The Health Benefits of Invertase
- Natural Immune Booster. Enzymes found in honey, such as invertase have been studied for their metabolic activity. ...
- Antioxidant Support. Invertase has many antioxidant properties, and it is a powerful agent against harmful organisms. ...
- Ulcers. ...
- Naturally Toxic to Harmful Organisms. ...
- Natural Respiratory Support. ...
- Cancer Support. ...
What class of enzyme does invertase belong?
VIA INITIAL RATE DETERMINATION
- Objectives. To measure the kinetic parameters of invertase.
- Introduction. Sucrose, commonly known as table sugar, is a disaccharide composed of an alpha-D-glucose molecule and a beta-D-fructose molecule linked by an alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond.
- List of Reagents and Instruments. ...
- Procedures. ...
- Notes. ...
- Questions. ...
- Data Forms. ...
What can I substitute for invertase?
What can I substitute for invertase?
- Honey – The Nearest Substitute of Invertase.
- Inverted Sugar Syrup – The Best Substitute Of Invertase.
- Sucrose – A Sweet Substitute Of Invertase.
- Simple Sugar Syrup – An Easy Alternative.
What is invertase and how is it used?
Invertase is used for the hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose. The resulting invert sugar syrup is sweeter than sucrose and is widely used in confectionery, bakery, and pastries, as it features enhanced moisture-preserving properties and is less prone to crystallization.
What is invertase used for?
Invertase is used in making candy fillers and liquid candy centers. Sweet fondant candies, delicious chocolate-covered cherries, and sweet creme eggs have the main secret item of invertase in them. Some shopkeepers also sell invertase as a liquid item so people can make candy at home. But most of the time, invertase is not easily available.
See more

What does invertase do in the human body?
Invertase in plants is essential not only for metabolism but also help in osmoregulation, development and defense system. In humans, the enzyme acts as an immune booster, as an antioxidant, an antiseptic and helpful for bone cancer or stomach cancer patients in some cases.
What is the purpose of adding invertase?
Invertase Uses When invertase is added to sugar candy recipes, like fondant candy fillings, it gradually liquefies the fondant. This is one way of producing the liquid center in candies like cherry cordials. The reaction takes a few days to occur, so there is a waiting period when making liquid centers with invertase.
What is the reaction catalyzed by invertase enzyme?
Invertase, also known as β-d-fructofuranosidefructohydrolase, β-fructofuranosidase, sucrase, saccharase. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose and related glycosides. It is commercially important due to its use for the hydrolysis of sucrose and is widely employed in food and beverage industries.
What can invertase break down?
Invertase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis (breakdown) of sucrose (table sugar) into fructose and glucose.
What enzyme breaks down sucrose?
enzyme sucrase-isomaltaseThe SI gene provides instructions for producing the enzyme sucrase-isomaltase. This enzyme is found in the small intestine and is responsible for breaking down sucrose and maltose into their simple sugar components. These simple sugars are then absorbed by the small intestine.
What enzyme converts sucrose to ethanol?
Zymase enzyme converts glucose into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. Alcoholic fermentation converts one mole of sucrose into two moles of ethanol and two moles of carbon dioxide, producing two moles of ATP in the process. Diastase transforms starch into maltose and after that, it converts it this into glucose.
What enzyme converts fructose into ethanol?
ZymaseThe correct answer is Zymase.
Where is invertase produced in the body?
Invertase is found in human saliva. It is produced by the bacteria, Streptococcus mutans, present in dental plaque.
What converts sucrose into glucose and fructose?
SucraseSolution : Sucrase is the enzyme which converts sucrose into glucose and fructose.
Is invertase a digestive enzyme?
An invertase is an enzyme of the glycoside hydrolase family. In the presence of water molecules, it allows the breakdown of sucrose into glucose and fructose, known as « invert sugars », hence the name of the enzyme. Invertase is involved in the digestion process.
Do humans have invertase enzyme?
Invertase in Humans Invertase's ability to break down (hydrolyze) the bond between fructose and glucose makes it a vital part of the digestion of complex sugars into blood sugar (glucose) which can be used as a ready fuel source by the body. Invertase is an essential enzyme in the human body.
What does invertase do in chocolate?
Once you have put a spoonful of fondant into the centre of your chocolate shell, add a few drops of invertaste. Cover and fill the remainder of the mould with Melted chocolate. Leave it for 1-2 days and the invertase will break the sugar in the fondant down and turn it into liquid.
