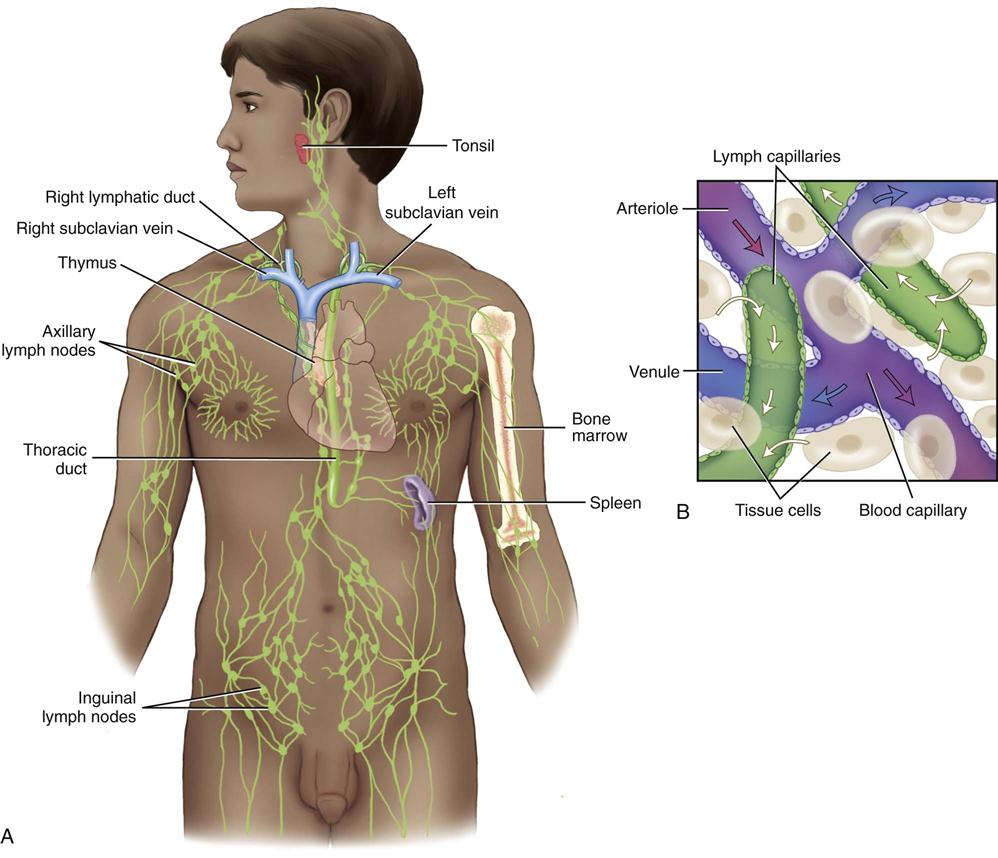
Lymph is a fluid that circulates throughout the body in the lymphatic system. It forms when tissue fluids/blood plasma (mostly water, with proteins and other dissolved substances) drain into the lymphatic system. It contains a high number of lymphocytes (white cells that fight infection).
What diseases are caused by the lymphatic system?
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) – destroys the myelin sheaths of the brain and spinal cord
- Myasthenia gravis – impairs communication between nerves and skeletal muscles; as a result, muscles are weakened (drooping eyelids, difficulty in swallowing, talking, overall muscle fatigue)
- Type 1 diabetes – destroys pancreatic Beta cells that produce insulin
How does lymph move through the lymphatic system?
The lymph is moved through the body in its own vessels making a one-way journey from the interstitial spaces to the subclavian veins at the base of the neck. Since the lymphatic system does not have a heart to pump it, its upward movement depends on the motions of the muscle and joint pumps.
What are the main organs of lymphatic system?
- The thymus: The thymus is located in the thoracic cavity, just under the neck. ...
- The spleen: The spleen is located in the upper-left part of the abdomen. ...
- The tonsils: The tonsils are masses of lymphoid tissue found in the back of the throat and nasal cavity. ...
What is major role of the lymphatic system in your bodies?
The lymphatic system is a network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste and other unwanted materials. The primary function of the lymphatic system is to transport lymph, a fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells, throughout the body.
What is the lymphatic system?
