Additionally, a microscope for visual observation can be equipped with a digital camera, so it can be used in a similar manner as a digital microscope. Magnification is the ability of a microscope to produce an image of an object at a scale larger (or even smaller) than its actual size.
How do you calculate the magnification of a microscope?
On-Screen Magnification
- Firstly, you need to know the magnification of the microscope's objective lens. It is generally printed on the side of the lens. ...
- Now you have to locate the number written on the c-mount adapter. ...
- You have then to measure the diagonal of the screen of the monitor. ...
- Finally, you need to detect the size of the sensor camera present. ...
How to calculate total magnification?
Magnification Equation
- f is the focal length of the lens
- Do is the distance from the object to the lens
- Di is the distance from the lens to the in-focus projected image
How do you calculate the magnifying power of a microscope?
… Working out magnification:
- Measure the scale bar image (beside drawing) in mm.
- Convert to µm (multiply by 1000).
- Magnification = scale bar image divided by actual scale bar length (written on the scale bar).
What are the 5 types of microscopes and their uses?
Types of Microscopes
- The light microscope. ...
- objective. ...
- Other light microscopes. ...
- Electron microscopy. ...
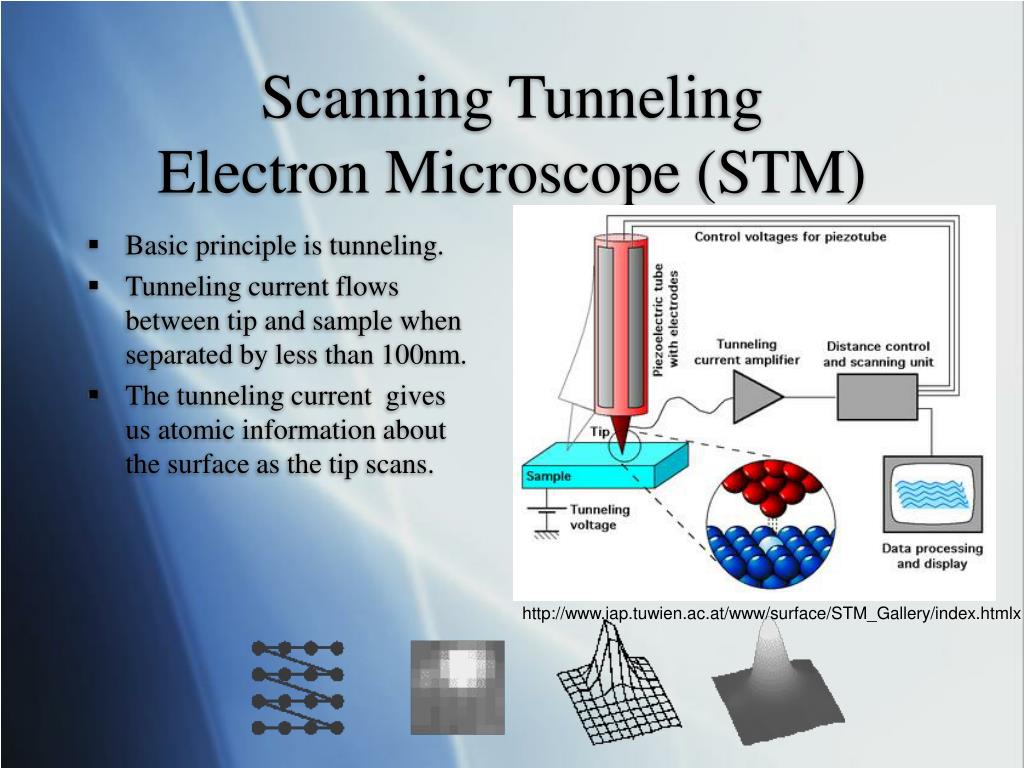
- scanning electron microscope (SEM) Although this microscope gives lower magnifications than the TEM, the SEM permits three‐dimensional views of microorganisms and other objects.
What does 1000x magnification mean?
At 1000x magnification you will be able to see 0.180mm, or 180 microns.
What is the total magnification at 4x 10x and 40x?