What is invertase in candy?
Invertase is one of the secret ingredients in the candy-making industry. It is an enzyme that is commonly used to make candy liquid centers, chocolate-covered cherries, ...
How long does it take for invertase to break down sucrose?
If you are using it for candy making purposes, plan ahead. The invertase needs a few days to at least a week in storage to make the solid turn into a liquid.
What enzyme caused sugar to change form?
After much research, the chemists isolated the enzyme that caused this: invertase. By the year 1900, the process for deriving invertase from yeast was commonly used. Over the course of the next 20 ...
Can you store invertase in the refrigerator?
The invertase itself should be stored in the refrigerator for longevity. Cold temperatures slow the invertase reaction. Candies with invertase should be stored at room temperature instead of in the refrigerator for the best and fastest results.
Can you substitute invertase for invertase?
Invertase Substitute. There are not really any known substitutions for invertase. Depending on what you are making, there may be some workaround solutions. For example, if you are making chocolate-covered cherries, you can omit the invertase.
Is invertase in honey safe?
For most people, the small quantities of invertase you ingest in candies are completely safe. However, it is possible to have an allergic reaction to it. Invertase is naturally found in honey; it has been shown to naturally boost the immune system and can help with digestion and gut health. 1 .
Enzymatic Sources of Invertase
Bees and humans produce invertase naturally. But for commercial production, invertase is sourced mainly from fungi and yeast. Yeast species such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida utilis are used for commercial production of the invertase enzyme. Out of fungi, the filamentous fungi of the Aspergillus genus are used as a source of invertase.
Chemically Produced Inverted Sugar Vs Enzymatically Produced Inverted Sugar
Traditionally inverted sugar syrup was produced by adding acid to the concentrated solution. Alkali was added after the completion of the inversion process to raise the pH of the solution. The inverted sugar syrup produced thus was economical but had off-colours and flavours that left something to be desired.
Invertase Enzyme-Working
Invertase hydrolyzes and breaks down the disaccharide sucrose and polysaccharides molecules into its monosaccharide forms of glucose and fructose. Sucrose does not dissolve fully at room temperature in water and as per its concentration, it will crystalize quickly.
Use of Invertase Enzyme in Food Industry
Due to the inversion process of sucrose/sugar, invertase enzymes are vital to the confectionery industry which uses sugar as one of the essential ingredients. Given below are some of the uses of invertase enzymes.
Conclusion
Enzymes are biocatalysts that hydrolyze and break down several organic compounds. Invertase is one such enzyme that hydrolyzes sugar into glucose and fructose to create uncrystallized inverted sugar.
What is invertase used for?
It is essentially used for the hydrolysis of sucrose to glucose and fructose (invert sugar syrup). Invert sugar syrup is used as sweetener in baking, beverage, canning and dairy processes. The good humectant properties of the syrup also contribute to improved shelf-life in confectionery products. Within the scope of the latter, invertase is directly used to promote the formation of soft fondant centers (Serna-Saldivar and Rito-Palomares, 2008; Simpson et al., 2012; Subin and Bhat, 2015 ). Under adequate operational conditions (high initial sucrose concentration, pH, temperature, enzyme source) invertase displays trans-fructosylation activity, which enables the synthesis of short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides (scFOS) from sucrose. These scFOS are a mixture of 1-kestose, nystose and β-1-fructofuranosyl nystose and are formed upon the cleavage of the β-1,2- glycosidic bond of sucrose and the transfer of the fructosyl moiety onto an acceptor such as sucrose or a FOS. FOS are used several in food formulations such as jam, ice cream and in beverages and confectionery applications (Khandekar et al., 2014; Khanvilkar and Arya, 2015 ).
Where are invertase isoenzymes found?
Invertase isoenzymes are potentially to be found in all compartments which may contain sucrose as a metabolite whether as a transient or a stored molecule. In the cytosol, sucrose synthase provides an important alternative to invertase action and sometimes even becomes the dominant obligatory route of sucrose cleavage. The degree of expression of each of the invertase isoenzymes can show large variation according to the physiological and developmental stage of the particular organ examined and may vary in different species of plants. The molecular basis for the regulatory patterns of invertase activity is little understood.
What is the family of enzymes that hydrolyze sucrose into glucose and fructose?