News. The lymphatic system is part of the immune system. It also maintains fluid balance and plays a role in absorbing fats and fat-soluble nutrients. The lymphatic or lymph system involves an extensive network of vessels that passes through almost all our tissues to allow for the movement of a fluid called lymph.
How does the lymphatic system fight infection?
The lymphatic system produces white blood cells, known as lymphocytes. There are two types of lymphocyte, T cells and B cells. They both travel through the lymphatic system.
What do the tonsils do?
In the back of the mouth, there are tonsils. These produce lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, and antibodies.
Why do lymph nodes swell?
The “swollen glands,” that occur, for example, in the neck during a throat infection, are in fact enlarged lymph nodes.
How do lymph vessels work?
They work in a similar way to the blood vessels. The lymph vessels work with the veins to return fluid from the tissues. Unlike blood, the lymphatic fluid is not pumped but squeezed through the vessels when we use our muscles.
Why does the lymphatic system stop working?
The lymphatic system can stop working properly if nodes, ducts, vessels, or lymph tissues become blocked, infected, inflamed, or cancerous.
How long does it take for lymph nodes to swell?
However, medical advice should be sought if: 1 lymph nodes stay swollen for longer than 1 to 2 weeks 2 a swollen lymph node feels hard or fixed in place 3 swelling is accompanied by fever, night sweats, or unexplained weight loss
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
The functions of the lymphatic system complement the bloodstream functions, as it regulates the balance of fluids in the body and filters the pathogens from the blood . The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and organs that regulates the amount of fluid in the human body and defends it against infections.
How much lymph does the body produce?
lymph produced in the gastrointestinal system is rich in fats). A body of a healthy individual produces an average of 2 liters of lymph per day, but this amount can vary greatly in pathological conditions.
What is the smallest lymphatic vessel?
Lymphatic capillaries are the smallest lymphatic vessels that collect the interstitial fluid from the tissues. They are organized in networks called lymphatic plexuses. Plexuses converge to make larger lymphatic vessels that carry the lymph away from the tissues and into the bloodstream.
Why does the small intestine have a vast lymphatic drainage?
This is why the small intestine has a vast lymphatic drainage, as it is the site where the lipids and proteins are absorbed from during food digestion. The lymphatic organs house numerous immune system cells which surveil the content of the lymph as it flows toward the venous system.
How many lymph nodes are there in the human body?
axillary, pelvic, mediastinal lymph nodes ). An adult human has an average of 450 lymph nodes, most of which are located in the abdomen .
What is the fluid that is made up of plasma?
Lymph. Lymph is a clear, yellowish fluid present in most tissues of the body. It is created as a result of the filtration of the plasma. The plasma from the blood diffuses through the porous capillary wall into the tissues to deliver nutrients.
What are the capillaries that absorb nutrients from the small intestine called?
There are also special types of lymphatic capillaries called lacteals. These capillaries absorb nutrients from the small intestine .
What is the lymphatic system?
See Article History. Lymphatic system, a subsystem of the circulatory system in the vertebrate body that consists of a complex network of vessels, tissues, and organs. The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance in the body by collecting excess fluid and particulate matter from tissues and depositing them in the bloodstream.
What is the role of the lymphatic system in the immune system?
In addition to serving as a drainage network, the lymphatic system helps protect the body against infection by producing white blood cells called lymphocytes, which help rid the body of disease-causing microorganisms.
How does lymph travel through the body?
The fluid and proteinswithin the tissues begin their journey back to the bloodstream by passing into tiny lymphatic capillaries that infuse almost every tissue of the body. Only a few regions, including the epidermisof the skin, the mucous membranes, the bone marrow, and the central nervous system, are free of lymphatic capillaries, whereas regions such as the lungs, gut, genitourinary system, and dermisof the skin are densely packed with these vessels. Once within the lymphatic system, the extracellular fluid, which is now called lymph, drains into larger vessels called the lymphatics. These vessels converge to form one of two large vessels called lymphatic trunks, which are connected to veinsat the base of the neck. One of these trunks, the right lymphatic duct, drains the upper right portion of the body, returning lymph to the bloodstream via the right subclavian vein. The other trunk, the thoracic duct, drains the rest of the body into the left subclavian vein. Lymph is transported along the system of vessels by musclecontractions, and valves prevent lymph from flowing backward. The lymphatic vessels are punctuated at intervals by small masses of lymph tissue, called lymph nodes, that remove foreign materials such as infectious microorganisms from the lymph filtering through them.
