
Features of Mitosis
- In each cycle of cell division, two daughter cells are formed from the parent cell.
- The cell is also known as equational cell division because the chromosome number in the parent cell and daughter cell is the same.
- In plants, mitosis leads to the growth of vegetative parts of the plant like root tip, stem tip, etc.
Full Answer
How many cell does a mitotic cell division make?
Mitosis is the process in cell division by which the nucleus of the cell divides (in a multiple phase), giving rise to two identical daughter cells.Mitosis happens in all eukaryotic cells (plants, animals, and fungi).Mitosis is the reason we can grow, heal wounds, and replace damaged cells.
Why do cells undergo mitotic cell division?
The major purpose of occurrence of mitosis is growth and repair. Some of the cells in the body do not undergo cell division like nerve cells and muscle cells. These cells are matured enough that they cannot grow again or undergo repair. The already existing ones in the body can be taken care of.
Is mitosis and cell division the same thing?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in the formation of four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Mitosis is the type of cell division that results in the formation of two daughter cells each with the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent cell.
What does meiotic cell division produce?
Meiotic cell division (meiosis followed by cytokinesis) separates homologous chromosomes and produces haploid cells with only one homologue from each pair. During interphase before meiosis, chromosomes are duplicated. The cell then undergoes two specialized divisions-meiosis I and meiosis II-to produce four haploid daughter cells.
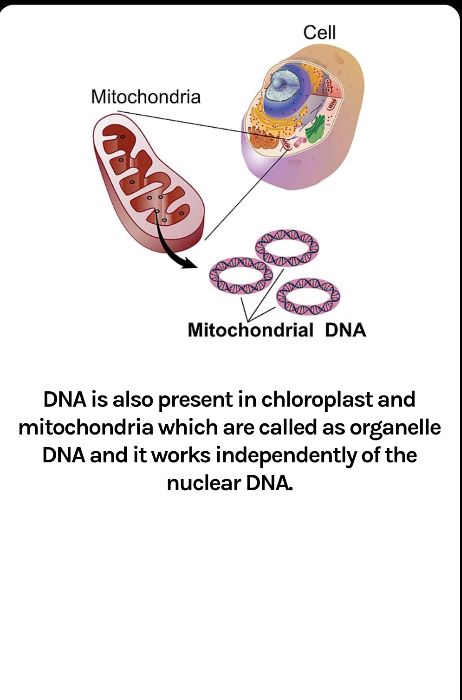
What is the meaning of mitotic cell division?
(my-TAH-tik SY-kul) The process a cell goes through each time it divides. The mitotic cycle consists of a series of steps during which the chromosomes and other cell material double to make two copies. The cell then divides into two daughter cells, each receiving one copy of the doubled material.
Is mitosis and mitotic cell division the same?
But it's important to note that, in the type of cells that undergo mitosis, the genetic material of the cell is contained within the cell's nucleus. So, while mitosis is often referred to as “cell division,” mitosis is technically the division of a cell's nucleus into two new, identical nuclei.
What happens in mitotic cell cycle?
Mitosis is the process in which a eukaryotic cell nucleus splits in two, followed by division of the parent cell into two daughter cells. The word "mitosis" means "threads," and it refers to the threadlike appearance of chromosomes as the cell prepares to divide.
What does mitotic mean?
(my-TAH-tik ak-TIH-vih-tee) Having to do with the presence of dividing (proliferating) cells. Cancer tissue generally has more mitotic activity than normal tissues.
Why is mitotic cell division important?
Why is mitosis important to organisms? Mitosis is important to multicellular organisms because it provides new cells for growth and for replacement of worn-out cells, such as skin cells. Many single-celled organisms rely on mitosis as their primary means of asexual reproduction.
What is mitotic and meiotic cell division?
There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Most of the time when people refer to “cell division,” they mean mitosis, the process of making new body cells. Meiosis is the type of cell division that creates egg and sperm cells. Mitosis is a fundamental process for life.
What are the stages of mitotic cell division?
Mitosis is conventionally divided into five stages known as prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Where is mitosis in cell cycle?
At the end of interphase comes the mitotic phase, which is made up of mitosis and cytokinesis and leads to the formation of two daughter cells. Mitosis precedes cytokinesis, though the two processes typically overlap somewhat.
What is the result of mitosis?
two identical daughter cellsMitosis results in two identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis results in four sex cells.
What is an example of mitotic cell division?
In some organisms, mitotic cell division can be used for reproduction, or the creation of new organisms. For example, single celled eukaryotic organisms, such as amoebas, reproduce using mitosis. One single celled organism grows and eventually divides into two, thus reproducing the original organism.
What is meiotic cell division?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells. This process is required to produce egg and sperm cells for sexual reproduction.
What is another name for mitosis?
Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division.
What is the difference between mitosis and mitotic cell division quizlet?
What is the difference between mitosis and mitotic cell division? Mitotic Cell division is the process of creating a new cell with the same DNA as the original cell. Mitosis is the process of replicating dividing chromosomes to distribute to each eukaryotic cell.
What two processes are involved in mitotic division?
