
Symptoms
Overview. Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea — the clear, dome-shaped tissue on the front of your eye that covers the pupil and iris. Keratitis may or may not be associated with an infection. Noninfectious keratitis can be caused by a relatively minor injury, by wearing your contact lenses too long or by a foreign body in the eye.
Causes
Any suspected symptoms of keratitis should be looked at right away. Your doctor can help make a diagnosis so that you can receive treatments before any complications arise. To diagnose keratitis, your doctor will first talk to you about the history of your symptoms and then look at your eyes.
Prevention
Basics of HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus) Keratitis. The infection usually heals without damaging the eye, but more severe infections can lead to scarring of the cornea or blindness. HSV keratitis is a major cause of blindness worldwide 1. HSV-1, which is the type of HSV that also causes cold sores on the mouth, is the most common cause...
Complications
Although less common, keratitis is more likely to have an impact on vision because it affects the cornea. Symptom of keratitis include blurred vision and light sensitivity, though some people with pink eye experience those symptoms as well. Although both are uncomfortable, keratitis tends to be more painful.
What is keratitis in eye?
How do I know if I have keratitis?
What are the basics of HSV keratitis?
What is the difference between keratitis and pink eye?
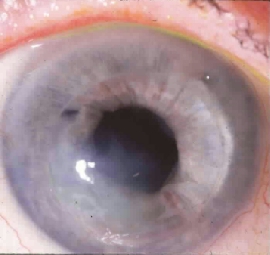
How do you know if you have keratitis?
Signs and symptoms of keratitis include:Eye redness.Eye pain.Excess tears or other discharge from your eye.Difficulty opening your eyelid because of pain or irritation.Blurred vision.Decreased vision.Sensitivity to light (photophobia)A feeling that something is in your eye.
Does keratitis go away by itself?
A very mild case of noninfectious keratitis will usually heal on its own. For mild cases, your eye doctor may recommend that you use artificial tear drops. If your case is more severe and includes tearing and pain, you may need to use antibiotic eye drops to help with symptoms and prevent infection.
Is keratitis serious?
Keratitis is usually easy to treat and clears up quickly. But if an infection goes deeper than the surface of your cornea, it can leave scars that damage your vision or even cause blindness.
How long does keratitis last?
In cases of keratitis caused due to bacterial, fungal, parasitic or viral infection, the situation starts improving within the first 28 to 48 hours of treatment. After that the inflammation of the cornea gradually goes away within a few days.
What is the best treatment for keratitis?
For mild bacterial keratitis, antibacterial eyedrops may be all you need to effectively treat the infection. If the infection is moderate to severe, you may need to take oral antibiotics to get rid of the infection.
What eye drops are used for keratitis?
The recommended fortified antibiotic combination for bacterial keratitis is gentamicin or tobramycin (9-14 mg/mL), together with cefazolin (50 mg/mL), to ensure coverage against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
When should I go to the doctor for keratitis?
Infectious keratitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. If you have eye redness or other symptoms of keratitis, make an appointment to see your doctor. With prompt attention, mild to moderate cases of keratitis can usually be effectively treated without loss of vision.
Does keratitis affect both eyes?
Keratitis may affect one eye or both eyes. Keratitis may be mild, moderate, or severe and may be associated with inflammation of other parts of the eye. Keratoconjunctivitis is inflammation of both cornea and the conjunctiva.
Can dry eyes cause keratitis?
Causes of Keratitis Keratitis has a number of different potential causes, including dry eyes, infection, chemical or physical injury, and the onset of underlying illnesses or medical conditions. Some of the most common causes of keratitis include: Dry Eye.
How is keratitis transmitted?
Keratitis may be transmitted through an infection. This can happen if you come into contact with an infectious substance and then touch your eyes. It can also occur if you get sick and then the infection spreads to your eyes. In some cases, you can even transmit keratitis to yourself.
What bacteria causes keratitis?
About 80 % of bacterial keratitis is caused by Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Pseudomonas species, though prevalence can depend on geographical regions. Certain bacteria are known to penetrate the intact epithelium which include Neisseria, Corynebacterium, Shigella and Listeria.
Do you need surgery for keratitis?
In summary, infectious keratitis often needs surgical intervention to control the infection and maintain structural integrity. The type of surgical intervention performed depends on the location, size and etiology of the infection and must be adapted to the individual patient's needs.
How long does bacterial keratitis take to heal?
In conclusion, persons with bacterial keratitis experienced marked improvement in visual acuity in the first 3 months after starting treatment, and experienced a smaller but still significant improvement in vision from 3 to 12 months after starting treatment.
