
Statistical Notation of Parameter and Statistics
| Statistics | Parameter |
| x̄ = Sample Mean | μ = Population Mean |
| s = Sample Standard Deviation | σ = Population Standard Deviation |
| p̂ = Sample Proportion | P = Population Proportion |
| x = Data Elements | X = Data Elements. |
What is used to estimate the population parameter?
There are two types of estimates: point and interval. A point estimate is a value of a sample statistic that is used as a single estimate of a population parameter. Interval estimates of population parameters are called confidence intervals.
Which describes a population parameter?
Updated on May 14, 2019. In statistics, a population parameter is a number that describes something about an entire group or population. This should not be confused with parameters in other types of math, which refer to values that are held constant for a given mathematical function. Note also that a population parameter is not a statistic, which is data that refers to a sample, or subset, of a given population.
How do population and variables differ in statistics?
explain how populations and variables differ a population is a set of units of interest to a study. a variable is a characteristic or property of the units being studied what is statistics?
Which symbol represents a population parameter?
The population mean and standard deviation are two common parameters. In statistics, Greek symbols usually represent population parameters, such as μ (mu) for the mean and σ (sigma) for the standard deviation. A statistic is a characteristic of a sample.
How do you define a population parameter?
A parameter is any summary number, like an average or percentage, that describes the entire population. The population mean (the greek letter "mu") and the population proportion p are two different population parameters.
What is a population parameter in statistics example?
A parameter is a number describing a whole population (e.g., population mean), while a statistic is a number describing a sample (e.g., sample mean). The goal of quantitative research is to understand characteristics of populations by finding parameters.
What is the difference between sample statistics and population parameter?
sample statistic. When you collect data from a population or a sample, there are various measurements and numbers you can calculate from the data. A parameter is a measure that describes the whole population. A statistic is a measure that describes the sample.
Are population parameters random variables?
All statistics are estimators of population parameters that are calculated from samples and therefore all statistics are random variables.
What happens if the population distribution is normal?
If we know that the population distribution is normal, then the sampling distribution will also be normal, regardless of the size of the sample. If the population is not normal, meaning it’s either skewed right or skewed left, then we must employ the Central Limit Theorem.
What is sampling distribution?
A sampling distribution is a probability distribution obtained from a larger number of samples drawn from a specific population. In other words, it’s the distribution of frequencies for a range of different outcomes that could occur for a statistic of a given population.
What is sampling error?
Sampling error is the error that occurs because of chance variation. It’s the difference between a statistic and parameter (i.e., the difference between the sample and the population). The best way to reduce sampling error is to increase the sample size. Some errors can occur with the choice of sampling, such as convenient sampling, ...
What is the type of error that occurs when sampling?
This type of error is called non-sampling error.
What letters are used to identify parameters?
We typically use Greek letters like mu and sigma to identify parameters, and English letters like x-bar and p-hat to identify statistics.
Is the bite from the apple a sample statistic?
But if the bite from the apple is mushy, then you can infer that the rest of the apple is mushy and bad to eat. Hence, the bite from the apple is a sample statistic, and the conclusion you draw relates to the entire apple, or the population parameter.
What are population parameters?
Population parameters refer to the statistical measures that are fixed and when used as variables, they make the population distribution descriptive hen ce descriptive statistics. A good example of population parameters is the mean and variance in a normal distribution. When these two variables are clearly stated it is possible to determine ...
What is a point estimate of a population parameter?
The point estimate of a population parameter on the other hand is a statistical value used to describe that particular population. An example of this is the mean of sample data which is taken to be the point estimate of the mean for the population. The point estimate of a population can never be 100% precise but the level of accuracy is dependent on the characteristics of the distribution that is whether it is a normal distribution, t – distribution, chi-square distribution, and so on. The level of errors in the point estimate can be known from the shape of the distribution and this also applies to the credibility of the point estimate. In other words, the point estimate of a population parameter refers to the most reliable estimate available to that parameter.
What is the difference between standard deviation and variance?
Both variance and standard deviation are used to determine the same statistical inference, but the difference is that standard deviation has units of measurement which are the same as that of the population in question while variance does not. Besides measuring the variability from the mean, the standard deviation also measures the degree ...
What is the assumption of the mean of the population?
The mean of the population is the anticipated outcome in that when the unbounded number of observations is considered, it results in the average of the same number of observations.
What does standard deviation mean?
Standard deviation refers to the measure of variation from the mean. When this value is low, it is an indication that the observations are clustered around the mean and when it is high, the observations seem to be dispersed away from the mean.
What is range in statistics?
Range in descriptive statistics is the value of the distance between the least observation and the greatest observation. In a normal distribution, this is calculated by subtracting the variable with the least number of observations from the variable with the greatest number of observations. The range is usually measured according to the units used in the population or sample. If the observation is in the currency, for example, the range will be in the currency as well.
Why is a sample drawn from a population?
This is why a sample is drawn from the population for statistical inference. A sample is a representation of the whole population normally drawn from the population under scrutiny. This is what is studied in statistics and ...
What is population parameter?
