
What star has the highest luminosity?
What stars have the highest luminosity? Hot blue stars, over 30,000 Kelvin, at left; and cool red stars, less than 3,000 Kelvin, at right. The most luminous stars – over 1,000,000 solar – are at top, and the least luminous stars – 1/10,000 solar – at bottom. Astronomers call the true, intrinsic brightness of a star its luminosity.
What is the equation for luminosity?
What is the luminosity distance formula? More generally, the luminosity, apparent flux, and distance are related by the equation f = L/4`pi’d2. If we measure a star’s parallax and its apparent brightness, we can determine its luminosity, which is an important intrinsic property.
What is the relationship between luminosity and mass?
mass-luminosity relation, in astronomy, law stating that the luminosity of a star is proportional to some power of the mass of the star. More massive stars are in general more luminous. This means that if the mass is doubled, the luminosity increases more than tenfold.
What is the luminosity scale?
Luminosity is the total energy emitted by a star per second - measured in Joules per second (also known as Watts). The Absolute Magnitude is the 'brightness' of a star seen from 10 parsecs away. The apparent magnitude is the 'brightness' of the star as seen from Earth. Luminosity is the straightforward way of saying how bright something is.
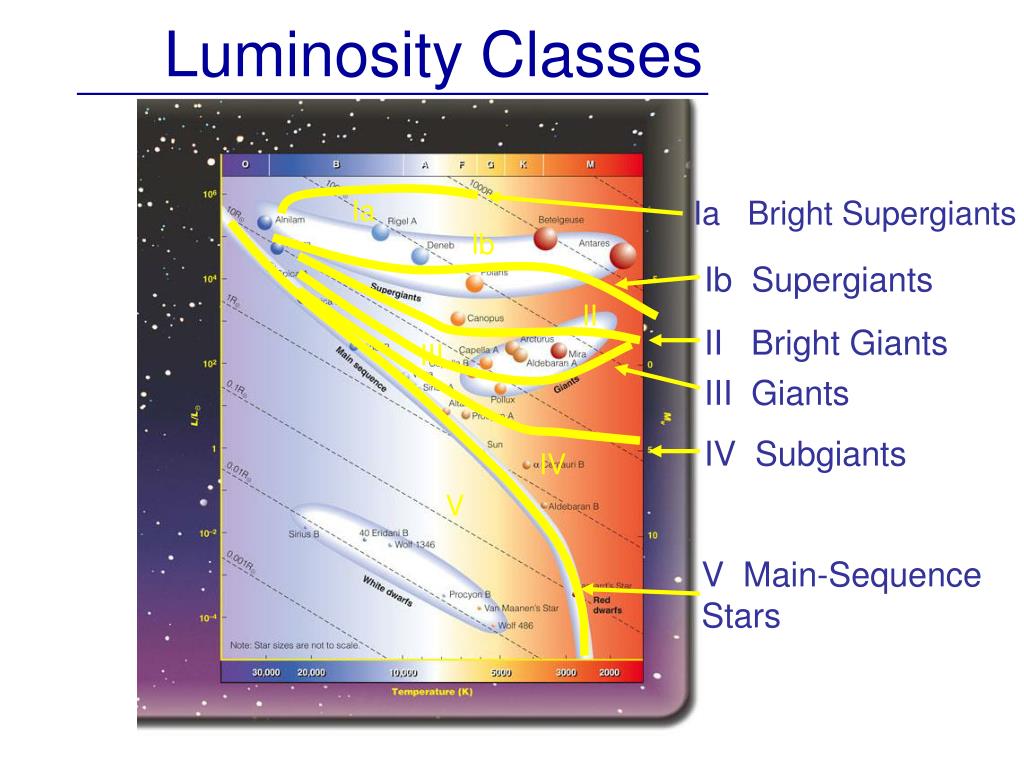
What does the luminosity class of a star tells an astronomer?
Luminosity, L, is a measure of the total amount of energy radiated by a star or other celestial object per second. This is therefore the power output of a star. A star's power output across all wavelengths is called its bolometric luminosity.
What is a luminosity class?
luminosity class in American English Astronomy. a classification of stars of a given spectral type according to their luminosity, breaking them down into dwarfs, giants, and supergiants.
Why is the luminosity important?
The luminosity that matters when it comes to understanding what's powering an object, from stars to quasars, is the intrinsic luminosity. That's a measure of the amount of energy it actually emits in all directions each second regardless of where it lies in the universe.
What physical property of a star does the luminosity class describe?
The luminosity class designation describes the size (gravitational acceleration in photosphere) of a star from the atmospheric pressure.
Which luminosity class is the most luminous?
Ia-0The most luminous stars knownIbLuminous SupergiantsIIBright GiantsIIIGiantsIVSubgiants4 more rows
Why did Scientist create the MK luminosity class?
In other words, it cannot distinguish between main sequence (dwarf) stars, giant stars and supergiant stars. For this reason, the Morgan-Keenan luminosity class (MK or MKK) was established.
What is the relationship between star size and luminosity?
As the size of a star increases, luminosity increases. If you think about it, a larger star has more surface area. That increased surface area allows more light and energy to be given off. Temperature also affects a star's luminosity.
