What are the characteristics of a phenol?
Phenols occur either as colourless liquids or white solids at room temperature and may be highly toxic and caustic. An oxygen atom normally forms two σ bonds with other atoms; the water molecule, H2O, is the simplest and most common example.... Phenols are widely used in household products and as intermediates for industrial synthesis.
Is phenol a solid liquid or gas?
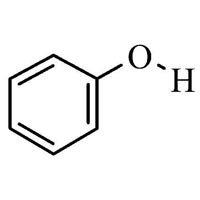
?) Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C 6 H 5 OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group (−C 6 H 5) bonded to a hydroxy group (−OH).
What is a phenol acid peel and does it work?
A phenol acid peel is the most aggressive, deep chemical peel available. This skin resurfacing procedure can be extremely effective at treating signs of severe sun damage, including deep wrinkles, fine lines, sunspots or freckles, and discoloration ( hyperpigmentation ), as well as acne scars, precancerous growths, and other blemishes.
What is the generic name for phenol?
Phenol, any of a family of organic compounds characterized by a hydroxyl (−OH) group attached to a carbon atom that is part of an aromatic ring. Besides serving as the generic name for the entire family, the term phenol is also the specific name for its simplest member, monohydroxybenzene (C6H5OH), also known as benzenol, or carbolic acid.
How do you identify phenol?
Compounds with a phenol group will form a blue, violet, purple, green, or red-brown color upon addition of aqueous ferric chloride. This reaction can be used as a test for phenol groups. To Conduct Demonstration: Mix several drops or a few crystals of compound to be tested in a beaker or in a 200mm test tube.
What is the Colour of phenol?
Colorless to light pink crystalline solid. [Note: Phenol liquefies by mixing with about 8% water.]
What is the structure of a phenol?
C6H6OPhenol / Formula
What do you use phenol for?
Phenol is used primarily in the production of phenolic resins and in the manufacture of nylon and other synthetic fibers. It is also used in slimicides (chemicals that kill bacteria and fungi in slimes), as a disinfectant and antiseptic, and in medicinal preparations such as mouthwash and sore throat lozenges.
What happens when phenol is exposed to air?
Phenol gets slowly oxidised to a pink coloured compound p-benzoquinone when exposed to air.
Does phenol turn red?
Chemical structure and properties A solution of phenol red is used as a pH indicator, often in cell culture. Its color exhibits a gradual transition from yellow (λmax = 443 nm) to red (λmax = 570 nm) over the pH range 6.8 to 8.2. Above pH 8.2, phenol red turns a bright pink (fuchsia) color. and is orange-red.
Can phenol cause death?
Accidental and intentional ingestions of phenol have been reported. As little as 50 to 500 mg has been fatal in infants. Deaths in adults have resulted after ingestions of 1 to 32 g.
How much phenol is toxic?
Phenol is a general protoplasmic poison (denatured protein) with corrosive local effects. Phenol derivates are less toxic than pure phenol. The lethal dose is between 3 to 30 g, but may be as little as 1 g. Phenol is well absorbed by inhalation, dermal application, and ingestion.
Is phenol toxic?
Phenol is highly irritating to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes in humans after acute (short-term) inhalation or dermal exposures. Phenol is considered to be quite toxic to humans via oral exposure.
Where can phenol be found?
Phenol is found to be present naturally in coal tar and creosote. It is also produced during natural fires, and through benzene degradation in the atmosphere under the influence of ultraviolet light radiation [14].
What is the another name of phenol?
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH.
Can you buy phenol over-the-counter?
You can buy over-the-counter phenol spray almost anywhere. The most common brand is Chloraseptic.
What color is phenol red?
Phenol red, also known as phenolsulfonphthalein, is a pH indicator dye that exhibits a gradual transition from yellow to red over a pH range of 6.2 to 8.2 (Figure 2). Above 8.2 the dye turns a bright fuchsia color.
What is the example of phenol?
In consumer products and as intermediates for industrial synthesis, phenols are commonly used. In household cleaners and in mouthwash, for example, phenol itself is used in low concentrations) as a disinfectant. It is likely that Phenol was the first surgical antiseptic.
Is phenol an alcohol?
Publisher Summary. Phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols. They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen.
What is the other name of phenol?
carbolic acidnoun Chemistry. Also called carbolic acid, hydroxybenzene, oxybenzene, phenylic acid. a white, crystalline, water-soluble, poisonous mass, C6H5OH, obtained from coal tar, or a hydroxyl derivative of benzene: used chiefly as a disinfectant, as an antiseptic, and in organic synthesis.