400xGrades 1-8 typically will buy a monocular compound microscope with 3 objective lenses: 4x, 10x, 40x for maximum total magnification of 400x.
What is a good magnification for a microscope?
How to choose a microscope? Answer these two questions: – Is standard 400x magnification okay, or do you need 1000x magnification to see greater cell detail? 400x is ideal for high school biology; 1000x is best for college microbiology.
What does 40x on a microscope mean?
A 40x objective makes things appear 40 times larger than they actually are. Comparing objective magnification is relative—a 40x objective makes things twice as big as a 20x objective while a 60x objective makes them six times larger than a 10x objective. The eyepiece in a typical desktop microscope is 10x.
What is 100x magnification?
The total magnification of a low power objective lens combined with a 10x eyepiece lens is 100x magnification, giving you a closer view of the slide than a scanning objective lens without getting too close for general viewing purposes.
What is the total magnification of 100x?
MagnificationTotal MagnificationScanning4x40xLow Power10x100xHigh Power40x400xOil Immersion100x1000xAug 1, 2021
What does 20x magnification mean?
x20 or 20x means it will appear 20 times larger than seen by the naked eye. – Adrian Howard. Dec 22, 2019 at 13:13. i've got a lot of lenses, none of them produce magnification with the factor written on it, i.e. X20 lens gives magnification about 2, X40 about 4 = they convert 1mm to 2 in the image, 1 to 4mm ...
What can you see at 2000X magnification?
With a limit of around 2000X magnification you can view bacteria, algae, protozoa and a variety of human/animal cells. Viruses, molecules and atoms are beyond the capabilities of today's compound microscopes and can be viewed only with an electron microscope.
What can you see with 10x magnification?
With 10x magnification and a larger aperture, you have excellent viewing capabilities for daytime and some low-light use. If you're looking 10 miles away with 10x magnification, you'll see that target as if it appears one mile away.
What is the difference between 4x 10X and 40x on a microscope?
For example, optical (light) microscopes are usually equipped with four objectives: 4x and 10x are low power objectives; 40x and 100õ are powerful ones.
What is the total magnification of 10X and 4x?
Total Magnification:To figure the total magnification of an image that you are viewing through the microscope is really quite simple. To get the total magnification take the power of the objective (4X, 10X, 40x) and multiply by the power of the eyepiece, usually 10X.Return To Top of Page11 more rows
What is 10X 40x magnification?
A microscope's total magnification is a combination of the eyepieces and the objective lens. For example, a biological microscope with 10x eyepieces and a 40x objective has 400x magnification.
What is the difference between 4x 10X and 40x on a microscope?
For example, optical (light) microscopes are usually equipped with four objectives: 4x and 10x are low power objectives; 40x and 100õ are powerful ones.
What is the total magnification of a 10X ocular and 40x high power objective lens?
Terms and DefinitionsObjective lens X Ocular lens =Total magnificationFor example:low power:(10X)(10X) = 100Xhigh dry:(40X)(10X) = 400Xoil immersion:(100X)(10X) = 1000X
How is total magnification calculated?
Total Magnification: To figure the total magnification of an image that you are viewing through the microscope is really quite simple. To get the total magnification take the power of the objective (4X, 10X, 40x) and multiply by the power of the eyepiece, usually 10X.
How do I calculate magnification?
0:152:36How to calculate magnification - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou must divide the image size by the actual size.MoreYou must divide the image size by the actual size.
What is Magnification in Microscope?
Magnification in a microscope refers to the amount or degree of visual enlargement of an observed object. Magnification is measured by multiples, such as 2X, 4X, and 10X, indicating that the object is enlarged to twice as big, four times as big, or 10 times as big, respectively.
How Is Total Magnification Calculated in Microscope?
The total magnification of a microscope is understood as the magnification of the objective lens multiplied by that of the optical lens.
What is a simple magnifying glass?
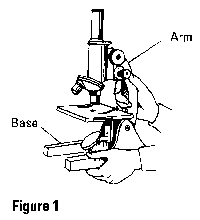
A simple microscope or magnifying glass ( lens) produces an image of the object upon which the microscope or magnifying glass is focused. Simple magnifier lenses are bi-convex, meaning they are thicker at the center than at the periphery as illustrated with the magnifier in Figure 1. The image is perceived by the eye as if it were at a distance ...
