How do you write an electron configuration?
How do you write electronic configuration? The symbols used for writing the electron configuration start with the shell number (n) followed by the type of orbital and finally the superscript indicates how many electrons are in the orbital. For example: Looking at the periodic table, you can see that Oxygen has 8 electrons.
What is the electron configuration for neon atomic number 10?
What is the electron configuration for neon atomic number 10? Neon symbol is Ne, atomic number 10 that locate in 2 period of noble gas group. Ne has 20.1797 atomic mass , 10 electrons and protons, 10.1797 neutrons, electron configuration is [He]2S22p6.
What is the full electron configuration of neon?
Properties of neon atom
- The atomic number of neon atoms is 10. ...
- The active atomic mass of the neon atom is 20.1797.
- Neon is an inert element.
- The valency (valence) of a neon atom is zero and the valence electrons of a neon atom are 8.
- Neon atoms are the 2nd period of the periodic table and an element of the 18-group.
- The electron configuration of neon ends in a p-orbital. ...
What are some examples of electron configurations?
Electron configurations of atoms follow a standard notation in which all electron-containing atomic subshells (with the number of electrons they hold written in superscript) are placed in a sequence. For example, the electron configuration of sodium is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. However, the standard notation often yields lengthy electron ...

How do you find the electron configuration of Ne?
In writing the electron configuration for neon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Ne go in the 2s orbital. The remaining six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the Ne electron configuration will be 1s22s22p6.
What is the electron configuration of Ne 11?
Electron configurations of the elements (data page)Legend10 Ne neon : [He] 2s2 2p61s22s22p62811 Na sodium : [Ne] 3s1128 more rows
What has the same electron configuration as Ne?
The sodium ion, Na+, has the electron configuration with an octet of electrons from the second principal energy level. It is now the same as that of the noble gas neon. The term isoelectronic refers to an atom and an ion of a different atom (or two different ions) that have the same electron configuration.
What is NS2 in chemistry?
Dithioxoammonium | NS2 | ChemSpider.
How do you write electron configuration?
1:2710:19Electron Configuration - Basic introduction - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo here's what we need to do first start with 1s. So i'm going to write 1s2 because s can hold up toMoreSo here's what we need to do first start with 1s. So i'm going to write 1s2 because s can hold up to 2 electrons. Next move on to the 2s sublevel 2s can also hold 2 electrons.
How many core electrons does Ne?
The atomic number of neon is 10. The first shell consists of 2 electrons and the second (outermost) shell consists of 8 electrons. Therefore, The number of core and valence electrons in neon is 2 and 8, respectively.
Which element has the electron configuration 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p²?
Germanium has the electron configuration 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p².
Which element has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p5?
The electron configuration for chlorine is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5. Christmas bulbs, Electron configuration, Holiday decor.
What is the configuration number of neon?
Fact boxGroup18−248.59°C, −415.46°F, 24.56 KBlockp0.000825Atomic number1020.180State at 20°CGas20NeElectron configuration[He] 2s22p67440-01-92 more rows
What is ns2 np4?
ns2 np4 electronic configuration is for the 16th group (VIA) group which are known as chalcogens.
Which element has electronic configuration as ns2 formula?
Carbon, Silicon, Germanium, Tin, and Lead.
Which family has general electronic configuration ns2?
Solution : Oxygen family.
What atom matches this electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10?
antimony atomSo, an antimony atom with charge +2 has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p1.
What is the configuration number of neon?
Fact boxGroup18−248.59°C, −415.46°F, 24.56 KBlockp0.000825Atomic number1020.180State at 20°CGas20NeElectron configuration[He] 2s22p67440-01-92 more rows
What is the electronic configuration of 13al?
Atomic number of aluminium = 13. Therefore number of electrons = 13. Thus, electronic configuration of aluminium is 283K L M.
What is meant by the electronic configuration of an element?
The electronic configuration of an element is a symbolic notation of the manner in which the electrons of its atoms are distributed over different...
What are the three rules that must be followed while writing the electronic configuration of elements?
The three rules that dictate the manner in which electrons are filled in atomic orbitals are: The Aufbau principle: electrons must completely fill...
Why are electronic configurations important?
Electron configurations provide insight into the chemical behaviour of elements by helping determine the valence electrons of an atom. It also help...
List the electron configurations of all the noble gases.
The electronic configurations of the noble gases are listed below. Helium (He) – 1s 2 Neon (Ne) – [He]2s 2 2p 6 Argon (Ar) – [Ne]3s 2 3p 6 Krypton...
What is the electronic configuration of copper?
The electronic configuration of copper is [Ar]3d 10 4s 1 . This configuration disobeys the aufbau principle due to the relatively small energy gap...
Which atom has two electrons?
Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = + 1 2 ).
Why do we see a periodic recurrence of similar electron configurations in the outer shells of these?
When their electron configurations are added to the table (Figure 3.1. 6 ), we also see a periodic recurrence of similar electron configurations in the outer shells of these elements. Because they are in the outer shells of an atom, valence electrons play the most important role in chemical reactions. The outer electrons have the highest energy of the electrons in an atom and are more easily lost or shared than the core electrons. Valence electrons are also the determining factor in some physical properties of the elements.
How does orbital energy affect atomic structure?
Orbital Energies and Atomic Structure. The energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of l differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order s < p < d < f.
What is the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom called?
The arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom . We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( Figure 3.1. 2 ):
What order do electrons fill in the periodic table?
