
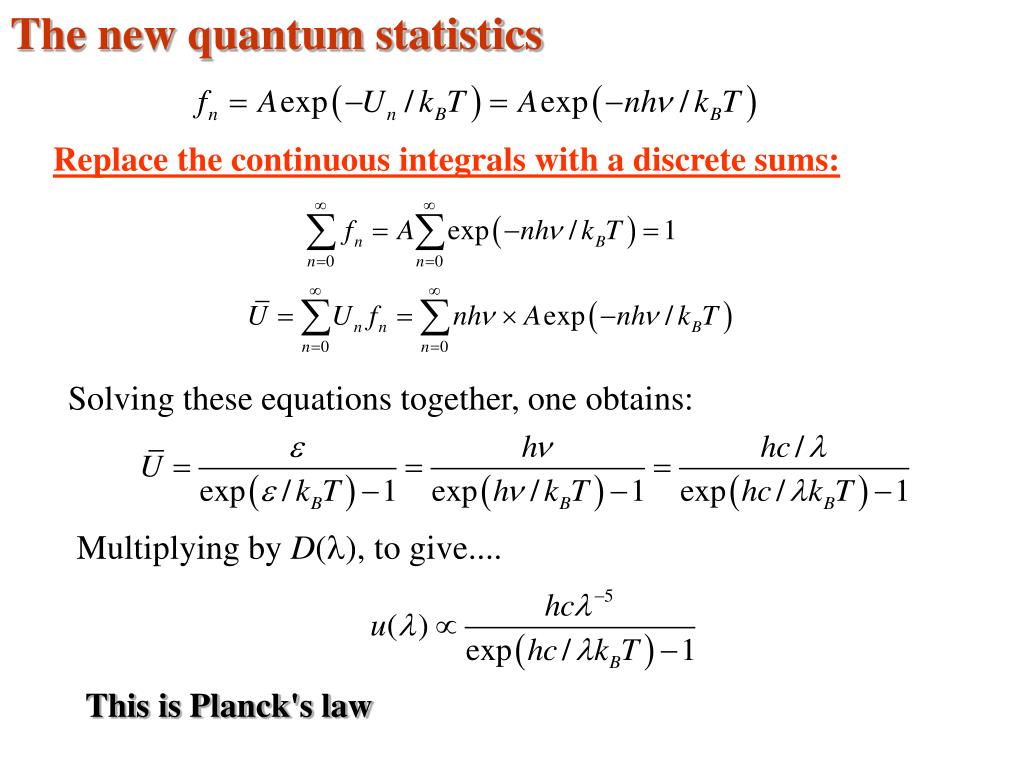
Planck’s Law – Planck’s Hypothesis
- Bν(v,T) is the spectral radiance (the power per unit solid angle and per unit of area normal to the propagation) density of frequency ν radiation per unit frequency at thermal ...
- h is the Planck constant
- c is the speed of light in a vacuum
- kB is the Boltzmann constant
- ν is the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation
What does Planck's theory state?
What is Planck’s Quantum Theory?
- Matter radiates energy or absorbs energy in discrete quantities, discontinuously in the form of small packets or bundles.
- The smallest bundle or packet of energy is known as quantum. In the case of light, a quantum of light is known as a photon.
- The energy of the quantum absorbed or emitted is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. ...
What did Planck contribute to the atomic theory?
What did Planck contribute to the atomic theory? He proposed that only certain amounts of energy could be emitted – i.e. quanta. Classical physics held that all values of energy were possible. This was the birth of quantum theory. Planck found that his new theory, based on quanta of energy, accurately predicted the wavelengths of ]
What does Planck's curve explain?
Planck Curve Planck Curve: The quantum theory of absorption and emission of radiation announced in 1900 by Planck ushered in the era of modern physics. He proposed that all material systems can absorb or give off electromagnetic radiation only in "chunks" of energy, quanta E, and that these are proportional to the frequency of that radiation E = h.
How did Planck discover his constant?
How did Planck discover his constant? In principle, the Planck constant can be determined by examining the spectrum of a black-body radiator or the kinetic energy of photoelectrons, and this is how its value was first calculated in the early twentieth century. The Planck constant (Planck’s constant) links the amount of energy a photon carries ...
What does Planck's quantum theory state?
According to Planck's quantum theory, Different atoms and molecules can emit or absorb energy in discrete quantities only. The smallest amount of energy that can be emitted or absorbed in the form of electromagnetic radiation is known as quantum.
