Unit elastic demand is referred to as a demand in which any change in the price of a good leads to an equally proportional change in quantity demanded. In other words, the unit elastic demand implies that the percentage change in quantity demanded is exactly the same as the percentage change in price.
What does it mean if demand is unitary elastic?
Unitary elastic demand is a type of elasticity of demand where the product demand changes in a similar proportion to the price. This is where a price reduction equally raises the demand, and a price increase equally falls demand. Unitary elastic demand does not help to generate more revenue based on the change in the product price.
What is an example of unitary elastic demand?
While there are no perfect examples of unitary elastic demand in real life, a close example is clothing. Decreases in price of the supply, whether from a sale or discount store, often creates an approximately equal increase in demand.
What is the formula for unitary elasticity of demand?
Formula to calculate the price elasticity of demand. The formula for calculating this economic indicator is. PED = % change in the quantity demanded / % change in price. The equation can be further expanded to: PED = [ (Q1 – Q0) / (Q1 + Q0)]/ [ (P1 – P0) / (P1 + P0)] Q0 is the initial quantity. Q1 is the final quantity.
What does "elasticity of demand" mean?
As per the elasticity of demand definition, the demand contracts or extends with rising or fall in the prices. This quality of demand is called Elasticity of Demand when the change in its virtue and the price changes (low or high).

How do you know if demand is unit elastic?
The demand is elastic if E(p)>1. That is to say, the demand is elastic if the percentage change in demand is greater than the percentage change in price. The demand is unitary if E(p)=1. That is to say, the demand is unitary if the percentage change in demand and price are relatively equal.
What does in mean when demand is elastic inelastic or unit elastic?
An elastic demand or elastic supply is one in which the elasticity is greater than one, indicating a high responsiveness to changes in price. An inelastic demand or inelastic supply is one in which elasticity is less than one, indicating low responsiveness to price changes.
At what point is demand unit elastic?
If the formula creates an absolute value greater than 1, the demand is elastic. In other words, quantity changes faster than price. If the value is less than 1, demand is inelastic. In other words, quantity changes slower than price.
What is unit elastic elastic and inelastic?
Elasticity = (% Change in Quantity)/(% Change in Price) If elasticity is greater than 1, the curve is elastic. If it is less than 1, it is inelastic. If it equals one, it is unit elastic.
Is unit elastic good or bad?
The concept of unit elastic helps business analysts and economists to explain changes in demand or supply of goods. Particularly, the concept is helpful when there is a price change of the goods or when consumers' income changes.
Which of the following is true when the demand is unit elastic?
Which of the following is true when the demand is unit elastic? The percentage change in quantity demanded is not correlated with the percentage change in price.
What products have unit elastic demand?
Unit elastic goods are those for which demand or supply is affected by price change. For example, if the price of bananas decreases, the number of people buying it may increase because now they can afford to buy more since prices have decreased. This would be an example of unit elastic demand/supply.
What is the difference between price elastic and unit elastic?
To determine how a price change will affect total revenue, economists place price elasticities of demand in three categories, based on their absolute value. If the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1, demand is termed price elastic. If it is equal to 1, demand is unit price elastic.
How do you know if demand is elastic or inelastic or unit elastic?
The price elasticity of demand is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in price. If the quotient is greater than or equal to one, the demand is considered to be elastic. If the value is less than one, demand is considered inelastic.
How does one determine whether demand is elastic inelastic or unit elastic?
An elastic demand is one in which the change in quantity demanded due to a change in price is large. An inelastic demand is one in which the change in quantity demanded due to a change in price is small. If the formula creates an absolute value greater than 1, the demand is elastic.
How do you know if demand is elastic or inelastic or unit elastic?
The price elasticity of demand is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage change in price. If the quotient is greater than or equal to one, the demand is considered to be elastic. If the value is less than one, demand is considered inelastic.
Is unit elastic more elastic?
As one moves down the demand curve from top left to bottom right, the measured elasticity is much greater than one (very elastic), then just greater than one (somewhat elastic), then equal to one (unitary elastic, then less than one (somewhat inelastic), and finally much less than one (very inelastic).
What is an example of unit elastic?
The unit elastic theory assumes that there's another similar good on the market at a competitive price. Example: An office supply store sells a specific type of pen for $1.41. It sells 1,000 of these pens per month, making a profit of $1,410. The owner believes the store could sell more pens if the price was lower.
Is supply elastic inelastic or unit elastic?
If the supply changes little with a change in price, then supplies are considered inelastic. Supply is elastic if there are large changes in supply for a small change in price. If the percentage change in price is equal, though opposite, to the percentage change in quantity, then supply elasticity is unit elastic.
What does unit elastic demand mean?
The midpoint of the demand curve, is unit elastic demand. It means that if the price of a good changes by a certain percentage then the quantity de...
What is an example of unit elastic demand?
An example of unit elastic demand is the demand for a good or service.
What is unit elastic?