Does keratitis affect both eyes?
Keratitis may affect one eye or both eyes. Keratitis may be mild, moderate, or severe and may be associated with inflammation of other parts of the eye. Keratoconjunctivitis is inflammation of both cornea and the conjunctiva.
Can keratitis blur vision?
Decreased vision, often described as blurry or hazy, is a frequent complaint of patients with keratitis. When inflammation affects the front surface of the cornea, it is usually associated with tremendous sharp pain and light sensitivity, sometimes along with redness and tearing.
Do you need surgery for keratitis?
In summary, infectious keratitis often needs surgical intervention to control the infection and maintain structural integrity. The type of surgical intervention performed depends on the location, size and etiology of the infection and must be adapted to the individual patient's needs.
How do you know if you have keratitis?
Signs and symptoms of keratitis include: Eye redness. Eye pain. Excess tears or other discharge from your eye. Difficulty opening your eyelid because of pain or irritation. Blurred vision. Decreased vision. Sensitivity to light (photophobia) A feeling that something is in your eye.
What is keratitis in the eye?
Overview. Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea — the clear, dome-shaped tissue on the front of your eye that covers the pupil and iris. Keratitis may or may not be associated with an infection. Noninfectious keratitis can be caused by a relatively minor injury, by wearing your contact lenses too long or by a foreign body in the eye.
What causes keratitis on the cornea?
Causes. Causes of keratitis include: Injury. If any object scratches or injures the surface of your cornea, noninfectious keratitis may result. In addition, an injury may allow microorganisms to gain access to the damaged cornea, causing infectious keratitis. Contaminated contact lenses.
What causes keratitis in a gonorrhea patient?
Bacteria. The bacterium that causes gonorrhea can cause keratitis.
What happens if you have a damaged cornea?
Eye injury. If one of your corneas has been damaged from an injury in the past, you may be more vulnerable to developing keratitis.
How to prevent keratitis?
Caring for your contact lenses. If you wear contact lenses, proper use, cleaning and disinfecting can help prevent keratitis. Follow these tips: Choose daily wear contacts, and take them out before going to sleep. Wash, rinse and dry your hands thoroughly before handling your contacts.
Can keratitis cause eye redness?
Infectious keratitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. If you have eye redness or other symptoms of keratitis, make an appointment to see your doctor. With prompt attention, mild to moderate cases of keratitis can usually be effectively treated without loss of vision. If left untreated, or if an infection is severe, keratitis ...
How to prevent keratitis?
The best way to prevent keratitis is to look out for symptoms such as eye redness, pain, discomfort and change in vision. Contact lens hygiene is also essential to prevention. “If you wear contacts, it’s so important to follow the proper steps to clean and disinfect your lenses and change them out when needed," says Liu. "This prevents bacteria and other unsanitary bodies from infecting your eyes.”
Can a doctor diagnose keratitis?
Your eye doctor can diagnosis keratitis during an exam. In some cases, a sample of the corneal surface using a cotton swap, or a biopsy, may be needed.
How many types of keratitis are there?
Keratitis is divided into two main types:
What is infectious keratitis?
Also known as microbial keratitis, infectious keratitis is caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites.
What Causes Keratitis?
Keratitis has many potential causes. The common causes include the following:
What is the inflammation of the cornea?
Keratitis is the inflammation of the cornea (the clear outer layer of the eye that focuses light).
What causes swelling in the center of the cornea?
Disciform keratitis. Associated with herpes simplex virus (HSV) and causes swelling in the center of the cornea.
What is the condition that causes dry eyes?
Filamentary keratitis. This condition is associated with corneal swelling and dry eyes. It's characterized by strands made up of epithelial cells and mucus on the surface of the cornea.
What is the cause of bacterial keratitis?
Bacterial keratitis. Caused by bacteria, this form of keratitis occurs mainly due to improper and unhygienic use of contact lenses. The two types of bacteria associated with bacterial keratitis are Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.3

Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea — the clear, dome-shaped tissue on the front of your eye that covers the pupil and iris. Keratitis may or may not be associated with an infection. Noninfectious keratitis can be caused by a relatively minor injury, by wearing your contact lenses too long or by a foreign body in the eye. Infectious keratiti...
Prevention
- Signs and symptoms of keratitis include: 1. Eye redness 2. Eye pain 3. Excess tears or other discharge from your eye 4. Difficulty opening your eyelid because of pain or irritation 5. Blurred vision 6. Decreased vision 7. Sensitivity to light (photophobia) 8. A feeling that something is in your eye