Plant invertases (β-D-fructofuranosidase EC 3.2.1.26) constitute a family of enzymes that hydrolyse sucrose into glucose and fructose. Three types of invertase, namely cell-wall, vacuolar and cytoplasmic, have been purified from a number of species and characterized at the biochemical level. Plant invertases , implicated in source/sink relationships, phloem loading and unloading, growth and other developmental processes, play important biological functions. However, the physiological roles of the individual members of the invertase family are not yet established and many questions remain to be elucidated.
What is the name of the enzyme that converts sucrose to glucose?
Invertase is S-bD-fructo-furanosidase isolated from S. cerevisiae and other microorganisms. Hydrolysis from sucrose to fructose and glucose is catalyzed by this enzyme. The production of inverted sugar is one of invertase ’s numerous applications.
What enzymes cleave sucrose?
Invertase and SS are the two enzymes capable of cleaving sucrose present in plants. Invertases catalyze the irreversible hydrolysis of sucrose to free glucose and fructose. Based on optimum pH of their activity, invertases are grouped into acidic (optimum pH 4.0–5.5) and alkaline/neutral types (optimum pH 7.0–8.0). Acidic invertases are mainly found in cytosol and occasionally in cell walls, whereas alkaline/neutral types are abundant in vacuoles and cell walls. Alkaline/neutral invertases have recently been reported in chloroplasts and mitochondria. Alkaline invertases are sucrose-specific, while neutral invertase from carrot can also mediate raffinose and stachyose hydrolyses. The cell wall invertases hydrolyze the incoming translocated sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules.
Why does sucrose accumulate in tomatoes?
In the ripening fruits of strains of cultivated tomatoes, sucrose accumulates because of a very low ability to produce acid invertase, whereas other strains which are strong acid invertase producers accumulate glucose and fructose ( Miron & Schaffer, 1991; Yelle et al., 1991; Stommel, 1992; Klann et al., 1993 ).
What happens when you add invertase to semisyrup?
For processors who make a semisyrup and hold it in a tank for further evaporation, this holding tank is one point in the process when the enzyme may be added. As long as the semisyrup remains below 65°C, the enzyme will continue to break sucrose down into its two monosaccharides (glucose and fructose). Adding the enzyme in the semisyrup tank allows the processor to experiment with how long to allow the enzyme to work to best prevent crystallization. When the semisyrup is evaporated to the final syrup, the enzyme will be inactivated.
What bond does an invertase cleave?
Invertases cleave the O-C (fructose) bond, whereas the sucrases cleave the O-C (glucose) bond. For industrial use, invertase is usually derived from yeast. It is also synthesized by bees, which use it to make honey from nectar.
Can invertase be used to make fructose?
Applications and examples. Invertase is expensive, so it may be preferable to make fructose from gluco se using glucose isomerase, instead. Chocolate-covered cherries, other cordials, and fondant candies include invertase, which liquefies the sugar.
What is invertase used for?
Invertase is used for the hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose. The resulting invert sugar syrup is sweeter than sucrose and is widely used in confectionery, bakery, and pastries, as it features enhanced moisture-preserving properties and is less prone to crystallization.
What happens to invertase during the invertase reaction?
These products accumulate during the invertase reaction, reach a maximum (less than 10% of the total sugar 10)) and then decompose completely as the reaction proceeds.
How is sucrose hydrolysed?
Of the naturally occurring sugars only sucrose is hydrolysed by invertase to give equal parts of glucose and fructose. If the invertase contains melibiase, then 1 mole of glucose and fructose are formed from raffinose. If it contains maltase, then 2 moles of glucose are formed from maltose.
What does it mean when a pure invertase gives more fructose than glucose?
With the use of pure invertase, an analytical result giving more fructose than glucose always indicates the presence of raffinose in the sample. Since equal parts of fructose and glucose are formed in the hydrolysis of sucrose by invertase the smallest value is taken for the calculations.
Why does sucrose accumulate in tomatoes?
In the ripening fruits of strains of cultivated tomatoes, sucrose accumulates because of a very low ability to produce acid invertase, whereas other strains which are strong acid invertase producers accumulate glucose and fructose ( Miron & Schaffer, 1991; Yelle et al., 1991; Stommel, 1992; Klann et al., 1993 ).
What is the function of the invertase in Salmonella?
