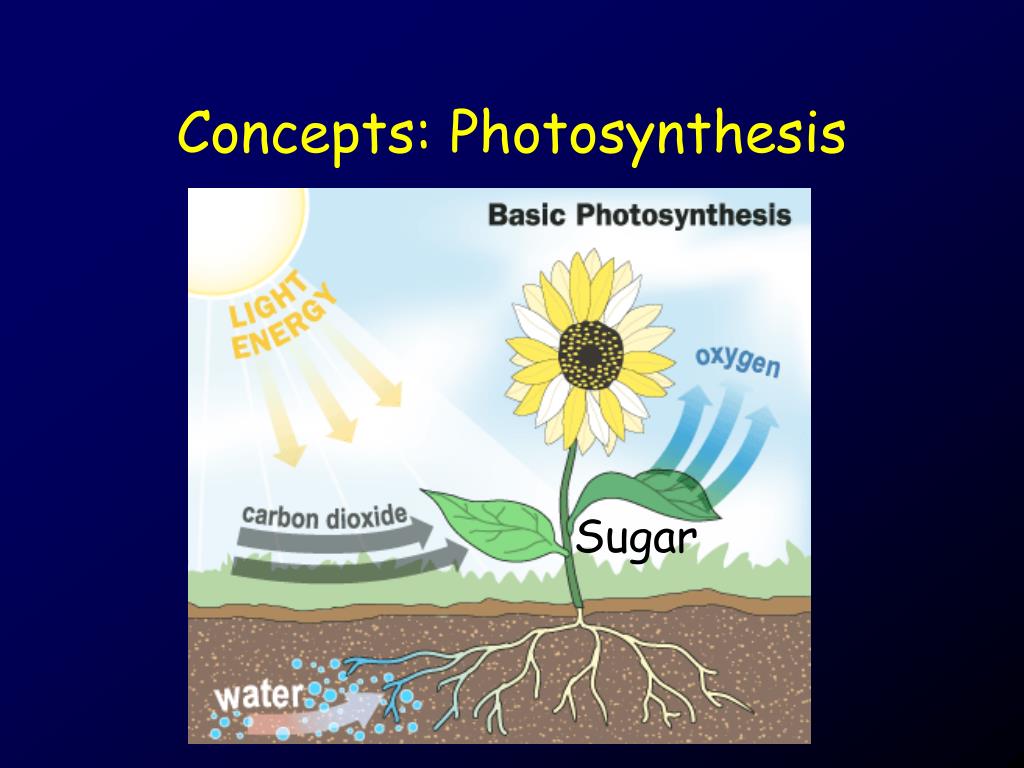
Which compound is released by photosynthesis?
There are different types of photosynthesis, including C3 photosynthesis and C4 photosynthesis. C3 photosynthesis is used by the majority of plants. It involves producing a three-carbon compound called 3-phosphoglyceric acid during the Calvin Cycle, which goes on to become glucose.
What are the three things needed for photosynthesis?
What are the three things needed for photosynthesis?
- Light intensity. Without light, plants cannot photosynthesize, even if there is enough water and carbon dioxide in the environment.
- Carbon dioxide concentration. Carbon dioxide is a necessary reagent for the process to occur.
- Amount of chlorophyll. ...
- Water. ...
- Temperature. ...
- Minerals and nutrients. ...
What is the final product of photosynthesis?
The products and reactants for photosynthesis are reversed in cellular respiration: The reactants of photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water, which are the products of cellular respiration.
What organisms are capable of photosynthesis?
What are 5 organisms that use photosynthesis?
- Plants.
- Algae (Diatoms, Phytoplankton, Green Algae)
- Euglena.
- Bacteria (Cyanobacteria and Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria)

What is released during photosynthesis?
Within the plant cell, the water is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons, while the carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose. The plant then releases the oxygen back into the air, and stores energy within the glucose molecules.
What does photosynthesis release into the atmosphere?
Plants use photosynthesis to capture carbon dioxide and then release half of it into the atmosphere through respiration. Plants also release oxygen into the atmosphere through photosynthesis.
What are the products of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose. Glucose is used as food by the plant and oxygen is a by-product. Cellular respiration converts oxygen and glucose into water and carbon dioxide.
What is the final output of photosynthesis?
Glucose and oxygen are the final products of photosynthesis.
Does photosynthesis release water into the atmosphere?
The leaves of the plant release this oxygen into the atmosphere. Photosynthesis produces water as well. The oxygen atoms in the carbon dioxide molecules contain this water.
What is produced and released into the atmosphere?
During cellular respiration, glucose and oxygen are changed into energy and carbon dioxide. Therefore, carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere during the process of cellular respiration. Respiration is also the process by which once-living (organic) organisms are decomposed.
Does photosynthesis add oxygen to the atmosphere?
Oxygen (O2) production by photosynthesis is by far the dominant global process that replenishes atmospheric and oceanic oxygen essential to sustain all aerobic life.
What does photosynthesis remove from the atmosphere?
Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide naturally — and trees are especially good at storing carbon removed from the atmosphere by photosynthesis.
Why is photosynthesis important?
The last requirement for photosynthesis is an important one because it provides the energy to make sugar. How does a plant take carbon dioxide and water molecules and make a food molecule? The Sun! The energy from light causes a chemical reaction that breaks down the molecules of carbon dioxide and water and reorganizes them to make the sugar (glucose) and oxygen gas. After the sugar is produced, it is then broken down by the mitochondria into energy that can be used for growth and repair. The oxygen that is produced is released from the same tiny holes through which the carbon dioxide entered. Even the oxygen that is released serves another purpose. Other organisms, such as animals, use oxygen to aid in their survival.