How does luminosity relate to energy?
LUMINOSITY is the amount of energy an object gives off per unit time. This quantity is often given in units of joules/second, otherwise known as Watts (W). This is the same unit that's used in electric circuits, but in the form of radiated energy rather than electric power.
What is luminosity related to?
The luminosity of an object is a measure of its intrinsic brightness and is defined as the amount of energy the object emits in a fixed time. It is essentially the power output of the object and, as such, it can be measured in units such as Watts.
What is the relationship between luminosity and temperature?
" The Luminosity of a star is proportional to its Effective Temperature to the 4th power and its Radius squared."
What is the relationship between star temperature and luminosity in the main sequence?
The greater the mass of a main sequence star, the greater its effective temperature. This, combined with the larger radius of higher mass main sequence stars accounts for their much greater luminosity. Remember, L ∝ T4 and L ∝ R2 so even a small increase in effective temperature will significantly increase luminosity.
What is the difference between brightness and luminosity?
When I say apparent brightness, I mean how bright the star appears to a detector here on Earth. The luminosity of a star, on the other hand, is the amount of light it emits from its surface. The difference between luminosity and apparent brightness depends on distance.
What are the classes of stars?
The classes are called O, B, A, F, G, K and M. Stars in the 'O' class are the most massive and hottest, with temperatures above 30,000 °C. Stars in the 'M' class are the smallest and coolest, with temperatures below 3,000 °C. If you look closely at stars in the sky, you notice they are not all the same colour.
What objects are in luminosity class V?
Type V stars are like the Sun, dwarf or Main Sequence stars, which are fainter than the larger stars.
Which of the following luminosity classes refers to red giants?
Red supergiants (RSGs) are stars with a supergiant luminosity class (Yerkes class I) of spectral type K or M. They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of volume, although they are not the most massive or luminous.
Which luminosity class is a rare group of giant stars?
II: Bright Giants - This is a relatively rare group of giant stars that are very luminous.
Which type of stars are the brightest?
For stars of a given temperature, narrow lines correlate with low pressure atmospheres, large stellar radii, and hence a high luminosity: Type Ia, therefore, are the brightest supergiant stars, and type Ib are the fainter supergiants. Type III stars are still large stars of intermediate brightness, and are termed giants.
What is the second classification of stellar spectra?
A second classification of stellar spectra therefore may be done on the basis of the appearance of the absorption lines, with the narrowest line spectra designated I (subdivided into Ia and Ib) through types II, III, and IV, to V, the broadest line spectra.
How does the pressure of a star affect its absorption?
The gas pressure in the photospheric layer of a star can also affect the way absorption features appear. If the pressure is low (as would be the case in the atmosphere of a supergiant star due to the large size giving it a low surface gravity), the atoms absorb at the specific wavelengths set by their internal atomic energy levels.
What are the luminosity classes of stars?
Luminosity classes are labeled with Roman numerals from I to V: I are supergiant stars, II are bright giants, III are ordinary giants, IV are subgiants, and V are ordinary main sequence stars. The complete spectral classification for a star is then given by specifying both the spectral class and the luminosity class.
What is luminance class?
Luminosity classes correspond to horizontal and diagonal bands on the HR diagram that are related to the size of a star. This somewhat qualitative classification is exhibited in the adjacent table and in the HR diagram displayed below.
Is the luminosity of supergiants constant?
The luminosities within the giant and supergiant classes are relatively constant as a function of spectral class (they consist of almost horizontal lines on the HR diagram). However, note that luminosity class V (main sequence stars) covers a very large range of absolute brightness, since blue main sequence stars are much brighter ...
What happens to the brightness of a light when you double the distance from a source?
If you double the distance from a source of light, that lights brightness will decrease by a factor of 4.
Why do less massive stars have longer lifetimes?
Less massive star have longer lifetimes because they are burning the hydrogen in their cores at a slower rate than more massive stars.
Why does the spectral sequence have the order it goes?
The spectral sequence has the order it goes because it was originally classified in a different more alphabetical order based on the strength of the hydrogen lines, but the order was wrong and was rearranged to be correct into the current one. Another woman redid it and found some categories could be gotten rid of and that they fell into a natural order that was different from the original system.
What do spectral lines show?
Spectral lines can show if there are a lot of ionized elements in a star, which would indicate great heat. Stars with lots of molecules are relatively cool, otherwise the atoms wouldn't survive. O stars in the spectral sequence are the hottest and it decreases until you reach M stars, the coolest.
What is apparent magnitude?
Apparent magnitude is how bright it appears in the sky. Apparent magnitude is inversely related to apparent brightness. Absolute magnitude is what the apparent magnitude of a star would be if it was 10 parsecs from Earth.
How do astronomers measure parallax?
Astronomers can measure parallax by measuring the position of a nearby star very carefully with respect to more distant stars behind it, then measuring those distances again six months later when the Earth is on the opposite side of its orbit. The shift is tiny... less than an arcsecond even for the nearest star. It was not until telescopes were invented that astronomers could measure parallaxes at all accurately.