What is the precursor to polycarbonates?
Condensation with acetone gives bisphenol-A, a key precursor to polycarbonates and epoxide resins. Condensation of phenol, alkylphenols, or diphenols with formaldehyde gives phenolic resins, a famous example of which is Bakelite. Partial hydrogenation of phenol gives cyclohexanone, a precursor to nylon.
What is the route analogous to cumene?
It is oxidized to a hydroperoxide, akin to the production of cumene hydroperoxide. Via the Hock rearrangement, cyclohexylbenzene hydroperoxide cleaves to give phenol and cyclohexanone. Cyclohexanone is an important precursor to some nylons.
What is reduced to benzene when distilled with zinc dust?
Phenol is reduced to benzene when it is distilled with zinc dust or when its vapour is passed over granules of zinc at 400 °C: C 6 H 5 OH + Zn → C 6 H 6 + ZnO. When phenol is reacted with diazomethane in the presence of boron trifluoride (BF 3 ), anisole is obtained as the main product and nitrogen gas as a byproduct.
What is the name of the compound that reacts with dilute nitric acid at room temperature?
Phenol reacts with dilute nitric acid at room temperature to give a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol while with concentrated nitric acid, more nitro groups get substituted on the ring to give 2,4,6-trinitrophenol which is known as picric acid .
How much phenol is in scotch?
Phenol is a measurable component in the aroma and taste of the distinctive Islay scotch whisky, generally ~30 ppm, but it can be over 160ppm in the malted barley used to produce whisky. This amount is different from and presumably higher than the amount in the distillate.
What is the chemical formula for phenol?
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C 6 H 5 OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group (−C 6 H 5) bonded to a hydroxy group (−OH). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns .
Why is phenol acidic?
Resonance structures of the phenoxide anion. One explanation for why phenol is more acidic than aliphatic compounds containing an -OH group is resonance stabilization of the phenoxide anion by the aromatic ring. In this way, the negative charge on oxygen is delocalized on to the ortho and para carbon atoms through the pi system.
How is chlorobenzene converted to chlorobenzene?
Hydrolysis of chlorobenzene (the Dow process) Benzene is easily converted to chlorobenzene by a variety of methods, one of which is the Dow process. Chlorobenzene is hydrolyzed by a strong base at high temperatures to give a phenoxide salt, which is acidified to phenol.
Why are phenols highly reactive?
Phenols are highly reactive toward electrophilic aromatic substitution, because the nonbonding electrons on oxygen stabilize the intermediate cation. This stabilization is most effective for attack at the ortho or para position of the ring; therefore, the hydroxyl group of a phenol is considered to be activating (i.e., its presence causes the aromatic ring to be more reactive than benzene) and ortho- or para -directing.
How is benzene converted to isopropylbenzene?
Benzene is converted to isopropylbenzene (cumene) by treatment with propylene and an acidic catalyst. Oxidation yields a hydroperoxide ( cumene hydroperoxide ), which undergoes acid-catalyzed rearrangement to phenol and acetone. Although this process seems more complicated than the Dow process, it is advantageous because it produces two valuable industrial products: phenol and acetone.
How much hydrogen bond does phenol form in water?
The ability of phenols to form strong hydrogen bonds also enhances their solubility in water. Phenol dissolves to give a 9.3 percent solution in water, compared with a 3.6 percent solution for cyclohexanol in water.
What was the purpose of the phenol used in 1865?
In 1865 the British surgeon Joseph Lister used phenol as an antiseptic to sterilize his operating field. With phenol used in this manner, the mortality rate from surgical amputations fell from 45 to 15 percent in Lister’s ward.
What is the name of the compound that is attached to a carbon atom?
phenol, any of a family of organic compounds characterized by a hydroxyl (―OH) group attached to a carbon atom that is part of an aromatic ring. Besides serving as the generic name for the entire family, the term phenol is also the specific name for its simplest member, monohydroxybenzene (C 6 H 5 OH), also known as benzenol, or carbolic acid. ...
What is BHT in food?
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) has a much lower toxicity and is a common antioxidant in foods. In industry, phenol is used as a starting material to make plastics, explosives such as picric acid, and drugs such as aspirin.
What makes a phenol?
phenol, any of a family of organic compounds characterized by a hydroxyl (―OH) group attached to a carbon atom that is part of an aromatic ring. ... Phenols are similar to alcohols but form stronger hydrogen bonds. Thus, they are more soluble in water than are alcohols and have higher boiling points.