What does Planck's law say?
Planck's Law Of course, the sun is a big nuclear furnace, so it makes sense that it emits all sorts of electromagnetic radiation. However, Planck's Law states that every object emits over the entire electromagnetic spectrum. That means that you emit radiation at all wavelengths, and so does everything around you!
What is Planck's constant theory?
Planck's constant is the ratio of a particle's energy to its frequency. Mathematically this is written h = E ÷ f, where h is the symbol for the constant. So, if a particle's frequency increases, its energy must also increase. If its frequency decreases, its energy will decrease as well.
What is Planck's law simple?
Planck's law in British English noun. physics. a law that is the basis of quantum theory, which states that the energy of electromagnetic radiation is confined to indivisible packets (quanta), each of which has an energy equal to the product of the Planck constant and the frequency of the radiation.
What was Planck's assumption of the nature of energy?
Planck found that the energy radiated from a heated body is exactly proportional to the wavelength of its radiation. So, a black body would not radiate all frequencies equally. As temperature goes up, energy increases and it's more likely that quanta with higher energy will be radiated.
What are the main postulates of Planck's quantum theory?
Planck's quantum theory states the following postulates:The energy is not radiated or emitted continuously. ... Radiation when in the form of light, each particle is known as a photon. ... The energy of a photon or one quantum of energy is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.More items...
What did Planck discover?
Max Planck was a German theoretical physicist who discovered the quantum of action, now known as Planck's constant, h, in 1900. This work laid the foundation for quantum theory, which won him the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1918.
What are the assumptions of Planck's law?
Answer to Problem 1Q. Planck's made two assumptions, that the energy of radiating oscillator is quantized and the emission or absorption of energy in discrete packets.
What are the basic postulates of Planck's law of radiation?
Postulates of Planck's quantum theory The energy is not radiated or emitted continuously. It is emitted in small proportions in the form of energy packets called quanta. 2. Radiation when in the form of light, each particle is known as a photon.
Which law is used for radiation?
Planck's law: The primary law governing blackbody radiation is Planck's Radiation Law. According to Planck's law, every body will emit radiation at all wavelengths and at all times.
Answer
Max Planck suggested that the energy of light is proportional to its frequency, also showing that light exists in discrete quanta of energy.so C is the most logical answer
Answer
Correct answer is C (Energy radiated by a body is in the form of packets called quanta)
New questions in Physics
Hello, happy new year. pls help me.Could you please tell me the words and phrases that apply to (1) to (6)? (In the case of a numerical value, it is 3 …
What is Planck’s Quantum Theory?
Planck’s quantum theory explains emission and absorption of radiation. Postulates of Planck’s quantum theory are as follows –
What did scientists discover about the nature of energy?
By the end of 19th century, scientists were able to explain most of the natural phenomenon by Newton’s Laws of classical mechanics or classical theory. By this time matter and energy used to considered as distinct and unrelated. Scientists were able to define the properties of radiant energy by Maxwell’s equations given by James Clerk Maxwell, a Scottish Physics in 1873. However, by the 20th century scientists were able to discover that phenomenon such as black body radiation, photoelectric effect can’t be explained by classical theory or classical mechanics. During this time, German physicist Max Planck put forward his theory of quantized nature of energy of electromagnetic wave. In this article we will discuss Max Planck’s quantum theory of radiation or quantum theory of radiation, black body radiation, electromagnetic radiation, evidences for a particle theory of energy.
What is Planck's law?
Planck’s law for the energy Eλradiated per unit volume by a cavity of a blackbody in the wavelength interval λ to λ + Δλ (Δλ denotes an increment of wavelength) can be written in terms of Planck’s constant (h), the speed of light(c), the Boltzmann constant(k), and the absolute temperature(T):
What is Planck's radiation law?
Planck’s radiation law, a mathematical relationship formulated in 1900 by German physicist Max Planck to explain ...
What did Planck assume about radiation?
Planck assumed that the sources of radiation are atoms in a state of oscillation and that the vibrational energy of each oscillator may have any of a series of discrete values but never any value between. Planck further assumed that when an oscillator changes from a state of energy E1 to a state of lower energy E2, ...
What theory of light did physicists accept?
By the end of the 19th century, physicists almost universally accepted the wave theory of light. However, though the ideas of classical physics explain interference and diffraction phenomena relating to the propagation of light, they do not account for the absorption and…
Which theory of light was accepted by physicists at the end of the 19th century?