Why is the lymphoid organ important?
The importance of the primary lymphoid organs is demonstrated by its involvement in autoimmune disease. Two autoimmune diseases, DiGeorge syndrome and Nezelof disease, result in the failure of the thymus to develop and in the subsequent reduction in T cell numbers, and removal of the bursa from chickens results in a decrease in B cell counts.
What system removes fluid from tissues?
The lymphatic system removes this fluid and these materials from tissues, returning them via the lymphatic vessels to the bloodstream. The lymphatic system also helps defend the body against infection. Read more about the circulatory system.
Which organs are the major sites of differentiation and proliferation?
The organs and tissues of the lymphatic system are the major sites of production, differentiation, and proliferation of two types of lymphocytes—the T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes, also called T cells and B cells, respectively. Although lymphocytes are distributed throughout the body, it is within the lymphatic system that they are most likely ...
How does bone marrow affect the immune system?
The destruction of bone marrow also has devastating effects on the immune system, not only because of its role as the site of B cell development but also because it is the source of the stem cells that are the precursors for lymphocyte differentiation. Read more below: Diseases of the lymphatic system.
What is the lymphatic system?
Anatomical terminology. The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the circulatory system and the immune system. It is made up of a large network of lymph, lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the ...
What is lymphoid tissue?
Lymphoid tissue associated with the lymphatic system is concerned with immune functions in defending the body against infections and the spread of tumours. It consists of connective tissue formed of reticular fibers, with various types of leukocytes (white blood cells), mostly lymphocytes enmeshed in it, through which the lymph passes. Regions of the lymphoid tissue that are densely packed with lymphocytes are known as lymphoid follicles. Lymphoid tissue can either be structurally well organized as lymph nodes or may consist of loosely organized lymphoid follicles known as the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT).
How does blood flow into the body?
Fluid from circulating blood leaks into the tissues of the body by capillary action, carrying nutrients to the cells. The fluid bathes the tissues as interstitial fluid, collecting waste products, bacteria, and damaged cells, and then drains as lymph into the lymphatic capillaries and lymphatic vessels.
What is lymph node?
A lymph node showing afferent and efferent lymphatic vessels. Regional lymph nodes. A lymph node is an organized collection of lymphoid tissue, through which the lymph passes on its way back to the blood. Lymph nodes are located at intervals along the lymphatic system.
How much plasma is filtered in the circulatory system?
The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered plasma is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid.
Why is lymphatic drainage important?
The study of lymphatic drainage of various organs is important in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of cancer. The lymphatic system, because of its closeness to many tissues of the body, is responsible for carrying cancerous cells between the various parts of the body in a process called metastasis.
What are the functions of the spleen?
The main functions of the spleen are: 1 to produce immune cells to fight antigens 2 to remove particulate matter and aged blood cells, mainly red blood cells 3 to produce blood cells during fetal life.