How does a microscope work?
Now we will describe how a microscope works in somewhat more detail. The first lens of a microscope is the one closest to the object being examined and, for this reason, is called the objective. Light from either an external or internal (within the microscope body) source is first passed through the substage condenser, which forms a well-defined light cone that is concentrated onto the object ( specimen ). Light passes through the specimen and into the objective (similar to the projection lens of the projector described above), which then projects a real, inverted, and magnified image of the specimen to a fixed plane within the microscope that is termed the intermediate image plane (illustrated in Figure 6). The objective has several major functions: 1 The objective must gather the light coming from each of the various parts or points of the specimen. 2 The objective must have the capacity to reconstitute the light coming from the various points of the specimen into the various corresponding points in the image (Sometimes called anti-points). 3 The objective must be constructed so that it will be focused close enough to the specimen so that it will project a magnified, real image up into the body tube.
How does an eyepiece work in a microscope?
In modern microscopes, the eyepiece is held into place by a shoulder on the top of the microscope observation tube, which keeps it from falling into the tube. The placement of the eyepiece is such that its eye (upper) lens further magnifies the real image projected by the objective. The eye of the observer sees this secondarily magnified image as if it were at a distance of 10 inches (25 centimeters) from the eye; hence this virtual image appears as if it were near the base of the microscope. The distance from the top of the microscope observation tube to the shoulder of the objective (where it fits into the nosepiece) is usually 160 mm in a finite tube length system. This is known as the mechanical tube length as discussed above. The eyepiece has several major functions:
Why are microscopes so efficient?
The primary reason that microscopes are so efficient at magnification is the two-stage enlargement that is achieved over such a short optical path, due to the short focal lengths of the optical components. Eyepieces, like objectives, are classified in terms of their ability to magnify the intermediate image.
How does an infinity corrected objective work?
For such objectives, the object or specimen is positioned at exactly the front focal plane of the objective . Light from such a lens emerges in parallel rays from every azimuth. In order to bring such rays to focus, the microscope body or the binocular observation head must incorporate a tube lens in the light path, between the objective and the eyepiece, designed to bring the image formed by the objective to focus at the plane of the fixed diaphragm of the eyepiece. The magnification of an infinity-corrected objective equals the focal length of the tube lens (for Olympus equipment this is 180mm, Nikon uses a focal length of 200mm; other manufacturers use other focal lengths) divided by the focal length of the objective lens in use. For example, a 10X infinity-corrected objective, in the Olympus series, would have a focal length of 18mm (180mm/10).
What is the object examined by the eyepiece?
The "object" examined by the eyepiece is the magnified, inverted, real image projected by the objective. When the human eye is placed above the eyepiece, the lens and cornea of the eye "look" at this secondarily magnified virtual image and see this virtual image as if it were 10 inches from the eye, near the base of the microscope.
How to understand a microscope?
An easy way to understand the microscope is by means of a comparison with a slide projector, a device familiar to most of us. Visualize a slide projector turned on its end with the lamp housing resting on a table. The light from the bulb passes through a condensing lens , and then through the transparency , and then through the projection lens onto a screen placed at right angles to the beam of light at a given distance from the projection lens. The real image on this screen emerges inverted (upside down and reversed) and magnified. If we were to take away the screen and instead use a magnifying glass to examine the real image in space, we could further enlarge the image, thus producing another or second-stage magnification.
What is the working distance of a microscope?
Other considerations: The working distance is the distance from the bottom of the microscope (lens) to the part of the specimen that is in focus. As you increase the magnification, you decrease the working distance. If you need to work under the microscope, you will need a large working distance.
What size object would fill up the whole viewing area at 10x?
This means that an object 20mm (2cm, or about 3/4 inch) wide would fill up the whole viewing area at 10x and an object about 6.7mm wide would fill up the whole area at 30x. As you can see, having the highest power may not be best for your particular application. When you move to greater magnifications, you sacrifice field of view.
Why is field of view important?