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
If we were to write a formula for photosynthesis, it would look like this: 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light energy → C6H12O6 (sugar) + 6O2. The whole process of photosynthesis is a transfer of energy from the Sun to a plant.
How do plants make glucose?
By taking in water (H2O) through the roots, carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air, and light energy from the Sun, plants can perform photosynthesis to make glucose (sugars) and oxygen (O2). CREDIT: mapichai/Shutterstock.com
What happens to oxygen after sugar is produced?
After the sugar is produced, it is then broken down by the mitochondria into energy that can be used for growth and repair. The oxygen that is produced is released from the same tiny holes through which the carbon dioxide entered. Even the oxygen that is released serves another purpose.
Why are plants called autotrophs?
Plants are called autotrophs because they can use energy from light to synthesize, or make, their own food source. Many people believe they are “feeding” a plant when they put it in soil, water it, or place it outside in the Sun, but none of these things are considered food. Rather, plants use sunlight, water, and the gases in the air to make glucose, which is a form of sugar that plants need to survive. This process is called photosynthesis and is performed by all plants, algae, and even some microorganisms. To perform photosynthesis, plants need three things: carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight.
What do plants need to survive?
Rather, plants use sunlight, water, and the gases in the air to make glucose, which is a form of sugar that plants need to survive. This process is called photosynthesis and is performed by all plants, algae, and even some microorganisms. To perform photosynthesis, plants need three things: carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight.
What gas does a plant use to make photosynthesis?
Plants, however, take in and use carbon dioxide gas. for photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide enters through tiny holes in a plant’s leaves, flowers, branches, stems, and roots.
What is the process of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the chemical process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use the energy from sunlight to transform carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) from the atmosphere, and water, into organic compounds such as sugars. These sugars are then used to make complex carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, as well as the wood, leaves, ...
How long has photosynthesis been around?
The subsequent rise in atmospheric oxygen (a byproduct of photosynthesis) about a billion years later played a major role in shaping the evolution of life on Earth over the last 2.5 billion years.
What is the process of eutrophication?
This process is known as eutrophication. Human freshwater use, which can limit the amount of water available for plants and trees in an ecosystem. The release of pollutants and waste, which can reduce growth and reproduction or kill plants.
What is the purpose of fertilizer?
The use of fertilizers for agricultural activities that increase the amount of nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorous, in soil or water. These nutrients increase plant and algae growth, including growth of species that are toxic to other organisms. Increased nutrients is not always a good thing.
How do species affect biomass?
Species that reduce or increase the success of other species alter population sizes, thus affecting productivity and biomass. Evolutionary processes that can change the growth and reproduction rates of photosynthesizing organisms over time, as well as the growth and reproduction of rates of the organisms that eat them.
What are the nutrients that are used in photosynthesizing?
Nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorus, which when limited can decrease productivity, but when abundant can increase productivity and biomass. Photosynthesizing organisms extract nutrients from the environment, and return them to the soil when they die and decay.
How have humans altered the rate of photosynthesis?
Humans have altered the rate of photosynthesis, and in turn productivity, in ecosystems through a variety of activities, including: Deforestation, habitat destruction, and urbanization, which remove plants and trees from the environment and disrupt ecosystems.
What is the process of photosynthesis?
The photosynthesis process on Earth is responsible for the oxygen that is in the atmosphere. Without plants and other green living things that turn light energy from the sun into chemical nutrients for the plant, releasing oxygen into the atmosphere, life would probably not exist in its form today. Sciencing_Icons_Science.
When did the photosynthesis process increase?
University of California Merced Professor Elliott Campbell and his team of researchers noted in an April 2017 article in "Nature," an international journal of science, that the photosynthesis process increased dramatically during the 20th century. The research team discovered a global record of the photosynthetic process straddling two hundred years.
What happens when the stomata closes?
When the stomata close, photosynthesis cannot occur, as the plant cannot take in carbon dioxide. This causes carbon dioxide levels in the plant to drop. When the daylight hours become too hot and dry, the stroma closes to conserve moisture.
Why do stomata close?
Stomata exist on the bottom of leaves, facing away from the sun, to minimize water loss. Little guard cells surrounding the stomata control the opening and closing of these mouth-like openings by swelling or shrinking in response to the amount of water in the atmosphere. When the stomata close, photosynthesis cannot occur, as the plant cannot take in carbon dioxide. This causes carbon dioxide levels in the plant to drop. When the daylight hours become too hot and dry, the stroma closes to conserve moisture.
How does respiration occur in plants?
Respiration occurs within the plant cell happens when the sugars produced during the photosynthetic process combines with oxygen to make energy for the cell, forming carbon dioxide and water as byproducts of respiration. A simple equation for respiration is opposite that of photosynthesis: glucose + oxygen = energy + carbon dioxide + light energy.
What is the light absorbing pigment in plants?
Chlorophyll is the light-absorbing pigment, inside the leaves of plants and trees, that begins the photosynthesis process. As an organic pigment within the chloroplast thylakoid, chlorophyll only absorbs energy within a narrow band of the electromagnetic spectrum produced by the sun within the wavelength range of 700 nanometers (nm) to 400 nm. Called the photosynthetically active radiation band, green sits in the middle of the visible light spectrum separating the lower energy, but longer wavelength reds, yellows and oranges from the high energy, shorter wavelength, blues, indigoes and violets.
How much did plant photosynthesis increase?
This led them to conclude that the total of all plant photosynthesis on the planet grew by 30 percent during the years they researched. While the research did not specifically identify the cause of an uptick in the photosynthesis process globally, the team's computer models suggest several processes, when combined, that could result in such a large increase in global plant growth.