How does phenol look like?
Phenol is a type of organic compound. While toxic to consume on its own, it's available in tiny doses in many household products like mouthwash and spray cleaners. In its pure form, it may be colorless or white. It has a mildly sugary scent that might remind you of somewhere that's sterile, such as a hospital room.
Is Phenol A planar?
Examples of phenolic compounds. All carbon atoms forming aromatic ring are sp 2 hybridized. Therefore, phenyl has hexagonal planar structure with all bond angles 120° and delocalized π-electrons distributed over the ring. The C-O bond is formed from Csp 2 -Osp 3 and the O-H bond is formed from Osp 3 -H1s.
What makes a phenol?
phenol, any of a family of organic compounds characterized by a hydroxyl (―OH) group attached to a carbon atom that is part of an aromatic ring. ... Phenols are similar to alcohols but form stronger hydrogen bonds. Thus, they are more soluble in water than are alcohols and have higher boiling points.
How does phenol look like?
Phenol is a type of organic compound. While toxic to consume on its own, it's available in tiny doses in many household products like mouthwash and spray cleaners. In its pure form, it may be colorless or white. It has a mildly sugary scent that might remind you of somewhere that's sterile, such as a hospital room.
Is Phenol A planar?
Examples of phenolic compounds. All carbon atoms forming aromatic ring are sp 2 hybridized. Therefore, phenyl has hexagonal planar structure with all bond angles 120° and delocalized π-electrons distributed over the ring. The C-O bond is formed from Csp 2 -Osp 3 and the O-H bond is formed from Osp 3 -H1s.
What is a phenol peel?
A phenol acid peel is the most aggressive, deep chemical peel available. This skin resurfacing procedure can be extremely effective at treating signs of severe sun damage, including deep wrinkles, fine lines, sunspots or freckles, and discoloration ( hyperpigmentation ), as well as acne scars, precancerous growths, and other blemishes.
What are the pros and cons of a phenol peel?
A phenol chemical peel can improve the quality of your skin in just a single treatment, yielding dramatic results.
How much does a phenol peel cost?
The price you pay will depend on your provider’s level of experience, their practice location, whether you have IV sedation, and other details of your procedure.
How does a phenol peel work?
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid) exfoliates so deeply that it removes the outer layers of skin, eradicating damaged skin cells, promoting collagen production, improving acne scarring, and resurfacing skin. When you’ve fully healed, you’ll be left with a smoother, younger-looking layer of skin.
Are phenol peels dangerous?
When administered by an experienced plastic surgeon or dermatologist and for the right candidate (someone with a fair skin tone, a low risk of hyperpigmentation, and no underlying medical issues), phenol peel treatments can be safe.
How long does it take for a phenol peel to heal?
Most people can return to their normal activities about two weeks after a phenol peel, and you can start applying makeup at that point, if you’re healing well.
What is needed for a face peel?
This type of peel requires a sedative and/or IV anesthesia during the procedure, as well as an anesthetic cream to numb your face.
Is phenol acidic or basic?
Phenol is a very weak acid and the position of equilibrium lies well to the left. Phenol can lose a hydrogen ion because the phenoxide ion formed is stabilised to some extent. The negative charge on the oxygen atom is delocalised around the ring.
What is phenol used for medically?
Phenol is used to relieve pain and irritation caused by sore throat, sore mouth, or canker sores. This medicine is available without a prescription; however, your doctor may have special instructions on the proper use and dose for your medical problem.
How do you detect phenol?
Dissolve the given organic compounds in water. Add neutral solution of ferric chloride slowly dropwise. Observe the change in colour. A red, blue, green or purple colouration indicates the presence of phenol.
What does phenol do to the body?
Phenol is considered to be quite toxic to humans via oral exposure. Anorexia, progressive weight loss, diarrhea, vertigo, salivation, a dark coloration of the urine, and blood and liver effects have been reported in chronically (long-term) exposed humans.
What is the formula of formaldehyde?
Formaldehyde is a colorless gas synthesized by the oxidation of methanol. The chemical formula for the highly toxic organic chemical compound is CH2O. Its CAS number is 50-00-0. In solution, formaldehyde has a wide range of uses.
What is the general formula of Alcohol & phenol?
Phenols differ from alcohols in that they are slightly acidic in water. They react with aqueous sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form salts. The parent compound, C6H5OH, is itself called phenol.