Mitosis and Cytokinesis During cell division a cell undergoes two major processes. First, it completes mitosis, during which the duplicated information enclosed in the nucleus is distributed between two daughter nuclei. Cytokinesis then occurs, dividing the cytoplasm and cell body into two new cells.
What is meiotic cell division?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells. This process is required to produce egg and sperm cells for sexual reproduction.
What is the Function of Mitotic Cell Division?
Why is mitosis important to all living things? The importance of mitosis is because cells use it to reproduce and make more cells. This is an essential process for living things. Cells can only come from other cells. Thus, to continue life on Earth, mitosis must occur. Mitosis occurs in several steps that first replicate the genetic material, move it to opposite ends of the cell and then allow the cell to divide in two.
What is the process of one cell with a nucleus dividing to form two identical daughter cells?
Mitotic cell division, also known as mitosis, is the process of one cell with a nucleus dividing to form two identical daughter cells. Mitosis is a type of cell division, where one cell divides to create more cells. Meiosis is another type of cell division in eukaryotes which produces gametes for sexual reproduction. Mitosis is important for three main processes:
How do organisms reproduce?
Multicellular organisms can also reproduce using mitosis in a process called budding. Sea anemones for example grow appendages that will form entirely new organisms through the process of mitosis. Some organisms, like Planaria worms, can regenerate themselves when cut in half using mitosis to produce entirely new organisms. Using mitosis for reproduction is also a common strategy in plants. Many plants can be cut and rooted in water to produce new plants that can then be planted in the ground. Some plants will even reproduce into entirely new organisms when leaves fall into the soil. This is a common reproduction strategy in succulents.
What is the process of one cell dividing to create two or more daughter cells?
Cell division is the process of one cell dividing to create two or more daughter cells. Eukaryotic cells are cells with a nucleus, like animal cells, including human cells, and plant cells. Eukaryotic cells carry out two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
What is mitosis used for?
In some organisms, mitotic cell division can be used for reproduction, or the creation of new organisms. For example, single celled eukaryotic organisms, such as amoebas, reproduce using mitosis. One single celled organism grows and eventually divides into two, thus reproducing the original organism.
What cells are activated during an infection?
During an active infection, immune cells are activated and proceed through mitosis and cell differentiation. This allows for a rapid increase in immune cells , such as macrophages, B-cells and T-cells, that are needed to fight the infection.
What is the function of mitosis?
Mitosis is essential for healing in multicellular organisms. Both plants and animals are injured during their lifetime and need to repair. In addition, worn out cells die off and need to be replaced . This is an essential function of mitosis. For example, during wound healing in the skin of animals, cells on the edge of the wound divide and replace the damaged cells. These cells also make skin proteins, such as collagen that support the structure of the skin. Blood vessel cells, called vascular endothelial cells, also experience mitosis and form new blood vessels that are needed in the wound area.
How are mitosis and meiosis similar?
That’s a lot of differences, right? But there are also several similarities between the processes of mitosis and meiosis. Here they are: 1 Both mitosis and meiosis begin with a diploid parent cell, or a parent cell with two sets of chromosomes 2 Mitosis and meiosis go through the same phases, in the same order—prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase—but the phases occur only once during mitosis and twice during meiosis 3 Both mitosis and meiosis end with cytokinesis, the cytoplasmic division of a eukaryotic cell into two daughter cells
How many times does mitosis occur?
Mitosis and meiosis go through the same phases, in the same order—prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase—but the phases occur only once during mitosis and twice during meiosis. Both mitosis and meiosis end with cytokinesis, the cytoplasmic division of a eukaryotic cell into two daughter cells.
What is the name of the cell that divides one time?
So we’ve explained that mitosis is the part of the cell cycle when cell division occurs, but let’s get a little more detailed than that. During mitosis, one cell divides one time, and the cell that’s being divided is always called the “parent cell.” When the process of dividing the parent cell is complete, the result is two “daughter cells.” These cells are called daughter cells because, during mitosis, the genetic material of the parent cell is passed on to each new daughter cell.
How many phases of mitosis are there?
We have a much longer article that covers the four phases of mitosis in more detail, but we do want to give you an overview of what the four phases of mitosis are and what happens during each phase here. If you’re looking for a deep dive into the four phases of mitosis, take a look at our article, “A Detailed Breakdown of the 4 Phases of Mitosis”!
What is the process of mitosis?
The first thing we need to do is answer the question, “What is mitosis?” In cell biology, mitosis is a part of what is called the cell cycle . The cell cycle, sometimes called the cell-division cycle, is the series of events that occur in a cell that lead to duplication of that cell’s DNA and, ultimately, the creation of new cells. During mitosis, the cell division part of the cell cycle, a single parent cell’s replicated genetic material—called chromosomes—divides to produce two new, genetically-identical daughter cells.
What happens during mitosis?
During mitosis, the cell division part of the cell cycle, a single parent cell’s replicated genetic material—called chromosomes—divides to produce two new, genetically-identical daughter cells. In the cell cycle, the cell’s DNA is replicated in interphase, the phase that precedes mitosis. Mitosis alternates with interphase to make up ...
