Full Answer
What are the advantages and disadvantages of non probability sampling?
Definition:Non-probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher selects samples based on the subjective judgment of the researcher rather than random selection. It is a less stringent method. This sampling method depends heavily on the expertise of the researchers.
What are the different types of nonprobability sampling?
Non-probability sampling (sometimes nonprobability sampling) is a branch of sample selection that uses non-random ways to select a group of people to participate in research. Unlike probability sampling and its methods , non-probability sampling doesn’t focus on accurately representing all members of a large population within a smaller sample group of participants.
What is the definition of nonprobability sampling?
What is non-probability sampling? In non-probability sampling, the sample is selected based on non-random criteria, and not every member of the population has a chance of being included. Common non-probability sampling methods include convenience sampling, voluntary response sampling, purposive sampling, snowball sampling, and quota sampling.
What are the types of non random sampling?
Nonprobability sampling describes any method for collecting survey data which does not utilize a full probability sampling design. Nonprobability samples are usually cheaper and easier to collect than probability samples. However, there are a number of drawbacks.

What do you mean by non-probability sampling?
Non-probability sampling is a method of selecting units from a population using a subjective (i.e. non-random) method. Since non-probability sampling does not require a complete survey frame, it is a fast, easy and inexpensive way of obtaining data.Sep 2, 2021
What is an example of non probabilistic sampling?
Examples of nonprobability sampling include: Convenience, haphazard or accidental sampling – members of the population are chosen based on their relative ease of access. To sample friends, co-workers, or shoppers at a single mall, are all examples of convenience sampling.
What is the difference between probability and non-probability sampling methods?
Generally, nonprobability sampling is a bit rough, with a biased and subjective process. This sampling is used to generate a hypothesis. Conversely, probability sampling is more precise, objective and unbiased, which makes it a good fit for testing a hypothesis.Jul 22, 2019
What is the meaning of non-probability?
Web Service. OECD Statistics. French Equivalent: Sondage non probabiliste. Definition: A sample of units where the selected units in the sample have an unknown probability of being selected and where some units of the target population may even have no chance at all of being in the sample.Aug 21, 2002
What are the three types of non-probability sampling?
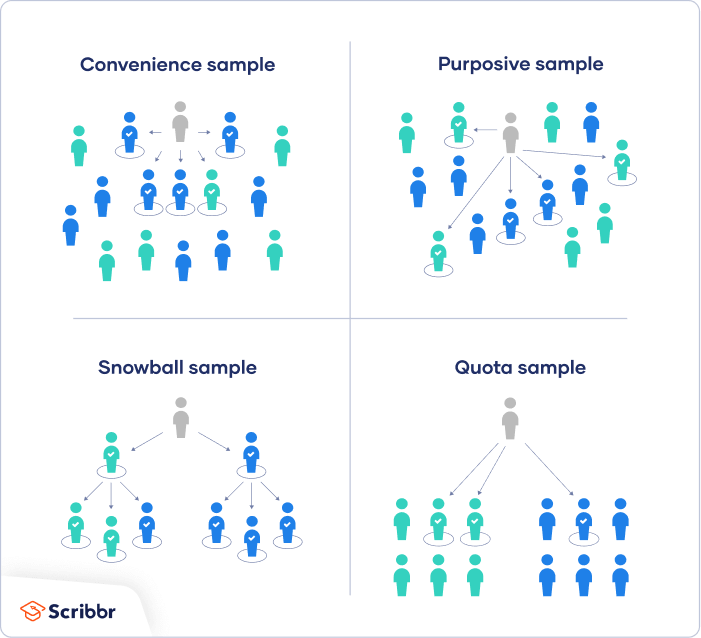
There are five main types of non-probability sample: convenience, purposive, quota, snowball, and self-selection.
What are the four types of non-probability sampling?
There are five types of non-probability sampling technique that you may use when doing a dissertation at the undergraduate and master's level: quota sampling, convenience sampling, purposive sampling, self-selection sampling and snowball sampling.
What is non-probability sampling and probability sampling?
There are two types of sampling methods: Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. Non-probability sampling involves non-random selection based on convenience or other criteria, allowing you to easily collect data.Sep 19, 2019
What are the advantages of non-probability sampling?
A major advantage with non-probability sampling is that—compared to probability sampling—it's very cost- and time-effective. It's also easy to use and can also be used when it's impossible to conduct probability sampling (e.g. when you have a very small population to work with).
What is probability and non-probability sampling examples?
Probability sampling is based on the fact that every member of a population has a known and equal chance of being selected. For example, if you had a population of 100 people, each person would have odds of 1 out of 100 of being chosen. With non-probability sampling, those odds are not equal.