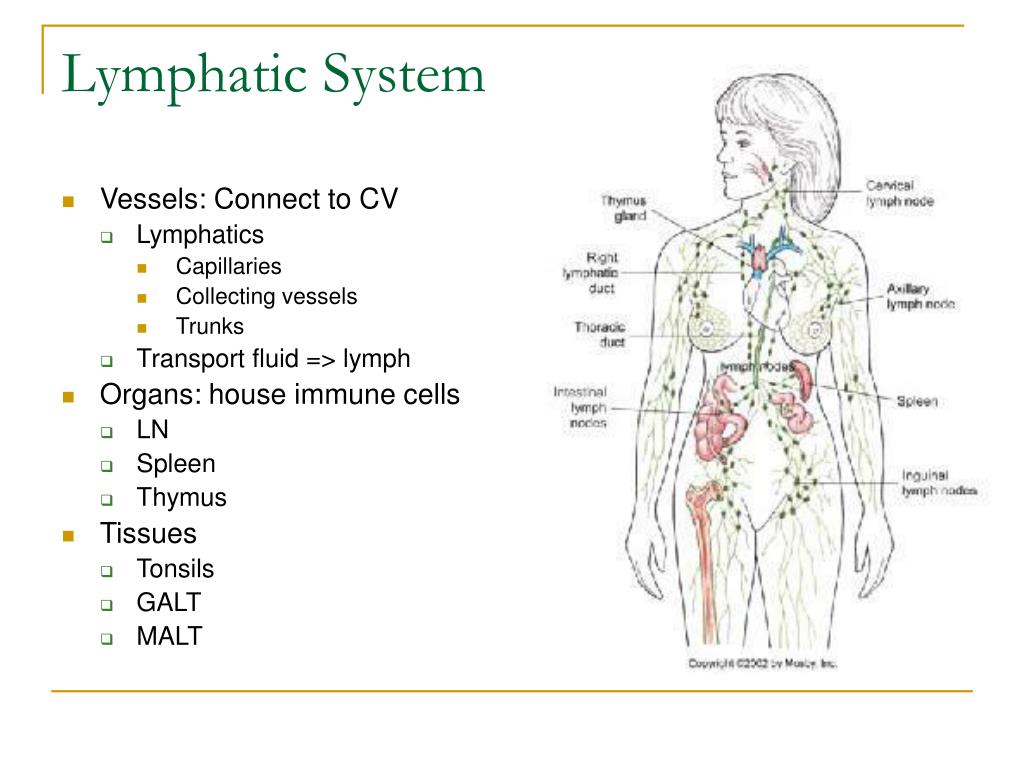
What are the components of the lymphatic system?
Components of the Lymphatic System. The lymphatic system consists of a fluid ( lymph ), vessels that transport the lymph, and organs that contain lymphoid tissue.
Where are lymphatic vessels found?
Lymph capillaries are found in all regions of the body except the bone marrow, central nervous system, and tissues, such as the epidermis, that lack blood vessels .
What is the wall of the lymph capillary?
The wall of the lymph capillary is composed of endothelium in which the simple squamous cells overlap to form a simple one-way valve. This arrangement permits fluid to enter the capillary but prevents lymph from leaving the vessel. The microscopic lymph capillaries merge to form lymphatic vessels. Small lymphatic vessels join to form larger ...
Where do lymphocytes come from?
The lymphocytes originate in the red bone marrow with other types of blood cells and are carried in the blood from the bone marrow to the lymphatic organs. When the body is exposed to microorganisms and other foreign substances, the lymphocytes proliferate within the lymphatic organs and are sent in the blood to the site of the invasion.
Why do lymphatic tributaries have thin walls?
Like veins, the lymphatic tributaries have thin walls and have valves to prevent backflow of blood. There is no pump in the lymphatic system like the heart in the cardiovascular system. The pressure gradients to move lymph through the vessels come from the skeletal muscle action, respiratory movement, and contraction of smooth muscle in vessel ...
What is the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system helps protect us from infection and disease. It is part of the body’s immune system. Lymph fluid passes through lymph nodes. A network of lymph vessels connects the lymph nodes together. You have nodes throughout your body.
What is the function of lymph fluid?
The lymph fluid carries the waste products and destroyed bacteria back into the bloodstream. The liver or kidneys then remove these from the blood. The body passes them out with other body waste, through bowel movements (poo) or urine (pee).
What do lymph nodes do?
The nodes act as a filter. They trap or destroy anything harmful that the body does not need. Inside the lymph nodes are white blood cells, also called lymphocytes. These white blood cells attack and break down bacteria, viruses, damaged cells or cancer cells.
Why do lymph nodes swell?
If there is cancer in the lymph nodes, they may swell, but are usually painless. There are different causes of swollen lymph nodes. But if you notice a painless, swollen lymph node, it is important to get it checked by your GP.
What system protects us from infection?
The lymphatic system . The lymphatic system helps protect us from infection and disease. Sometimes cancer cells can travel through lymph fluid to other parts of the body.
How many lymph nodes are there in the armpit?
Different parts of the body have different numbers of nodes. For example, there are about 15 to 30 small nodes in the armpit. Print page.
Where are lymph nodes located?
There are lymph nodes throughout your body, but mainly in the neck, armpits, groin and tummy (abdomen). They filter and break down bacteria (germs) or other harmful cells from the lymph fluid. Lymph nodes vary in size. Some are as small as a pinhead, and others are about the size of a baked bean.
