Full Answer
What is Milky Way and what does it consist of?
What is the Milky Way and what does it consist of? The Milky Way consists of a bar-shaped core region that is surrounded by a warped disk of gas, dust, and stars. The Milky Way is made up of about 90% dark matter, matter which cannot be seen and about 10% “luminous matter”, or matter that we can see with our eyes.
What is Milky Way best described as?
The Milky way appears "milky" because of the concentration of stars, dust and gas in the spiral arm that is visible to us in the night sky. As you are aware, the Milky Way is an immense disk of stars, with the solar system embedded in it at about 30,000 light-years from the core.
Why is the Milky Way called 'Milky Way'?
Well, even though i still can’t see it, it did look like milk to ancient civilizations. Our galaxy is named Milky Way because of its milky appearance as it spreads all over the sky. The name dates back to ancient Greece as the Greek word for galaxy derives from the word “milk” (gala).
What is Milky Way why is it named so?
The reason that our galaxy is called the Milky Way is because of its milky appearance. Indeed, the Milky Way was named by the Romans as the via lactea, which in Latin means the road of milk.
See more

Why is it called the Milky Way Galaxy?
The Milky Way Galaxy takes its name from the Milky Way, the irregular luminous band of stars and gas clouds that stretches across the sky as seen f...
How big is the Milky Way Galaxy?
The first reliable measurement of the size of the Milky Way Galaxy was made in 1917 by American astronomer Harlow Shapley. Assuming that the globul...
Is Earth in the centre of the Milky Way Galaxy?
The solar system is about 30,000 light-years from the centre of the Milky Way Galaxy. The Galaxy itself is thought to be about 100,000 light-years...
Where does the Milky Way light come from?
The light originates from the accumulation of unresolved stars and other material located in the direction of the galactic plane.
Why is the Milky Way a band?
From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe.
What is the dark area of the Milky Way?
Dark regions within the band, such as the Great Rift and the Coalsack, are areas where interstellar dust blocks light from distant stars. The area of sky that the Milky Way obscures is called the Zone of Avoidance . The Milky Way has a relatively low surface brightness.
How much mass is in the Milky Way?
In March 2019, astronomers reported that the mass of the Milky Way galaxy is 1.5 trillion solar masses within a radius of about 129,000 light-years, over twice as much as was determined in earlier studies, and suggesting that about 90% of the mass of the galaxy is dark matter.
What is the bright object on the lower right of the Milky Way?
A view of the Milky Way toward the constellation Sagittarius (including the Galactic Center ), as seen from a dark site with little light pollution (the Black Rock Desert, Nevada), the bright object on the lower right is Jupiter, just above Antares. Play media.
Why can't we see the Milky Way?
Maps of artificial night sky brightness show that more than one-third of Earth's population cannot see the Milky Way from their homes due to light pollution. As viewed from Earth, the visible region of the Milky Way's galactic plane occupies an area of the sky that includes 30 constellations.
How big is the Milky Way galaxy?
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with an estimated visible diameter of 100,000–200,000 light-years . Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter disk, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years. The Milky Way has several satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, which form part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster.
What is the Milky Way?
Milky Way. noun Astronomy. the spiral galaxy containing our solar system. With the naked eye it is observed as a faint luminous band stretching across the heavens, composed of approximately a trillion stars, most of which are too distant to be seen individually.
Where is the Milky Way located?
Made up of an estimated two hundred billion stars or more, it is seen from Earth as an irregular band of hazy light across the night sky. The solar system is located in one of the revolving spiral arms, about 50 light-years north of the galactic plane ...
How big is the Milky Way?
The Milky Way measures about 100,000 light-years in diameter and is the second largest galaxy, after the Andromeda Galaxy, in the cluster known as the Local Group. See also spiral galaxy. The American Heritage® Science Dictionary Copyright © 2011. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
What is the Milky Way?
n. 1. (Celestial Objects) the diffuse band of light stretching across the night sky that consists of millions of faint stars, nebulae, etc, within our Galaxy. 2. (Celestial Objects) another name for the Galaxy. [C14: translation of Latin via lactea]
How many stars are in the Milky Way?
Among these 5,000 nebulae there is one which has received the name of the Milky Way, and which contains eighteen millions of stars, each of which has become the center of a solar world.
What is the name of the galaxy that contains the sun, solar system, and all of the individually visible stars in the?
Milky Way. n. 1. The galaxy containing the sun, solar system, and all of the individually visible stars in the night sky, along with various nebulae, star clusters, and dust clouds, thought to have a super-massive black hole at its center of mass. 2.
How many stars are in a spiral galaxy?
the spiral galaxy containing our solar system, seen as a luminous band stretching across the night sky and composed of approximately a trillion stars. [1350–1400; Middle English, translation of Latin via lactea; compare galaxy] Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd.
Will the Milky Way end up in the same way?