The Hin invertase regulates flagellar phase variation in Salmonella, allowing the bacterium to evade a host immune response ( Figure 1A). In one orientation, a promoter located within the invertible segment of DNA directs the expression of the H2 flagellin gene (fljB), as well as a repressor of the H1 flagellin gene (fljC ). After Hin catalyzes a site-specific inversion event, the promoter becomes inverted and can no longer drive the expression of these genes. Consequently, the H1 flagellin gene is expressed from its unlinked site. The Gin invertase of bacteriophage Mu controls the alternate expression of tail fiber genes ( Figure 1B). Each orientation of the invertible segment in bacteriophage Mu encodes a different C-terminal portion of the tail fiber protein S. Site-specific inversion catalyzed by Gin switches the expression of the C-terminal part of the protein, which determines the host specificity range for the phage. The Cin-mediated reaction of phage P1 performs a similar function. Due to the homology of these proteins and the similarity of their recombination substrates, the characterized invertases are functionally interchangeable. The invertases belong to the resolvase/invertase (also known as the serine) family of recombinases which currently has over 50 members. Site-specific DNA inversions can also be catalyzed by recombinases belonging to the phage integrase (also known as tyrosine recombinase) family.
How long is yeast invertase stable?
All solutions should be prepared with doubly distilled water. All solutions should be stored at 4°C. Purified, dried preparations of yeast invertase are stable for at least 1 year.
Why do bees use invertase?
And for good reason. To store honey in its runny liquid form, the bees use invertase to break down the sucrose portion of nectar. Sucrose is a common ingredient of nectar, but after the bees add invertase, the nectar is inverted into its two main components.
What is invertase in chocolate?
Invertase is also the magic ingredient in chocolate-covered liquid cherries. Cherries are covered in a fondant that has been treated with a small bit of invertase and then coated with chocolate. Slowly, in a process that spans several days, the invertase breaks down the sucrose into the transparent, sweet, syrupy confection ...
Why is sucrose bad for honey?
Sucrose has a bad name, I think, because we tend to focus on the relative amounts of glucose and fructose in our honey. Meanwhile, we forget that, until the bees began processing it, the nectar they collected may have been up to 55% sucrose.
What enzymes do bees produce?
H oney bees produce a number of different enzymes that are important to their survival. One of these is invertase, the very same enzyme that is used in the baking industry. So what is invertase and what does it do?
Why are enzymes named after the substances they break down?
But sometimes enzymes are named after the things they do. Invertase, for instance, is named for the process of inverting (or separating) sucrose back into its component parts.
What is an enzyme?
In biochemistry, an enzyme is a substance that helps a biological process along. It’s a helper of sorts. Usually, an enzyme speeds up a reaction, so we call it a catalyst. When you see the letters “ase” at the end of the word, it often means the thing is an enzyme.
Is invertase found in cherries?
No invertase = no chocolate cherries. Invertase is very common in the natural world, especially in plants and various microorganisms. Plants like Japanese pear fruit, the common garden pea, and cereal oats are good sources of invertase.
Where are enzymes sequestered?
Substrate presentation is a process where the enzyme is sequestered away from its substrate. Enzymes can be sequestered to the plasma membrane away from a substrate in the nucleus or cytosol. Or within the membrane, an enzyme can be sequestered into lipid rafts away from its substrate in the disordered region. When the enzyme is released it mixes with its substrate. Alternatively, the enzyme can be sequestered near its substrate to activate the enzyme. For example, the enzyme can be soluble and upon activation bind to a lipid in the plasma membrane and then act upon molecules in the plasma membrane.
What are the motions of enzymes?
Enzymes are not rigid, static structures; instead they have complex internal dynamic motions – that is, movements of parts of the enzyme's structure such as individual amino acid residues, groups of residues forming a protein loop or unit of secondary structure, or even an entire protein domain. These motions give rise to a conformational ensemble of slightly different structures that interconvert with one another at equilibrium. Different states within this ensemble may be associated with different aspects of an enzyme's function. For example, different conformations of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase are associated with the substrate binding, catalysis, cofactor release, and product release steps of the catalytic cycle, consistent with catalytic resonance theory .
How do enzymes increase reaction rates?
