The Federal Reserve sets the interest rates that banks charge each other for overnight loans to meet reserve requirements. This rate, the benchmark federal-funds rate, influences the interest that financial institutions charge consumers to make purchases such as homes and cars, and finance student loans and credit cards.
What does it mean when the Fed raises interest rates?
“ [H]igher rates mean consumers who save this year will yield more returns than last year, and any bit helps, especially with inflation at a 40-year high,” McCeary said. According to Discover, an online bank and payment service provider, when the Fed raises interest rates, banks may increase savings account interest rates, too.
How much is the Fed going to raise interest rates?
The Federal Reserve is expected to raise its benchmark interest rate by 0.25% next week to curb inflation, which is running at a 40-year high. Additional hikes are likely later this year.
Should the Fed raise interest rates?
With unemployment now at very low levels, the least that one might expect from the Fed is that it should raise interest rates to return U.S. financial conditions to a more normal and less...
Is fed increasing interest rates?
In a much-anticipated move, the Federal Reserve announced on March 16 it would be raising interest rates for the first time since 2018. Implementing an interest rate hike is one of the various...
See more

What does it mean when the Fed adjusts interest rates?
When the Fed wants to adjust interest rates, it moves the range set by IORB and ON RRP rates higher or lower. This causes the banks to raise or lower their interest rates correspondingly. In turn, these rates affect all other interest rates in the economy.
What happens when feds raise interest rates?
A Fed rate increase can slow the economy by pushing up borrowing rates and raising the annual percentage rate on savings. If rates rise, it becomes more costly to borrow money. When the Fed boosts its lending rate, consumers and businesses can see increased costs for borrowing, which can discourage spending.
How does increasing interest rates help?
When the base rate goes up, interest rates may go up. It then costs more to borrow money, but it also means you can earn more on your savings – so people may be encouraged to borrow less and save more. This reduces demand for certain goods and services, which could slow inflation down.
What is the foundation of interest rates?
The Federal Funds Rate could be considered the foundation of all interest rates. Changes to the Target Federal Funds Rate pass through to business and consumer loans—there is a lag of up to a year or more as the change works its way through the system. So when the Fed makes a change to the Target Federal Funds rate, they are really making an educated guess as to where interest rates in the economy need to be a year from now.
What is the purpose of the Fed?
Like most Central Banks, the Fed has many duties including conducting monetary policy and regulating banks. “Monetary policy” means controlling the supply of money. The goal of the Fed’s monetary policy is to keep inflation under control and keep unemployment low. When it appears that inflation is increasing, the Fed works to contract the money supply to cut off inflation. When it appears that the economy is losing steam and unemployment is going up, the Fed expands the supply of money to incentivize companies to invest and consumers to spend.
How does the Fed control the money supply?
This control of the money supply doesn’t happen through a magical amulet in Ben Bernanke’s pocket; instead it happens mainly through interest rates. By manipulating interest rates, the Fed exerts control over the money supply to achieve its intended purposes. It doesn’t always work as planned, given the scale and complexity of our economy, but for the most part it has proven effective.
What is the main tool of the Fed?
The Fed has several tools at its disposal. The main tool it uses is the setting of the Target Federal Funds Rate.
Do banks set interest rates?
Interest rates are not set by the laws of supply and demand. Each bank that has money to lend doesn’t independently set rates based on what the market will bear. At their core, the interest rates that we pay on borrowed money for our businesses are set by the Federal Reserve.
What Happens When the Fed Raises Rates?
When the Fed raises the federal funds target rate, the goal is to increase the cost of credit throughout the economy. Higher interest rates make loans more expensive for both businesses and consumers, and everyone ends up spending more on interest payments.
Why are variable rate loans sensitive to Fed rate changes?
Variable rate loans are particularly sensitive to Fed rate changes as the interest rates they charge are based on benchmarks that reference the fed funds rate. New fixed-rate loans can see higher interest rates, but existing ones are immune to changes to the fed funds rate.
How does higher interest rates affect the stock market?
Over time, higher costs and less business could mean lower revenues and earnings for public firms, potentially impacting their growth rate and their stock values.