According to Kirkpatrick, Milky Way will eventually end up in the same way after its black hole becomes big enough to strip away the gas and dust. Astronomers Predict Death Of Milky Way Galaxy After Observing Quasars.
What is the Milky Way Galaxy?
The Milky Way Galaxy, the galaxy in which Earth is located; extension of the night sky phenomenon.
How does the Milky Way get its name?
This name derives from its appearance as a dim "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky, in which the naked eye cannot distinguish individual stars. The term "Milky Way" is a translation of the Classical Latin via lactea, from the Hellenistic Greek γαλαξίας κύκλος. The Milky Way appears like a band because it is a disk-shaped structure being viewed from inside. The fact that this faint band of light is made up of stars was proven in 1610 when Galileo Galilei used his telescope to resolve it into individual stars. In the 1920s, observations by astronomer Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy 100,000–120,000 light-years in diameter containing 100–400 billion stars. It may contain at least as many planets. The Solar System is located within the disk, around two thirds of the way out from the Galactic Center, on the inner edge of a spiral-shaped concentration of gas and dust called the Orion Arm. The stars in the inner ≈10,000 light-years form a bulge and one or more bars. The very center is marked by an intense radio source named Sagittarius A* which is likely to be a supermassive black hole. Stars and gas throughout the Galaxy rotate about the center at approximately the same speed, which contradicts the laws of Keplerian dynamics. This indicates that much of the mass of the Milky Way does not emit or absorb electromagnetic radiation; this mass is known as dark matter. The rotational period is about 200 million years at the position of the Sun. The Galaxy as a whole is moving at a velocity of approximately 600 km per second with respect to extragalactic frames of reference. The oldest known star in the Galaxy is about 13.2 billion years old, nearly as old as the Universe. Surrounded by several smaller satellite galaxies, the Milky Way is part of the Local Group of galaxies, which forms a subcomponent of the Virgo Supercluster.
What is the numerical value of Milky Way?
The numerical value of milky way in Chaldean Numerology is: 1
Why do galaxies look like train wrecks?
Most galaxies that we find early in the universe look like train wrecks because they underwent consistent and often' violent' merging, these hot mergers make Milky Waydifficult to form well-ordered, cold rotating disks like we observe in our present universe.
What is the Milky Way?
In all traditions the Milky Way is regarded as a roadway, built by the gods, linking their world with the Earth. It has also been compared with serpents, rivers, footprints, spurts of milk, seams and trees. Souls and birds use it for travelling between the two worlds. It symbolizes the road taken by pilgrims, explorers and mystics from one place to another on Earth, from one plane to another in the cosmos and from one level to another in the psyche. It also marks the boundaries between the busy world and the stillness of eternity.
What is the Milky Way called?
At festivals, members of this society put on shows of unbridled obscenity. The Milky Way is called the roof-tree of Heaven.

Overview
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term Milky Way is a translation of the Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλακτικός κύκλος (galaktikos kýklos), meaning "milky circle." From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galile…