Field of View or Field Diameter is very important in microscopy as it is a more meaningful number than "magnification". Field diameter is simply the number of millimeters or micrometers you will see in your whole field of view when looking into the eyepiece lens. It is just as if you put a ruler under the microscope and counted the number of lines.
Is the number below the same for all microscopes?
Note: The numbers below will not be the same for all brands of microscopes.
How does a microscope work?
An optical microscope (or light microscope) uses visible light and lenses to magnify objects that are not visible to the naked eye . The magnification of a light microscope is formed using a mixture of the powers of the eyepiece and the objective lens. The eyepiece produces a power of 10x and the objective lens can produce various different powers, so if it were to produce a power of 100x, the final magnification would be 1000x (10 x 100). So this would mean that to the naked eye, the image would appear 1000 times larger than it actually is. Light microscopes generally have three different objective lenses to allow the slide to be viewed in three separate manners. Such microscopes are known as compound light microscopes. The objective lenses on a compound light microscope doess have powers that start of as 4x on the smallest power, 10x on the middle power setting and 40x on the maximum power setting. This means that the object can be magnified either, 40x, 100x or 400x .
What is the measure of the ability of a lens or other optical instruments to magnify?
Magnification in physical terms is defined as "a measure of the ability of a lens or other optical instruments to magnify, expressed as the ratio of the size of the image to that of the object". This means, that an object of any size is magnified to form an enlarged image.
What is a compound light microscope?
Such microscopes are known as compound light microscopes. The objective lenses on a compound light microscope doess have powers that start of as 4x on the smallest power, 10x on the middle power setting and 40x on the maximum power setting. This means that the object can be magnified either, 40x, 100x or 400x .
Does the resolution of an image remain low?
So although the image will be more magnified, the resolution will remain low. This would therefore result in the image being very unclear. In fact, an increase in magnification past the optimum point could result in things such as visual artefacts appearing.
What is the magnification of a tube?
The magnification range is from 10× to 100×.
How does a microscope work?
If you want to know how does a microscope work, read this article properly. Microscopes are essential gears which produce enlarged images of the object or specimen that you can view, making decent, detailed picture visible. This enlargement process happens when light bends or refracts when it passes through the lenses. Although magnification is what the instrument mostly does, a microscope’s critical property is its resolution, so microscopic details of structures provide us clarity and understanding. Hence, it is also essential for us to know how a microscope works.
How many lenses does a simple microscope have?
Simple microscopes have only one lens, whereas compound microscopes have two lenses, one for viewing the object or specimen known as the objective lens and another used by the eye for viewing known as the ocular lens or the eyepiece. Compound microscopes can have multiple lenses as well. The eyepiece or the ocular lens is placed on top of the body tube.
What is a simple microscope?
Simple Microscopes – These have only one lens, which is fundamentally a small magnifying glass of high magnification usually used in jewellery stores and watch-makers. Some examples of simple microscopes are magnifying glasses, reading glasses, and jewellery eyepieces.
What is the stage below the objective lens?
That is the place just below the objective lenses where the specimen is placed; it also has clips to hold the specimen slides for stability. This stage is usually mechanical so that it can be moved according to the needs of the viewer. The set has been marked gradually and contains the X and Y coordinate to help the viewer find the specimen’s features on the slide. The stage also has a hole that allows the light to enter and help in viewing the sample.
Why is the resolution of a microscope low?
After getting your desired magnification, it’s time for resolution. If the points are closer together but are not focused properly, then the image’s quality will be low regardless of high magnification. A rule of physics from optics is that a shorter wavelength gives better resolution. Some microscopes allow the eyepiece to be pulled up for fine-tuning the focus.
How do microscopes use visible light?
Now, microscopes use visible light from the light source or the room either by refraction or reflection of the specimen.
How many microns can you see with 400x magnification?
At 400x magnification you will be able to see 0.45mm, or 450 microns.
What type of microscope is used to photograph Paulownia wood?
The images of Paulownia wood, hair, and frog's blood were captured with a high power compound microscope using a Nikon camera adapter. The compound microscope typically has three or four magnifications - 40x, 100x, 400x, and sometimes 1000x.