How does the Fed affect the economy?
This (very) simplified example shows how the Fed reduces the amount of money in the economy when it raises rates. Besides mortgages, rising interest rates impact the stock and bond markets, credit cards, personal loans, student loans, auto loans and business loans.
Why do bonds decline in price?
To reflect the higher overall rates, existing bonds will decline in price to make their comparatively lower interest rate payments more appealing to investors.
What is the average of the many constantly fluctuating rates that emerges as banks negotiate what they’ll charge for these?
The average of the many constantly fluctuating rates that emerges as banks negotiate what they’ll charge for these loans is called the effective federal funds rate. This in turn impacts other market rates, like the prime rate and SOFR.
Why do online savings accounts react more rapidly to Fed rate changes?
Typically online savings accounts react more rapidly to Fed rate changes because there is much more competition among online banks for deposits. APYs offered by conventional brick-and-mortar banks respond much more slowly to rate increases and generally don’t get very high even in the best of times.
Why do consumers care about the Fed funds rate?
Most consumers care about the fed funds rate for one main reason: It influences how much they pay to borrow and how much they’re paid to save.
What is the federal funds rate?
When you read headlines saying the Fed has hiked or cut interest rates, they mean the Fed has voted to adjust its key borrowing rate, the fed funds rate.
Why is the IOER rate low?
That in turn lowers the cost of borrowing money in the economy because it increases the credit supply.
How much percentage point does the Fed adjust?
Officials normally adjust it incrementally by a quarter of a percentage point. But in more extreme circumstances, the Fed can modify it by a half a percentage point or more. The Fed reduced rates on March 15 by a full percentage point at an emergency meeting, an extraordinary attempt to soften the economic blow from the coronavirus pandemic.
How did the Fed influence the market?
Before, the Fed would influence market rates by increasing the supply of banks’ reserves to balance out supply and demand. Extra cash in banks’ accounts would lower market rates. Less would increase interest rates.
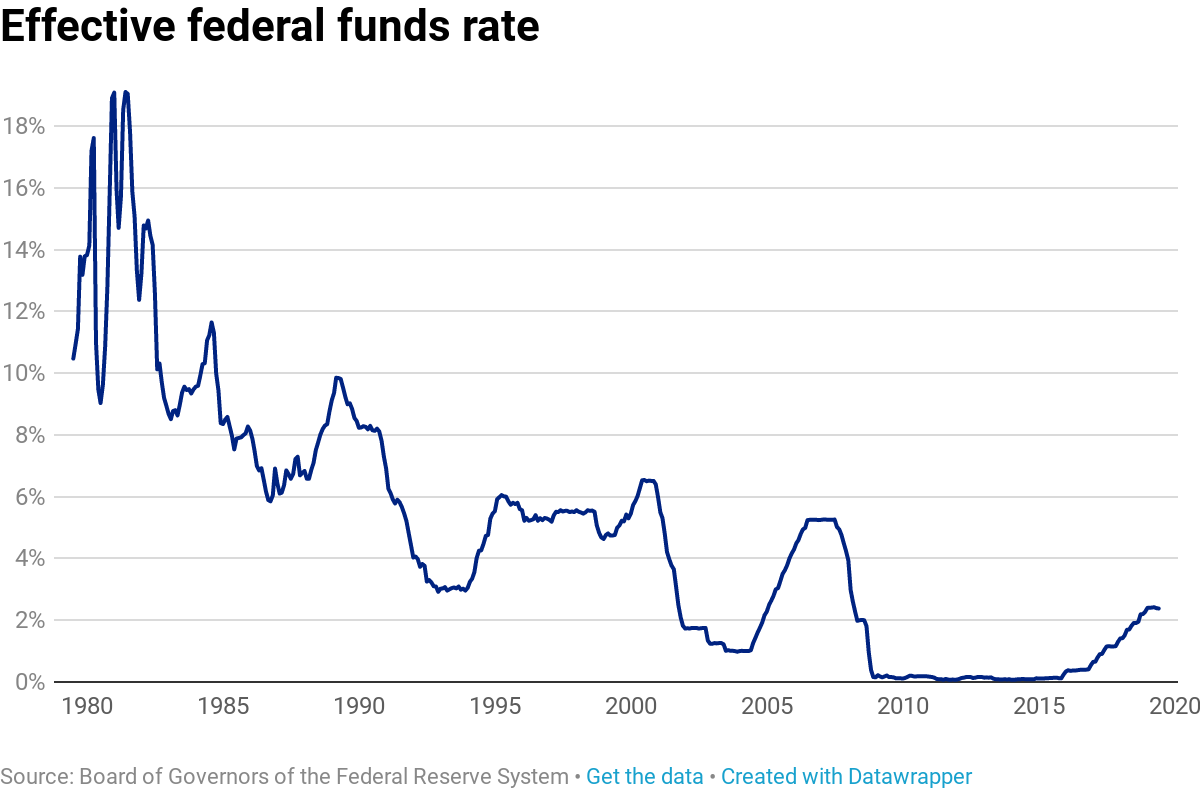
What was the Fed funds rate in the 1980s?