What is a condensed structural formula?
Condensed structural formulas show the order of atoms like a structural formula but are written in a single line to save space and make it more convenient and faster to write out. Condensed structural formulas are also helpful when showing that a group of atoms is connected to a single atom in a compound.
What is Shell Chemicals?
The expression “Shell Chemicals” refers to the companies of the Royal Dutch/Shell Group which are engaged in chemical businesses. Each of the companies which make up the Royal Dutch/Shell Group of companies is an independent entity and has its own separate identity.
How many gallon tanks does Shell have?
Shell's tank car fleet consists of 23,500 gallon lined tank cars which are insulated and equipped with low pressure steam external heating coils. Tank cars are equipped with facilities for top unloading only through a two inch line extending to the bottom of the car. A one inch inert gas connection is also included to allow unloading by pumping and/or pressurization.
What is phenol used for?
Phenol is a reactive organic chemical which is used in a wide variety of chemical products vital to the economy of the world. It is reacted in various ways with aldehydes, e.g., formaldehyde, to form what are commonly known as "phenolic resins", materials which are strong, water resistant and have good dielectric properties. They, in turn, are widely used as adhesives (plywood binders, brake linings, counter tops, insulation), structural shapes (automotive parts, electrical fixtures) and electrical laminates (circuit boards). Other uses for phenol include the manufacture of caprolactam (an intermediate in the manufacture of nylon), bisphenol-A (an intermediate in the manufacture of epoxy resins and polycarbonate engineering thermoplastics), herbicides, wood preservatives, hydraulic fluids, heavy duty surfactants, lube oil additives and extraction aids, pharmaceuticals, disinfectant materials, tank linings and coating materials, and as intermediates for plasticizers and other specialty chemicals.
Does Shell ship phenol?
Shell has facilities to load phenol into ocean-going vessels and barges. Due to the specialized nature of equipment required to handle marine parcels of phenol, early discussions with your Shell Sales Representative are necessary to determine the availability and proper configuration of equipment.
Overview
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group (−C6H5) bonded to a hydroxy group (−OH). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.
Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion k…
Properties
Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol to water mass ratios of ~2.6 and higher are possible. The sodium salt of phenol, sodium phenoxide, is far more water-soluble.
Phenol is a weak acid. In aqueous solution in the pH range ca. 8 - 12 it is in eq…
Production
Because of phenol's commercial importance, many methods have been developed for its production, but the cumene process is the dominant technology.
Accounting for 95% of production (2003) is the cumene process, also called Hock process. It involves the partial oxidation of cumene (isopropylbenzene) via …
Uses
The major uses of phenol, consuming two thirds of its production, involve its conversion to precursors for plastics. Condensation with acetone gives bisphenol-A, a key precursor to polycarbonates and epoxide resins. Condensation of phenol, alkylphenols, or diphenols with formaldehyde gives phenolic resins, a famous example of which is Bakelite. Partial hydrogenation of phenol gives cyclohexanone, a precursor to nylon. Nonionic detergents are produced by alkylatio…
History
Phenol was discovered in 1834 by Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge, who extracted it (in impure form) from coal tar. Runge called phenol "Karbolsäure" (coal-oil-acid, carbolic acid). Coal tar remained the primary source until the development of the petrochemical industry. In 1841, the French chemist Auguste Laurent obtained phenol in pure form.
In 1836, Auguste Laurent coined the name "phène" for benzene; this is the root of the word "phen…
Occurrences
Phenol is a normal metabolic product, excreted in quantities up to 40 mg/L in human urine.
The temporal gland secretion of male elephants showed the presence of phenol and 4-methylphenol during musth.
It is also one of the chemical compounds found in castoreum. This compound is ingested from the plants the beaver eats.
Biodegradation
Cryptanaerobacter phenolicus is a bacterium species that produces benzoate from phenol via 4-hydroxybenzoate. Rhodococcus phenolicus is a bacterium species able to degrade phenol as sole carbon source.
Toxicity
Phenol and its vapors are corrosive to the eyes, the skin, and the respiratory tract. Its corrosive effect on skin and mucous membranes is due to a protein-degenerating effect. Repeated or prolonged skin contact with phenol may cause dermatitis, or even second and third-degree burns. Inhalation of phenol vapor may cause lung edema. The substance may cause harmful effects on the central nervous system and heart, resulting in dysrhythmia, seizures, and coma. The kidneys m…