The Unit Elastic is a term that refers to the midpoint of the demand curve. If the coefficient of elasticity = 1, consumers will buy as much as the...
What are unit elastic goods?
Unit elastic goods are those for which demand or supply is affected by price change. For example, if the price of bananas decreases, the number of...
What is an elasticity of 1?
An elasticity of 1 is known as unit elastic. If the price of bananas decreases, demand for them increases. This means that the coefficient of suppl...
What is unit elastic example?
An example of a unit elastic good would be a change in the price of household appliances. If the overall price of household appliances fell by 10%,...
Which products are unit elastic?
Products that are unit elastic see a proportional change in demand and supply based on a change in price. These goods are called necessary goods be...
How do you find unit elasticity?
Finding unit elasticity is done by using the elasticity formula. To calculate elasticity, take the percentage change in either demand or supply and...
What Does Unit Elastic Demand Mean?
What is the definition of unit elasticity? The demand that changes proportionally to a change in price is elastic. A unit elastic demand follows a change in price when consumers have close substitute products to meet their needs.
Example
Frank is an apple producer. The retail price of apples is $1.40 per pound, but Frank notices that consumers would be happier if the price was lower. So, he decides to put apples on sale for $1.27 per pound.
Why is elastic demand also called unit elastic demand?
It is also known as unit elastic demand because of a unit increase by decrease unit price. Unit Price Unit Price is a measurement used for indicating the price of particular goods or services to be exchanged with customers or consumers for money.
What is unitary elastic demand?
Unitary elastic demand is a type of demand which changes in the same proportion to its price; this means that the percentage change in demand is exactly equal to the percentage change in price. In the unitary demand, the product elasticity is negative as the product price decrease does not help to generate more revenue.
What is demand curve?
Demand Curve Demand Curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the prices of goods and demand quantity and is usually inversely proportionate. That means higher the price, lower the demand.
How can a quantity of goods be sold off?
Any goods quantity that is produced can be sold off by decreasing the selling price.
How to calculate marginal cost?
Marginal Cost Marginal cost formula helps in calculating the value of increase or decrease of the total production cost of the company during the period under consideration if there is a change in output by one extra unit. It is calculated by dividing the change in the costs by the change in quantity. read more
Which rule applies to unitary demand?
Unitary demand applies the rule of demand and supply.
Is consumer expenditure impacted by market pricing?
As it is visible in the example shown above that the consumer expenditure on the product is not impacted by the market pricing. They adjust their consumption as per the prices prevailing in the market.
What is Unit Elastic?
How do people react when the price of a product goes up or down? What happens when incomes rise? What about when the supply of a product starts to slip? These questions all point to a concept in economics called elasticity.
Unit Elastic Graph
The unit elastic graph shows the different ways the unit elastic supply curve and unit elastic demand curve relate to each other. Notice how each line acts opposite based on the change in price. When the price rises, the demand lowers, but the supply rises. The following two graphs show each unit elastic graph separately and then combined.
Unit Elastic Examples
Unit elastic goods fall into a category of necessary goods, which means that they are important to most people's lives, but are not essential for survival. Products that see almost no change in demand are called essential goods. Since unit elastic goods are not essential, they have more elasticity.
What is elastic demand?
In perfectly elastic demand, the demand for a good drops to zero if the price is raised at all. This type of demand isn't common since several factors influence consumers' buying decisions other than the price. A consumer could consider their loyalty to the brand, the distance they need to travel to buy the product, the delivery time to get the product and the overall quality.
When is demand elastic?
When the percentage change in demand is more than the percentage change in price, the demand is relatively elastic. Small price changes can cause relatively substantial changes in volume. Luxury goods, like TVs and designer brands, are good examples of relatively elastic demand.
Why is unit elastic important?
Unit elasticity helps with making informed decisions about a company's customer base and the costs for goods and services. Organizations invest a lot of time, energy and money to understand customer behavior, and unit elasticity helps identify what business owners need to know about the market and how potential consumers settle on purchasing choices.
What is price elasticity?
One of the most common measures of price elasticity is unit elastic, which is an economic theory that the percentage change of the price of a good and the percentage change of the demand of the good is the same. In this article, we explain how unit elastic works and define the other types of price elasticity of demand.
How does elasticity affect supply and demand?
Elasticity is how supply and demand are influenced by price changes. Highly elastic products are greatly impacted by changes in the financial market. Along with unit elasticity, there are a variety of elastic and inelastic price demands. They have an effect on the supply and demand between businesses and consumers.
What is perfectly inelastic demand?
Perfectly inelastic demand. With perfectly inelastic demand, the interest for an item doesn't change proportionately with a fall or climb in its cost. Shoppers will continue to buy a product even if the product's price rises. Essential goods, such as food and medicine, sometimes have perfectly inelastic demand.
When the percentage for the demand is less than the percentage change in price, the demand is?
When the percentage for the demand is less than the percentage change in price, the demand is relatively inelastic. Most essential goods are often relatively inelastic.