In the 1980s, the effective fed funds rate soared to as high as 19.10 percent, the highest it’s been, as officials worked to combat inflation. Back then, the fed funds rate was in a target range of 15-20 percent, a much wider band than is typical from the Fed.
Why do banks lend money to second banks?
One bank lends its extra cash to a second bank so it can meet those requirements, with the promise that those funds are paid back overnight. Of course, since no one wants to just lend freely, it comes with an interest rate. That’s where the fed funds rate comes in.
Why did the Fed cut the interest rate to zero?
Recently, there was a Fed rate cut down to near zero in anticipation of the financial crisis due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Interest rates change with the state of the country. The more stable the job market and the economy, the higher the Fed raises interest rates. This is because the system—and Americans—can support it.
What is the Federal Reserve?
First things first—what exactly is the Federal Reserve (aka the Fed)? Basically, the Federal Reserve System is the United States’ central bank. Its goal is to “promote the effective operation of the U.S. economy and, more generally, the public interest.”
What are the three goals of the Fed?
These actions are “to achieve three goals specified by Congress: maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates in the United States. ”. This means they can tweak how much credit is available in the economy and how much credit costs you. Banks are most directly affected by the Fed interest rate.
What is the Fed's job?
The Fed’s services help with transactions and their research analyzes consumer issues and trends. They even delve into community economic development activities and administer consumer laws and regulations.
Do savings accounts earn less when interest rates are low?
Interest-bearing savings accounts may earn less when Fed interest rates are low . On the flip side, when national interest rates are high, your credit card and loans (such as home, auto, and business), will likely go up as well.
Do banks have to keep money on reserve?
Banks legally have to keep a minimum portion of their customers’ money on reserve. Since they’re not allowed to earn interest on that amount, they lend it back and forth to other institutions to stay as close to that limit as possible. Learn more about how banks work.
Is the Federal Reserve the be all end all?
While the Federal interest rate is not the be-all-end-all of your financial well-being, it can have an effect on large and small aspects of your personal wealth. Stay up to date on changes to the Federal Reserve interest rates here.
Which central bank sets the interest rate?
If it is, then at the start of that chain, is the US's central bank, the Federal Reserve. The interest rate set by the Fed is the one to which almost every other interest rate in the world is linked.
What is the target rate for the Federal Funds Rate?
When the FOMC issues its statement it identifies a range for the federal funds rate. Currently it's between 1-1.25%.
What happens if you pay 1.25% interest on your mortgage?
If your bank has to pay 1.25% interest on the money it needs to keep its reserve funds full, it's going to charge you a higher rate on your mortgage in order to make a profit, or pay you a lower rate on your savings.
What are the reserves of the Federal Reserve?
Reserves are the money banks have to keep on hand in case too many people try to withdraw their money at the same time.
Can you get a higher rate of return by taking money out of the bank and putting it into the stock market?
If you're sure you can get a higher rate of return by taking your money out of the bank and putting it into the stock market then usually you will. In this way the entire US economy can be seen as one long chain of interest rates. If it is, then at the start of that chain, is the US's central bank, the Federal Reserve.