What is non-probability sampling in qualitative research?
Entry. Subject Index Entry. Nonprobability sampling is a common technique in qualitative research where researchers use their judgment to select a sample.Dec 27, 2012
Which of the following is not an example of non-probability sampling?
In judgmental sampling researchers select units from the population based on their knowledge and judgement about the unit. This kind of sampling does not provide equal probability of a unit being chosen.
What’s the difference between method and methodology?
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and...
What’s the difference between quantitative and qualitative methods?
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Quantitative methods allow yo...
What is sampling?
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in...
What’s the difference between reliability and validity?
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something: Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the r...
What is the difference between internal and external validity?
I nternal validity is the degree of confidence that the causal relationship you are testing is not influenced by other factors or variables . Ext...
What is experimental design?
Experimental design means planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables . To design a controlled experiment, you ne...
What are independent and dependent variables?
You can think of independent and dependent variables in terms of cause and effect: an independent variable is the variable you think is the ca...
What is the difference between quantitative and categorical variables?
Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts (e.g. height, weight, or age). Categorical variables are any variables...
What is the difference between discrete and continuous variables?
Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables : Discrete variables represent counts (e.g. the number of objects in a...
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample. Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.
What is an example of random sampling?
The American Community Survey is an example of simple random sampling. In order to collect detailed data on the population of the US, the Census Bureau officials randomly select 3.5 million households per year and use a variety of methods to convince them to fill out the survey.
What is systematic sampling?
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method where researchers select members of the population at a regular interval – for example, by selecting every 15th person on a list of the population. If the population is in a random order, this can imitate the benefits of simple random sampling.
What is cluster sampling?
Cluster sampling is a probability sampling method in which you divide a population into clusters, such as districts or schools, and then randomly select some of these clusters as your sample. The clusters should ideally each be mini-representations of the population as a whole.
What is random selection?
Random selection, or random sampling, is a way of selecting members of a population for your study’s sample. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample into control and experimental groups.
What is a sample in research?
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
What is double blind study?
In a double-blind study, both participants and experimenters are blinded. In a triple-blind study, the assignment is hidden not only from participants and experimenters, but also from the researchers analyzing the data.
What are the types of non-probability samples?
There are five main types of non-probability sample: convenience, purposive, quota, snowball, and self-selection.
What is snowball sampling?
Snowball sampling. This is a type of convenience sampling in which those participants invited invite other participants and so on to create a pyramid effect. With probability sampling, you can choose a more scientific way to sample because you know the number and characteristics of the true population.
What are the two types of sampling?
There are two main types of samples: probability and nonprobability samples. Nonprobability samples are cases where you do not know of every unique member of the population in question (i.e., the entire user group in our case). Another way to describe it is when every member of the population does not have an equal chance of being invited to participate. Probability samples are when you do know of every unique member of the population and therefore each has a probabilistic chance of being invited for the sample (e.g., 100 users of a product, each has a 1/100 chance of being invited). Here's a taste of a couple of common nonprobability sampling techniques.
What are the advantages of web based surveys?
An advantage of Web-based surveys is that they are relatively easy to conduct. All that is needed is a Web site and some basic Web programming skills. Many surveys are created simply using Hypertext Markup Language (HTML); there are dozens of HTML editors available and they are becoming increasingly sophisticated and easy to use. Data from surveys can be captured either by programming the form to e-mail the data to a specified address or through a common gateway interface (CGI) script. Several HTML development packages automate the process of developing CGI scripts necessary to capture data from HTML forms. Internet survey companies have even developed computer programs that automatically create surveys.
What is a simple random sample?
Simple random samples (SRSs) constitute the reference standard against which all other samples are judged. The procedure for selecting a random sample requires two steps. First, make a list of all members of the population. Second, randomly select a specific number of cases from the total list.
What is quantitative research?
Quantitative research often begins with the researcher selecting the population (or universe) to be studied, based on the nature of the questions to be answered. The selected universe could be all the citizens of a designated nation, laborers in a sweatshop, or the homeless in a large urban center.
Why are survey panels so popular?
Because recruiting respondents over the Internet can be somewhat complicated, survey panels are popular. Rather than asking respondents to complete a single survey, Web-based survey panels recruit subjects to participate in a series of surveys. In order to obtain probability-based subjects, potential respondents are often initially contacted by telephone. Once respondents agree to participate in a survey panel, they are contacted by e-mail when they are required to complete a new survey. Using panels, researchers can draw samples from the registered respondents in order to undertake studies of specific subpopulations. Knowledge Networks claims that their Web-based survey panels is particularly effective for market research. Panels also offer the opportunity to examine temporal changes in respondent behavior and beliefs.