What Does Unit Elastic Mean?
In economics, elasticity is used to evaluate the degree of change that the supplied or demanded quantities of an item experience if the price of the item is changed . The higher the elasticity ratio the more sensible these quantities are to any change in the price.
When is a good considered unit elastic?
According to our concept, a good is considered unit elastic when a unitary change in one element causes a unitary change in the other. As we see, a 10% change in price will reduce the demand by 10%, which also means that a 1% change in price will reduce demand by 1%. This means that the brushes are unit elastic.
What is unitary elasticity?
Definition: A unitary elasticity is found when a unitary change in one element causes a unitary change in the other element. In other words, the value of both elements increases and decreases on an equally proportional basis.
Why is elasticity important in price setting?
This concept is particularly useful for price-setting decisions. Whenever a company is pursuing a campaign to increase profitability or production volumes by affecting the current price of the items they sell, the company must assess the elasticity of each item to understand what would be the most probable reaction of the market to these changes and conclude if the expected results would be possible.
How is demand elasticity determined?
In other words, demand elasticity or inelasticity for a product or good is determined by how much demand for the product changes as the price increases or decreases. An inelastic product is one that consumers continue to purchase even after a change in price. The elasticity of a good or service can vary according to the number ...
What is elasticity in economics?
Elastic is a term used in economics to describe a change in the behavior of buyers and sellers in response to a change in price for a good or service. In other words, demand elasticity or inelasticity for a product or good is determined by how much demand for the product changes as the price increases or decreases. An inelastic product is one that consumers continue to purchase even after a change in price. The elasticity of a good or service can vary according to the number of close substitutes available, its relative cost, and the amount of time that has elapsed since the price change occurred.
What Is Elastic?
Elastic is a term used in economics to describe a change in the behavior of buyers and sellers in response to a change in price for a good or service. In other words, demand elasticity or inelasticity for a product or good is determined by how much demand for the product changes as the price increases or decreases. An inelastic product is one that consumers continue to purchase even after a change in price. The elasticity of a good or service can vary according to the number of close substitutes available, its relative cost, and the amount of time that has elapsed since the price change occurred.
Why is elasticity important?
Elasticity is an important economic measure, particularly for the sellers of goods or services, because it indicates how much of a good or service buyers consume when the price changes. When a product is elastic, a change in price quickly results in a change in the quantity demanded.
What is the change that is observed for an elastic good?
The change that is observed for an elastic good is an increase in demand when the price decreases and a decrease in demand when the price increases.
Why is the airline industry elastic?
The airline industry is elastic because it is a competitive industry. If one airline decides to increase the price of its fares, consumers can use another airline, and the airline that increased its fares will see a decrease in the demand for its services.
What is elastic in business?
Companies that operate in highly competitive industries offer products and services that are elastic, as the companies tend to be price-takers. When the price of a good or service has reached the point of elasticity, sellers and buyers quickly adjust their demand for that good or service.
What is unit elastic demand?
Unit-elastic demand is where the price elasticity of demand is 1. A unit-elastic demand means that the percentage change in quantity demand and percentage change in price are equal. The total revenue of a unit-elastic product remains the same because any change in price is exactly offset by a corresponding opposite change in quantity demanded.
When is demand considered elastic?
Demand is considered elastic when the absolute value of price elasticity of demand is higher than 1. It means that the percentage change is quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change price.
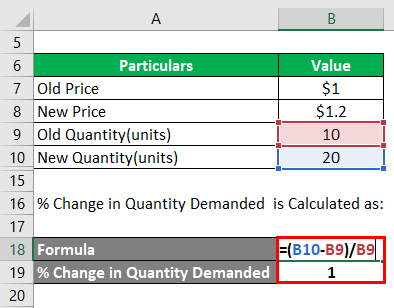
How to calculate price elasticity of demand?
It is calculated by dividing the percentage change in the quantity demanded by the percentage change in price. The percentage change is quantity demanded is calculated by dividing the difference between initial and final quantities by the average of both quantities. Similarly, percentage change in price equals the difference between final and initial price divided by the average of both prices.
What does it mean when demand is perfectly elastic?
Demand is perfectly-inelastic if it the quantity demanded doesn’t change regardless of any change in price. It means that the quantity demanded of such a product will not change in response to any change in its price. Perfectly-inelastic price elasticity is another extreme case and it is represented a vertical demand curve.
Why is the price elasticity quoted as an absolute number?
Because quantity demanded decreases with increase in price, the above equation generally gives us a negative number. The negative sign is generally ignored, and the price elasticity is quoted as an absolute number i.e. as a positive number.
What is the blue demand curve?
The blue demand curve on the chart above is a typical inelastic demand curve.
Why is price elasticity rare?
Right now i.e. in current economy, a perfectly-inelastic price elasticity rarely exists because most products have substitutes. Many life-savings drugs can exhibit close to perfectly-inelastic demand curves.