Population Parameter. In statistics, a population is defined as a set of all the observations of a study or experiment. To understand the nature of the population, some quantitative measurements of the population a needed and that measurement of the population is defined as population parameter. Thus, population parameter is a characteristic ...
What is population in science?
A population is defined as a set of all the observations of a study or experiment. To understand the nature of the population, some quantitative measurements of the population are needed that is defined as population parameter.
What is the difference between mean and standard deviation?
Consider that mean will give the central tendency measure about the population and standard deviation will give the measure of dispersion about the population. Thus, both mean and standard deviation exhibit some features of the population.
What is the population mean if the sample mean and standard error are and s?
More specifically, if a sample mean and standard error are and s, respectively, then the population mean will lie between .
What is the mean of a sample used for?
This mean of the sample is used as an estimator of the population mean.
What is a well defined sample?
A well-defined sample is stated as a subset of a population, where each element in the sample has an equal chance to be included in the sample from population. Thus, sample can be called a small version of population, which contains the main features of population.
Is mean and standard deviation a population parameter?
In this case, the mean and standard deviation are considered as population parameters.
What is parameter in statistics?
A parameter is a value that describes a characteristic of an entire population, such as the population mean. Because you can almost never measure an entire population, you usually don’t know the real value of a parameter. In fact, parameter values are nearly always unknowable.
What is sampling in statistics?
In statistics, sampling refers to selecting a subset of a population. After drawing the sample, you measure one or more characteristics of all items in the sample, such as height, income, temperature, opinion, etc. If you want to draw conclusions about these characteristics in the whole population, it imposes restrictions on how you collect the sample. If you use an incorrect methodology, the sample might not represent the population, which can lead you to erroneous conclusions.
How to get an unbiased sample?
The most well-known method to obtain an unbiased, representative sample is simple random sampling. With this method, all items in the population have an equal probability of being selected. This process helps ensure that the sample includes the full range of the population. Additionally, all relevant subpopulations should be incorporated into the sample and represented accurately on average. Simple random sampling minimizes the bias and simplifies data analysis.
Why do we use sample statistics?
You want unbiased estimates because they are correct on average. In inferential statistics, we use sample statistics to estimate population parameters.
Why are inferential statistics important?
Consequently, inferential statistics provide enormous benefits because typically you can’t measure an entire population.
How can subpopulations improve your analysis?
Subpopulations can Improve Your Analysis. Subpopulations share additional attributes. For instance, the population of the United States contains the subpopulations of men and women. You can also subdivide it in other ways such as region, age, socioeconomic status, and so on.
Why should you include male and female subpopulations in your analysis?
For example, if you’re analyzing the average height of adults in the United States, you’ll improve your results by including male and female subpopulations because their heights are systematically different . I’ll cover that example in depth later in this post!
What is population in science?
A population is a group of phenomena that have something in common. The term often refers to a group of people, as in the following examples: Often, researchers want to know things about populations but do not have data for every person or thing in the population.
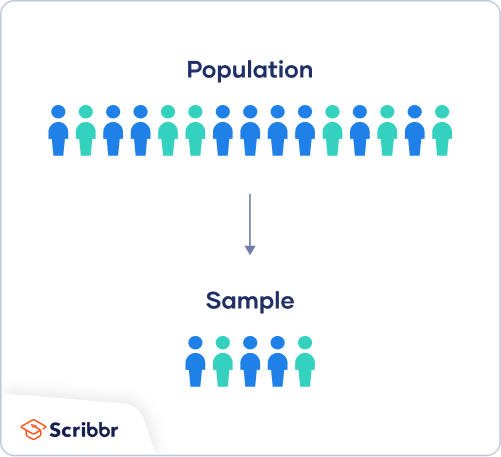
What is a sample in statistics?
A sample is a smaller group of members of a population selected to represent the population. In order to use statistics to learn things about the population, the sample must be random. A random sample is one in which every member of a population has an equal chance of being selected.
What is the field of inferential statistics?
The field of inferential statistics enables you to make educated guesses about the numerical characteristics of large groups. The logic of sampling gives you a way to test conclusions about such groups using only a small portion of its members. A population is a group of phenomena that have something in common.
What is the most commonly used sample?
The most commonly used sample is a simple random sample . It requires that every possible sample of the selected size has an equal chance of being used. A parameter is a characteristic of a population. A statistic is a characteristic of a sample.
What is parameter statistics?
A parameter in statistics implies a summary description of the characteristic of an entire population based on all the elements within it. For instance, all the children in one city, all female workers in a country, all the items in grocery stores globally, and so on.
Which is more reliable, parameter or statistics?
Parameter is more reliable, and dependable on the survey and statistics is less dependable on the survey
What is the difference between a sample and a statistic?
It is basically a part or portion of a population. While the parameter is drawn from the measurements of units in the entire population , a sample is drawn from the measurement of elements from the sample.
When is statistics used?
Statistics is used to get the actual outcome with respect to a certain characteristic and parameter is used to get the most possible estimated outcome
Is a random sample a good representative?
Only then would you be able to generalize conclusions for the whole population. A random sample here is most probably a good representative of a population.
Is a parameter a variable or a variable?