Do you pay interest on a car loan?
Do you pay interest? Probably. Anyone with a mortgage, a car loan, or a credit card does. Do you earn it? Again, it's very likely, if you've ever had money in a savings account.
How does the Fed influence interest rates?
The Fed heavily influences this rate using open market operations, the reserve requirement, and the discount rate. The Fed can also pay interest on bank reserves and purchase repos or reverse repos to fine-tune interest rates.
Why does the Fed lower its funds rate?
The member bank lowers its effective fed funds rate to lend extra reserves to other banks— as much as necessary to get rid of excess reserves. The bank would rather make a few cents lending the reserves than have reserves sitting on its ledger, earning nothing. To raise rates, the Fed takes the opposite steps.
What happens if the Fed lowers the Fed funds rate?
If the Fed wants to lower the fed funds rate, it takes securities out of the bank's reserves and replaces them with credit, which is like cash to a bank . Now, the bank has more than enough reserves to meet its requirement.
Why does the Fed buy securities?
The Fed buys massive amounts of securities from its member banks to keep Treasury yields low. In 2008, QE increased total assets to $2.2 trillion. In 2020, it topped $7.2 trillion. 7 8. When banks have plenty of funds, they don't have much incentive to borrow from each other to meet the reserve requirement.
What is the Federal Open Market Committee?
The Federal Reserve raises or lowers interest rates through the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). The Committee conducts open market operations for the Federal Reserve System. After reviewing current economic data, the FOMC sets a target for the fed funds rate at one of its eight meetings.
Why do banks use Fed funds?
Banks use the fed funds to meet the reserve requirement each night. The actual rate that banks set is called the effective fed funds rate. The Fed can only set a target for the fed funds rate as banks are private businesses that can set any rate they wish.
What is the term for funds kept in reserve?
Funds kept in reserve are called federal funds. Banks charge interest rates when giving other banks overnight loans from these funds. The Fed sets a target range for the fed funds rate by setting the upper and lower limits, which banks then base their loans off. The Fed averages the interest rate banks charge each other overnight—this is the effective federal funds rate.
What was the key policy interest rate used by the Fed?
Up until the financial crisis, the key policy interest rate used by the Fed was the federal funds rate. This is the rate banks charge each other for short-term (overnight, unsecured) loans. The Fed does not set this rate. Supply and demand in the market for bank reserves does. The Fed can increase or decrease the amount ...
How does the Fed affect the Fed funds rate?
The Fed can increase or decrease the amount of reserves in the banking system, thereby affecting the fed funds rate. However, it isn’t setting anything. The Fed influences a market rate by acting within the market. It buys or sells assets, which changes liquidity conditions in that market.
How is the Fed constrained?
Economically, the Fed is constrained here, too, by a combination of political and economic forces. Set the rate on excess reserves too low, and banks that keep their money at the Fed will find it more lucrative to put those funds to work, financing real economic activity .
What is monetary policy?
Monetary policy is about money. Good monetary policy adjust s the quantity of money supplied to meet changes in the demand to hold it. Effects on interest rates take a back seat. In econ-speak, we’d say interest rates aren’t the relevant transmission mechanism for monetary policy.
What is the key error in the “monetary policy is about interest rates” paradigm?
The key error in the “monetary policy is about interest rates” paradigm is that it confuses instruments and targets. An instrument is something the Fed controls. A target is what it’s trying to achieve. The financial press writes about interest rates as if they’re an instrument, when in reality they’re a target.
Does the Fed set the excess reserves rate?
Interest on excess reserves isn’t determined in a market. It’s determined by the Fed itself, similarly to the discount rate, which is the rate for borrowing directly from the Fed. So: Does the Fed set the excess reserves rate? Yes and no. Administratively, the Fed can hypothetically make this rate whatever it wants. Economically, the Fed is constrained here, too, by a combination of political and economic forces.
Does the Fed determine interest rates?
Wait, what? It is a basic truism of financial journalism that the Fed determines rates from on high. From the Wall Street Journal to the New York Times, central-bank control over interest rates is so thoroughly accepted that it’s hard even to think about things any other way.