Electrons in successive atoms on the periodic table tend to fill low-energy orbitals first. Thus, many students find it confusing that, for example, the 5 p orbitals fill immediately after the 4 d, and immediately before the 6 s. The filling order is based on observed experimental results, and has been confirmed by theoretical calculations. As the principal quantum number, n, increases, the size of the orbital increases and the electrons spend more time farther from the nucleus. Thus, the attraction to the nucleus is weaker and the energy associated with the orbital is higher (less stabilized). But this is not the only effect we have to take into account. Within each shell, as the value of l increases, the electrons are less penetrating (meaning there is less electron density found close to the nucleus), in the order s > p > d > f. Electrons that are closer to the nucleus slightly repel electrons that are farther out, offsetting the more dominant electron–nucleus attractions slightly (recall that all electrons have −1 charges, but nuclei have + Z charges). This phenomenon is called shielding and will be discussed in more detail in the next section. Electrons in orbitals that experience more shielding are less stabilized and thus higher in energy. For small orbitals (1 s through 3 p ), the increase in energy due to n is more significant than the increase due to l; however, for larger orbitals the two trends are comparable and cannot be simply predicted. We will discuss methods for remembering the observed order.
How do we determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another?
Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another. This allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. The specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom.
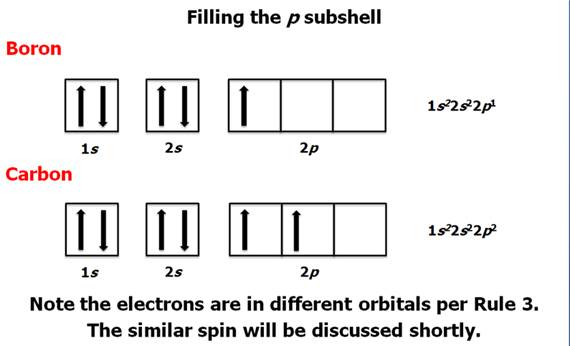
How many electrons are in a p subshell?
For example, the notation 2 p4 (read "two–p–four") indicates four electrons in a p subshell ( l = 1) with a principal quantum number ( n) of 2. The notation 3 d8 (read "three–d–eight") indicates eight electrons in the d subshell (i.e., l = 2) of the principal shell for which n = 3.
What is the abbreviated electron configuration of sodium?
In the abbreviated notation, the sequence of completely filled subshells that correspond to the electronic configuration of a noble gas is replaced with the symbol of that noble gas in square brackets. Therefore, the abbreviated electron configuration of sodium is [Ne]3s 1 (the electron configuration of neon is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6, which can be abbreviated to [He]2s 2 2p 6 ).
What is electron configuration?
The electron configuration of an element describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic orbitals. Electron configurations of atoms follow a standard notation in which all electron-containing atomic subshells (with the number of electrons they hold written in superscript) are placed in a sequence. For example, the electron configuration of ...
Why do the 1p, 2d, and 3f orbitals not exist?
Thus, it can be understood that the 1p, 2d, and 3f orbitals do not exist because the value of the azimuthal quantum number is always less than that of the principal quantum number.
How to find the maximum number of electrons in a shell?
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a shell is based on the principal quantum number (n). It is represented by the formula 2n 2, where ‘n’ is the shell number. The shells, values of n, and the total number of electrons that can be accommodated are tabulated below.
Which three rules dictate the manner in which electrons are filled in atomic orbitals?
The three rules that dictate the manner in which electrons are filled in atomic orbitals are: The Aufbau principle: electrons must completely fill the atomic orbitals of a given energy level before occupying an orbital associated with a higher energy level.
What are some exceptions to the Aufbau principle?
It is important to note that there exist many exceptions to the Aufbau principle such as chromium and copper. These exceptions can sometimes be explained by the stability provided by half-filled or completely filled subshells.
How many electrons can fit in an orbital?
The Pauli exclusion principle states that a maximum of two electrons, each having opposite spins, can fit in an orbital.
Why are electron configurations most stable?
Keep in mind, electron configurations are most stable when they are filled or half-filled. Also, the real electron configuration of an atom may differ from the prediction because of relativistic effects, shielding, etc.
How many electrons can an orbital hold?
The s orbital holds a maximum of 2 electro ns. The p orbital can hold 6. The d orbital can hold 10. The f orbital can hold 14 electrons. But, the orbitals overlap. The Madelung rule gives the order:
Which element is a good example of the order of the orbitals?
Oganesson (element 118 is a good example to show the order of the orbitals. Its electron configuration is:
What does an asterisk mean in a periodic table?
Values denoted by an asterisk are predictions based on periodic table trends. Actual configurations have not been verified.
What Does Electron Configuration Mean?
Electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals; for example, the electron configuration of a neon atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. From electron configuration, an atoms' reactivity and potential for corrosion can be determined.
What is the principle of electron configuration?
The electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, ...
Who proposed the electron configuration theory?
The electron configuration theory was proposed by Uhlig and is an extension of the adsorption theory of passivity. Uhlig noted that a number of transition metals become passive at certain critical compositions when alloyed with a second metal.
What are the physical and chemical properties of elements?
Many of the physical and chemical properties of elements can be correlated to their unique electron configurations. The most widespread application of electron configurations is in the rationalization of chemical properties, in both inorganic and organic chemistry. In effect, electron configurations, along with some simplified form ...