Which organs are related to the lymphatic system?
The spleen (the organ just above the stomach's left side that filters our blood) Lymphokines (a chemical made from white cells) Gastrointestinal (stomach and intestines) lymph areas. Bone marrow (the spongy center of the bones) Immunoglobulins (proteins that help the body fight infection) The lymphatic system is closely related to ...
What are the different types of lymphocytes?
There are three main types of lymphocytes: 1 B lymphocytes (B cells) make antibodies in response to invading bacteria, viruses or other microbes. B lymphocytes are present in the marrow. 2 T lymphocytes (T cells) have several functions, including helping B lymphocytes make antibodies against invading microbes. An antibody works by attaching itself to an invading microbe. The white cell recognizes the antibody and pulls it into the cell with the attached microbe. The white cell can then kill the microbe. 3 Natural killer (NK) cells attack virus-infected cells without requiring an antibody or other assistance.
How do T lymphocytes work?
T lymphocytes (T cells) have several functions, including helping B lymphocytes make antibodies against invading microbes. An antibody works by attaching itself to an invading microbe. The white cell recognizes the antibody and pulls it into the cell with the attached microbe. The white cell can then kill the microbe.
What is the fluid that moves around the body?
Lymphatic vessels connect lymph nodes throughout our bodies. The lymphatic vessels collect into large ducts, which empty into blood vessels. Lymphocytes enter the blood through these ducts.
What type of cells make antibodies?
Lymphocytes enter the blood through these ducts. There are three main types of lymphocytes: B lymphocytes (B cells) make antibodies in response to invading bacteria, viruses or other microbes. B lymphocytes are present in the marrow.
Where are white cells found?
White cells called lymphocytes are found in the lymph nodes (small oval-shaped organs found throughout the body that help trap and kill disease and infection that invade our bodies). Lymphocytes are also found in other parts of the lymphatic system, such as the skin, spleen, tonsils and adenoids, intestinal lining, ...
What is the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system includes a network of vessels, ducts, and nodes, as well as organs and diffuse tissue that support the circulatory system. These structures help to filter harmful substances from the bloodstream. Organs of the lymphatic system, such as the spleen, thymus, and tonsils, house specialized cells that destroy the harmful pathogens. ...
What are the two parts of the lymphatic system?
1. The Lymphatic System Consists of Two Main Parts: The Vessel Network and the Nodes and Organs . Lymphatic vessels and ducts provide the complex transportation network of the lymphatic system. These vessels carry a fluid called lymph away from body tissues and capillary beds to be filtered by nodes and organs, then returned to the bloodstream.
Why do nodes have lymphocytes?
Node lymphocytes can enter the lymph vessels in order to eliminate pathogens. 2. Lymph Organs Filter Unwanted Substances Out of the Bloodstream and Body Tissues. Lymph derives from interstitial fluid that surrounds the cells of body tissues. This interstitial fluid comes from the bloodstream, as capillaries exchange substances with tissue cells ...
What is the function of white blood cells in the lymphatic system?
The white blood cells can destroy pathogens and remove some unwanted substances from the interstitial fluid as it flows toward lymphatic tissues and lymph nodes. Here, concentrations of white blood cells called lymphocytes are added.
How do lymph nodes work?
Substances are exchanged between the bloodstream and body cells through interstitial fluid. Part of this fluid enters the lymphatic vessel network as lymph and travels toward the lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped structures that help filter unwanted substances from lymph. They contain a high concentration of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that proliferates in the lymphatic system to combat pathogens. Groups of lymph nodes sit where the head and limbs meet the torso—at the axilla (armpit), groin, and neck—and in the intestinal region. During an infection, inflamed lymph nodes can sometimes be felt in these areas.
Where does filtered lymph go?
Filtered lymph then moves toward major lymphatic ducts—namely, the thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct, located at the junction between the subclavian and internal jugular veins. These ducts empty the filtered lymph into the veins to rejoin the bloodstream. See more from our free eBook library.
Where does interstitial fluid come from?
This interstitial fluid comes from the bloodstream, as capillaries exchange substances with tissue cells and fluid leaves the capillaries. Much of the fluid reenters the capillaries directly. The rest moves into lymphatic capillaries and vessels as lymph. Lymph is clear and colorless and contains white blood cells.