scientists found interstitium in tissue from the lungs and aorta, the digestive tract and bladder, in the skin, and in many other spots -- all places that expand and contract, where a “shock absorber” is important to protect tissue.
What is the new method of looking at living tissue called?
A new method of looking at it within living tissue, called probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy, lets researchers see these spaces filled. The fact that they're connected raises the possibility that sampling the fluid in those spaces could help experts examine the spread of diseases.
What are the walls of collagen?
Experts have long thought parts of the body (like skin, veins and arteries, and the lining around muscles) contain walls of collagen, the main component of connective tissue. Instead, as the new study points out, those "walls" aren't walls at all. Instead, they're spaces filled with fluid that are simply supported by collagen.
Is interstitium an organ?
That’s why the discovery of what some scientists call a previously unrecognized organ is so fascinating. In a new study, researchers claim that interstitium -- fluid -filled spaces in tissue that are connected throughout the body -- should be considered a new “ organ” and that these spaces may play a major part in a lot of what goes on in your body.
Who was the first person to use a scalpel to see how our bodies work?
The study of human anatomy reaches back thousands of years, to the Romans and Greeks. Herophilus, the Greek anatomist, is considered the first to take a scalpel to skin to see how our bodies work. That was about 300 B.C., give or take a decade or two.