A parameter is fixed and unknown while the statistics is a variable and known number
What is a parameter in statistics?
Statistics - Parameters and Statistics. The terms 'parameter' and (sample) 'statistic' refer to key concepts that are closely related in statistics. They are also directly connected to the concepts of populations and samples.
What does sample statistics give us?
Sample statistics gives us estimates for parameters.
What are the two types of values describing how spread out the values are?
Variance and standard deviation are two types of values describing how spread out the values are.
What is parameter in statistics?
In statistics, a parameter is a number that describes some characteristic of a population.
What is parameter of interest?
A parameter of interest is the specific parameter that we’re interested in estimating during a data collection process.
Why do researchers collect random samples?
Since it’s often too time-consuming and costly to collect data on every individual element in a population, researchers will collect a random sample from the population and use a sample statistic to estimate the population parameter.
What is a parameter in statistics?
A parameter in statistics is the true value of something.
What is the difference between a population and a sample?
In the field of Statistics, we distinguish between parameters, which are values that define populations, and statistics, which are values that define samples. (If you need to review the difference: Population vs Sample .) For example, both populations and samples have averages. They are computed in the same way: add up all of the values that make up the distribution and divide by the number of values in the distribution. When that average is calculated from a whole population, it is called Mu (pronounced like “mew”) and when it is calculated from a sample it is called the Mean. Similarly, Sigma
What is a parameter of interest?
Parameter means some kind of number, like an average or a median. A parameter of interest is what your data is focused on. Perhaps you want to know the average weight of a 17 year old boy, your parameter of interest is the average weight of a 17 year old boy. Parameters are about an entire population, so you must state your population. Is it 17 year old boys worldwide, or in your country, or in your city, or in your high school? When you don’t have data about the entire population from a census, you will often use a sample statistic to approximate the parameter of interest. So instead of colle
How to estimate the number of deer in a forest?
Let's take capture/recapture as an example. You want to estimate the number of deer in a particular forest, so you go out, tag all the deer you find, and let them go. Then you come back the next day, do the same thing, and count the proportion of deer you find which have already been tagged. A little algebra on these numbers will give you an estimate of how many deer are in the forest.
Why do we draw samples from a population?
In statistics we draw samples from a population in order to be able to make inferences about that population . To do this we begin by making assumptions about how the values in the population are distributed.
Why is there not a census every year?
Not every year there is a Census and sometimes may not be any. That’s because it is hard to undertake and conduct such an encompassing study . Whatever the reason may be, if one wants to “ Estimate” the M, without a “ Census” the alternative is to take a Random Sample of size ‘n’ from that population age group satisfying the conditions of a “ Random sampl
What is interpolation and extrapolation?
Interpolation and Extrapolation is used to raise sample values to arrive at population values. Regression analysis

Sample Statistics vs Population Parameters
Sampling Error
Sampling Distribution
What Is The Central Limit Theorem?
How to Find Population Parameters
- Now, with all samples, surveys, or experiments, there is the possibility of error. Sampling erroris the error that occurs because of chance variation. It’s the difference between a statistic and parameter (i.e., the difference between the sample and the population). The best way to reduce sampling error is to increase the sample size. Some errors can occur with the choice of samplin…
Population Parameter – Lesson & Examples
- But why do we care? Well, we hope to draw inferences about probability distributions by analyzing sampling distributions. A sampling distributionis a probability distribution obtained from a larger number of samples drawn from a specific population. In other words, it’s the distribution of frequencies for a range of different outcomes that could occur for a statistic of a given population…
A Population Parameter and Its Point Estimate.
- The Central Limit Theorem (CLT) states that if a random sample of n observations is drawn from a non-normal population, and if n is large enough, then the sampling distribution becomes approximately normal (bell-shaped). In other words, the central limit theorem allows us to accurately predict a population’s characteristics when the sample size is sufficiently large. So, w…
A Population and A Corresponding Sample Mean
- For example, suppose a highway construction zone, with a speed limit of 45 mph, is known to have an average vehicle speed of 51 mph with a standard deviation of five mph, what is the probability that the mean speed of a random sample of 40 cars is more than 53 mph? Together, we will look at how to find the sample mean, sample standard deviation, and sample proportion…
Range
- 1 hr 11 min 1. Introduction to Video: Sample Means and Sample Proportions 2. 00:00:37– What is the difference between a parameter and a statistic? with Example #1 3. Exclusive Content for Members Only 1. 00:09:07– Identify the parameter and statistic for the following scenarios (Examples #2-4) 2. 00:14:09– Create a population distribution and a sampling distribution (Exam…
Variance
- Population parameters refer to the statistical measures that are fixed and when used as variables, they make the population distribution descriptive hence descriptive statistics. A good example of population parameters is the mean and variance in a normal distribution. When these two variables are clearly stated it is possible to determine the type...
Standard Deviation
- The population in statistics refers to the whole collection of objects being analyzed. This could be students in a school, vehicles in a certain street, trees in a forest, and patients in a hospital among others. A population consists of all the numbers of objects available irrespective of how many they are. Since it consists of a large number of objects, populations cannot be studied in their entiret…