Etymology and mythology
In the Babylonian epic poem Enūma Eliš, the Milky Way is created from the severed tail of the primeval salt water dragoness Tiamat, set in the sky by Marduk, the Babylonian national god, after slaying her. This story was once thought to have been based on an older Sumerian version in which Tiamat is instead slain by Enlil of Nippur, but is now thought to be purely an invention of Babylonian propagandists with the intention to show Marduk as superior to the Sumerian deities.
Appearance
The Milky Way is visible from Earth as a hazy band of white light, some 30° wide, arching the night sky. In night sky observing, although all the individual naked-eye stars in the entire sky are part of the Milky Way Galaxy, the term "Milky Way" is limited to this band of light. The light originates from the accumulation of unresolved stars and other material located in the direction of the galactic plane. Brighter regions around the band appear as soft visual patches known as star clouds. Th…
Astronomical history
In Meteorologica, Aristotle (384–322 BC) states that the Greek philosophers Anaxagoras (c. 500–428 BC) and Democritus (460–370 BC) proposed that the Milky Way is the glow of stars not directly visible due to Earth's shadow, while other stars receive their light from the Sun (but have their glow obscured by solar rays). Aristotle himself believed that the Milky Way was part of the Earth's upper atmosphere (along with the stars), and that it was a byproduct of stars burning tha…
Astrography
The ESA spacecraft Gaia provides distance estimates by determining the parallax of a billion stars and is mapping the Milky Way with four planned releases of maps in 2016, 2018, 2021 and 2024. A study in 2020 concluded that Gaia detected a wobbling motion of the galaxy, which might be caused by "torques from a misalignment of the disc's rotation axis with respect to the principle axis of a non-spherical halo, or from accreted matter in the halo acquired during late infall, or fro…
Size and mass
The Milky Way is the second-largest galaxy in the Local Group (after the Andromeda Galaxy), with its stellar disk approximately 170,000–200,000 light-years (52–61 kpc) in diameter and, on average, approximately 1,000 ly (0.3 kpc) thick. To compare the relative physical scale of the Milky Way, if the Solar System out to Neptune were the size of a US quarter (24.3 mm (0.955 in)), the Milky Way would be approximately the size of the contiguous United States. There is a ring-like filame…
Contents
The Milky Way contains between 100 and 400 billion stars and at least that many planets. An exact figure would depend on counting the number of very-low-mass stars, which are difficult to detect, especially at distances of more than 300 ly (90 pc) from the Sun. As a comparison, the neighboring Andromeda Galaxy contains an estimated one trillion (10 ) stars. The Milky Way may contain ten billion white dwarfs, a billion neutron stars, and a hundred million stellar black holes. F…
Structure
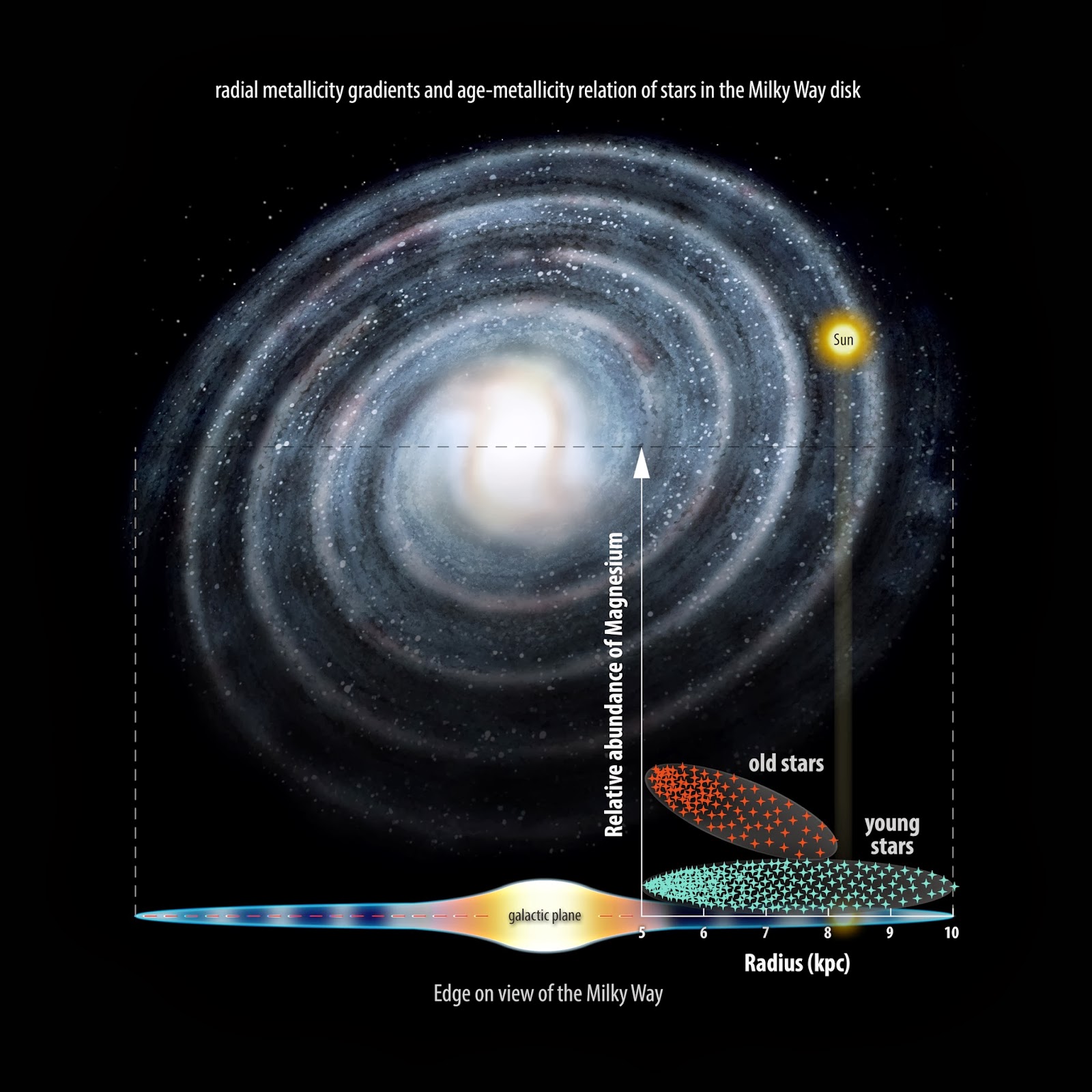
The Milky Way consists of a bar-shaped core region surrounded by a warped disk of gas, dust and stars. The mass distribution within the Milky Way closely resembles the type Sbc in the Hubble classification, which represents spiral galaxies with relatively loosely wound arms. Astronomers first began to conjecture that the Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy, rather than an ordinary spiral galaxy, in the 1960s. These conjectures were confirmed by the Spitzer Space Telescope observat…