How much is a one year subscription to Nature?
The big drawback of most academic research journals is that the subscription fees are hefty. A one-year subscription to Nature for students is $119. Don’t lose heart, though. A lot of times, schools and universities buy subscriptions to reputable journals, so it’s likely you could access articles or issues on mitosis through your school library’s online databases. If you’re in doubt, just ask a research librarian!
What is Mitosis?
Cell division is the driving process of reproduction at the cellular level. Most eukaryotic cells divide in a manner where the ploidy or the number of chromosomes remains the same, except in the case of germ cells where the number of chromosomes is halved.
How does mitosis help an organism?
Mitosis helps in the development of an organism. In single-celled organisms, mitosis is the process of asexual reproduction. Mitosis helps in the replacement of damaged tissues. The cells near the damaged cells begin mitosis when they do not sense the neighbouring cells.
What happens to the microtubules in prometaphase?
In the prometaphase, the nuclear envelop disintegrates. Now the microtubules are allowed to extend from the centromere to the chromosome. The microtubules attach to the kinetochores which allow the cell to move the chromosome around.
What is the process of completion of prophase?
The completion of prophase is characterised by the initiation of the assembly of the mitotic spindle, the microtubules and the proteinaceous components of cytoplasm that help in the process.
Why is mitosis also called equational cell division?
The cell is also known as equational cell division because the chromosome number in the parent cell and daughter cell is the same. In plants, mitosis leads to the growth of vegetative parts of the plant like root tip, stem tip, etc. Segregation and combination do not occur in this process. The processes occurring during mitosis have been divided ...
Why is mitosis important?
Mitosis is required for asexual reproduction, vegetative propagation in plants and also responsible for repair and regeneration of damaged tissues. Mitosis helps in maintaining purity of genome as no recombination or crossing over takes place.
What is the term for the splitting of sister chromatids?
Anaphase. The splitting of the sister chromatids marks the onset of anaphase. These sister chromatids become the chromosome of the daughter nuclei. The chromosomes are then pulled towards the pole by the fibres attached to the kinetochores of each chromosome.
How are chromosomes held in the metaphase plate?
Chromosomes are held at the metaphase plate by the equal forces of the polar fibers pushing on the centromeres of the chromosomes.
What is the phase of the cell cycle where chromosomes are evenly divided between two cells?
Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle where chromosomes in the nucleus are evenly divided between two cells. When the cell division process is complete, two daughter cells with identical genetic material are produced.
How do chromosomes move?
Chromosomes move randomly until they attach (at their kinetochores) to polar fibers from both sides of their centromeres.
When do diploid cells begin to form?
It begins prior to the end of mitosis in anaphase and completes shortly after telophase/mitosis. At the end of cytokinesis, two genetically identical daughter cells are produced. These are diploid cells, with each cell containing a full complement of chromosomes.
What happens during prophase?
In prophase, the chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes. The nuclear envelope breaks down and spindles form at opposite poles of the cell. Prophase (versus interphase) is the first true step of the mitotic process. During prophase, a number of important changes occur:
What is the S phase in biology?
S phase: The period during which DNA is synthesized. In most cells, there is a narrow window of time during which DNA is synthesized. The S stands for synthesis.
Why do centrioles move away from each other?
The two pairs of centrioles (formed from the replication of one pair in Interphase) move away from one another toward opposite ends of the cell due to the lengthening of the microtubules that form between them.
What are the phases of interphase?
The interphase further comprises three phases: 1 G0 Phase (Resting Phase): The cell neither divides nor prepares itself for the division. 2 G1 Phase (Gap 1): The cell is metabolically active and grows continuously during this phase. 3 S phase (Synthesis): The DNA replication or synthesis occurs during this stage. 4 G2 phase (Gap 2): Protein synthesis happens in this phase. 5 Quiescent Stage (G0): The cells that do not undergo further division exits the G1 phase and enters an inactive stage. This stage is known as the quiescent stage (G0) of the cell cycle.
What are the two types of cell division?
Types of Cell Division. There are two distinct types of cell division out of which the first one is vegetative division , wherein each daughter cell duplicates the parent cell called mitosis. The second one is meiosis, which divides into four haploid daughter cells. Mitosis: The process cells use to make exact replicas of themselves.
How does cell division occur?
Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle. All cells reproduce by splitting into two, where each parental cell gives rise to two daughter cells. These newly formed daughter cells could themselves divide and grow, giving rise to a new cell population that is formed by the division and growth of a single parental cell ...
What is the M phase?
M Phase (Mitosis phase): This is where the actual cell division occurs. There are two key steps in this phase, namely cytokinesis and karyokinesis.
What are the two main phases of the cell cycle?
There are two primary phases in the cell cycle: Interphase: This phase was thought to represent the resting stage between subsequent cell divisions, but new research has shown that it is a very active phase. M Phase (Mitosis phase): This is where the actual cell division occurs.
How many stages are there in the M phase?
There are four stages in the M Phase, namely:
Which type of cell division produces sperm instead of identical daughter cells?
Meiosis: In this type of cell division, sperm or egg cells are produced instead of identical daughter cells as in mitosis.