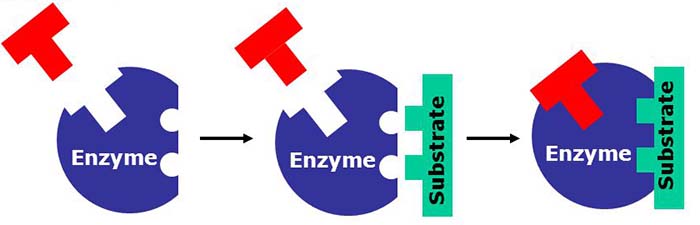
Enzymes increase reaction rates by lowering the energy of the transition state. First, binding forms a low energy enzyme-substrate complex (ES). Second, the enzyme stabilises the transition state such that it requires less energy to achieve compared to the uncatalyzed reaction (ES ‡ ).
How are enzymes named?
Following Buchner's example, enzymes are usually named according to the reaction they carry out: the suffix -ase is combined with the name of the substrate (e.g., lactase is the enzyme that cleaves lactose) or to the type of reaction (e.g., DNA polymerase forms DNA polymers).
How do enzymes differ from other catalysts?
Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific . Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many therapeutic drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors.
Why do enzymes denature?
An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH, and many enzymes are (permanently) denatured when exposed to excessive heat, losing their structure and catalytic properties . Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics.
What is the name of the enzyme that catalyzes the same chemical reaction?
Examples are lactase, alcohol dehydrogenase and DNA polymerase. Different enzymes that catalyze the same chemical reaction are called isozymes.

Enzymatic Sources of Invertase
- Bees and humans produce invertase naturally. But for commercial production, invertase is sourced mainly from fungi and yeast. Yeast species such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida utilis are used for commercial production of the invertase enzyme. Out of fungi, the filamentous fungi of the Aspergillus genus are used as a source of invertase. Aspergillus Nigero…
Chemically Produced Inverted Sugar vs Enzymatically Produced Inverted Sugar
- Traditionally inverted sugar syrup was produced by adding acid to the concentrated solution. Alkali was added after the completion of the inversion process to raise the pH of the solution. The inverted sugar syrup produced thus was economical but had off-colours and flavours that left something to be desired. The process was not organic, but chemical. Enzymatically derived inve…
Invertase Enzyme-Working
- Invertase hydrolyzes and breaks down the disaccharide sucrose and polysaccharides molecules into its monosaccharide forms of glucose and fructose. Sucrose does not dissolve fully at room temperature in water and as per its concentration, it will crystalize quickly. On the other hand, fructose and glucose have a higher solubility in water, so they d...
Use of Invertase Enzyme in Food Industry
- Due to the inversion process of sucrose/sugar, invertase enzymes are vital to the confectionery industry which uses sugar as one of the essential ingredients. Given below are some of the uses of invertase enzymes. 1. Invertase enzyme converts sucrose or table sugar to the inverted sugar solution. This is used to prevent the crystallization of sugar and used to make sweet, gooey liqui…
Conclusion
- Enzymes are biocatalysts that hydrolyze and break down several organic compounds. Invertase is one such enzyme that hydrolyzes sugar into glucose and fructose to create uncrystallized inverted sugar. Enzymatically produced inverted sugar is used prevalently in the food industry, especially to create soft and delicious confectioneries and baked items and to extend their shelf life.
Overview
Invertase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis (breakdown) of sucrose (table sugar) into fructose and glucose. Alternative names for invertase include EC 3.2.1.26, saccharase, glucosucrase, beta-h-fructosidase, beta-fructosidase, invertin, sucrase, maxinvert L 1000, fructosylinvertase, alkaline invertase, acid invertase, and the systematic name: beta-fructofuranosidase. The resulting mixture of fructose and glucose is called inverted sugar syrup. …
Production
Invertase is produced by various organisms like yeast, fungi, bacteria, higher plants, and animals. For example: S. cerevisiae, Saccharomyces carlsbergensis, S. pombe, Aspergillus spps, Penicillium chrysogenum, Azotobacter spps, Lactobacillus spps, Pseudomonas spps etc.
For industrial use, invertase is usually derived from yeast.
Applications and examples
Invertase is used to produce inverted sugar syrup.
Invertase is expensive, so it may be preferable to make fructose from glucose using glucose isomerase, instead.
Chocolate-covered cherries, other cordials, and fondant candies include invertase, which liquefies the sugar. Once the candy is manufactured, it needs at least a few days to a few weeks in storag…
Inhibition
Urea acts as a non-competitive inhibitor of invertase, presumably by breaking the intramolecular hydrogen bonds contributing to the tertiary structure of the enzyme.
See also
• List of enzymes
External links
• Invertase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)