Read More on This Topic. quantum mechanics: Planck’s radiation law. By the end of the 19th century, physicists almost universally accepted the wave theory of light. However, though the ideas of classical...
Who is Max Planck?
Max Planck, German theoretical physicist who originated quantum theory, which won him the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1918. Planck made many contributions to theoretical physics, but his…. History at your fingertips. Sign up here to see what happened On This Day, every day in your inbox!
When did physicists accept the wave theory of light?
By the end of the 19th century, physicists almost universally accepted the wave theory of light. However, though the ideas of classical...
What is Planck's law?
Planck's law describes the spectral density of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium at a given temperature T, when there is no net flow of matter or energy between the body and its environment.
How does Planck's law explain radiation?
Planck's law describes the unique and characteristic spectral distribution for electromagnetic radiation in thermodynamic equilibrium, when there is no net flow of matter or energy. Its physics is most easily understood by considering the radiation in a cavity with rigid opaque walls. Motion of the walls can affect the radiation. If the walls are not opaque, then the thermodynamic equilibrium is not isolated. It is of interest to explain how the thermodynamic equilibrium is attained. There are two main cases: (a) when the approach to thermodynamic equilibrium is in the presence of matter, when the walls of the cavity are imperfectly reflective for every wavelength or when the walls are perfectly reflective while the cavity contains a small black body (this was the main case considered by Planck); or (b) when the approach to equilibrium is in the absence of matter, when the walls are perfectly reflective for all wavelengths and the cavity contains no matter. For matter not enclosed in such a cavity, thermal radiation can be approximately explained by appropriate use of Planck's law.
What theory predicts that the total blackbody radiation intensity is infinite?
Classical physics led, via the equipartition theorem , to the ultraviolet catastrophe, a prediction that the total blackbody radiation intensity was infinite. If supplemented by the classically unjustifiable assumption that for some reason the radiation is finite, classical thermodynamics provides an account of some aspects of the Planck distribution, such as the Stefan–Boltzmann law, and the Wien displacement law. For the case of the presence of matter, quantum mechanics provides a good account, as found below in the section headed Einstein coefficients. This was the case considered by Einstein, and is nowadays used for quantum optics. For the case of the absence of matter, quantum field theory is necessary, because non-relativistic quantum mechanics with fixed particle numbers does not provide a sufficient account.
When did Planck first write about black body radiation?
Planck first turned his attention to the problem of black-body radiation in 1897. Theoretical and empirical progress enabled Lummer and Pringsheim to write in 1899 that available experimental evidence was approximately consistent with the specific intensity law Cλ−5e−c⁄λT where C and c denote empirically measurable constants, and where λ and T denote wavelength and temperature respectively. For theoretical reasons, Planck at that time accepted this formulation, which has an effective cut-off of short wavelengths.
What is Lambert's cosine law?
As explained by Planck, a radiating body has an interior consisting of matter, and an interface with its contiguous neighbouring material medium, which is usually the medium from within which the radiation from the surface of the body is observed.
Why can't you convert between the different forms of Planck's law?
In general, one may not convert between the various forms of Planck's law simply by substituting one variable for another, because this would not take into account that the different forms have different units. Wavelength and frequency units are reciprocal.
Who was Max Planck's teacher?
Gustav Kirchhoff was Max Planck’s teacher and surmised that there was a universal law for blackbody radiation and this was called “Kirchhoff’s challenge.” Planck, a theorist, believed that Wilhelm Wien had discovered this law and Planck expanded on Wien’s work presenting it in 1899 to the meeting of the German Physical Society. Experimentalists Otto Lummer, Ferdinand Kurlbaum, Ernst Pringsheim, and Heinrich Rubens did experiments that appeared to support Wien’s law especially at higher frequency short wavelengths which Planck so wholly endorsed at the German Physical Society that it began to be called the Wien-Planck Law. However, by September 1900, the experimentalists had proven beyond a doubt that the Wein-Planck law failed at the shorter wavelengths. They would present their data on October 19. Planck was informed by his friend Rubens and quickly created a formula within a few days. In June of that same year, Lord Raleigh had created a formula that would work for short lower frequency wavelengths based on the widely accepted theory of equipartition. So Planck submitted a formula combining both Raleigh’s Law (or a similar equipartition theory) and Wien’s law which would be weighted to one or the other law depending on wavelength to match the experimental data. However, although this equation worked, Planck himself said unless he could explain the formula derived from a “lucky intuition” into one of “true meaning” in physics, it did not have true significance. Planck explained that thereafter followed the hardest work of his life. Planck did not believe in atoms, nor did he think the second law of thermodynamics should be statistical because probability does not provide an absolute answer, and Boltzmann’s entropy law rested on the hypothesis of atoms and was statistical. But Planck was unable to find a way to reconcile his Blackbody equation with continuous laws such as Maxwell’s wave equations. So in what Planck called “an act of desperation,” he turned to Boltzmann’s atomic law of entropy as it was the only one that made his equation work. Therefore, he used Boltzmann’s constant k and his new constant h to explain the Blackbody radiation law which became widely known through his published paper.
What is Planck's law?
Planck’s Law: It states that electromagnetic radiation from heated bodies is not emitted as a continuous flow but is made up of discrete units or quanta of energy, the size of which involve a fundamental physical constant (Planck’s constant). Mathematically, Where, h = Planck’s Constant =. k = Boltzmann’s Constant = 1.381 × 10 -23 J/K.
What is Planck’s Equation?
The variable h holds the constant value equal to 6.63 x 10-34 J.s based on International System of Units and the variable describes the frequency in s-1. The Planck’s law help us calculate the energy of photons when their frequency is known.
What is Plank's constant?
Put differently, Plank’s constant describes the relevancy between the energy per quantum (photon) of electromagnetic radiation to its frequency.
Introduction
Table of Contents
Black Body Radiation
- Solids, when heated, emit radiation varying over a wide range of wavelengths. For example: when we heat solid colour, changes continue with a further increase in temperature. This change in colour happens from a lower frequency region to a higher frequency region as the temperature increases. For example, in many cases, it changes from red to blue. An ideal body which can emi…
Black Body Radiation
- Planck’s quantum theory
According to Planck’s quantum theory, 1. Different atoms and molecules can emit or absorb energy in discrete quantities only. The smallest amount of energy that can be emitted or absorbed in the form of electromagnetic radiation is known as quantum. 2. The energy of the radiation ab…
Black Body Radiation
- According to the temperature, all objects emit electromagnetic radiation. Objects having low temperature emit radio or microwaves (low-frequency waves) while objects having high temperature emit visible or ultraviolet light or even higher frequency radiations. A black body is an idealized object that can absorb all electromagnetic radiation that comes in contact with it. Afte…
What Is Planck’s Quantum Theory?
- Planck’s quantum theory explains the emission and absorption of radiation. Postulates of Planck’s quantum theory are as follows – 1. Matter radiates energy or absorbs energy in discrete quantities, discontinuously in the form of small packets or bundles. 2. The smallest bundle or packet of energy is known as quantum. In the case of light, a quantum...
The Discovery of Quantum
- The photoelectric effect is difficult to account for using the wave model. When light is focused on certain metals, it emits electrons, creating this effect. There is a minimum frequency of EM radiation at which the effect will occur for each metal. In contrast to what would be expected if light functioned strictly like a wave, replacing light with twice the intensity and half the frequenc…
Evidence in Support of Planck’s Quantum Theory
- Many experiments were performed to analyze Planck’s quantum theory. All experimental observations supported and worked as strong evidence for quantum theory. All shows that the energy of electron motion in the matter is quantized. A prism can separate the light according to its wavelengths. If light behaves only as a wave, then the prism should give a continuous rainbo…
Applications of Planck’s Quantum Theory
- Planck’s quantum theory is the fundamental theory of quantum mechanics. So, it has applications in all those fields where quantum mechanics is being used. It has applications in electrical appliances, the medical field, quantum computing, lasers, quantum cryptography etc.
Key Points
- Newtonian physics dominated the scientific worldview until the late 19th century. However, physicists discovered in the early 20th century that the laws of classical mechanics do not apply at the a...
- The photoelectric effect could not be explained using existing light theories since an increase in light intensity did not result in the same outcome as an increase in light energy.
- Newtonian physics dominated the scientific worldview until the late 19th century. However, physicists discovered in the early 20th century that the laws of classical mechanics do not apply at the a...
- The photoelectric effect could not be explained using existing light theories since an increase in light intensity did not result in the same outcome as an increase in light energy.
- Planck proposed that the energy of light is proportional to frequency, and Planck's constant (h) is the constant that relates them. Albert Einstein determined that light is made up of discrete quan...