What does a negatively skewed distribution mean?
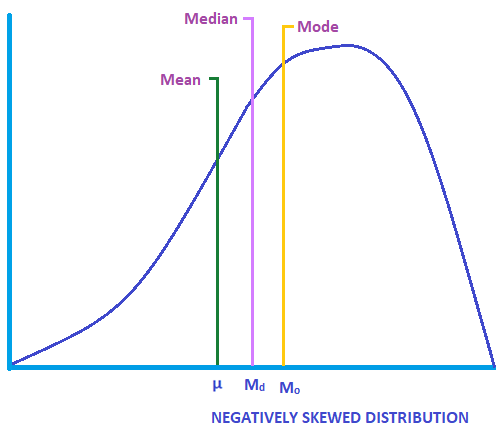
In statistics, a negatively skewed (also known as left-skewed) distribution is a type of distribution in which more values are concentrated on the right side (tail) of the distribution graph while the left tail of the distribution graph is longer. While normal distribution is the most commonly encountered type of distribution, examples of the negatively skewed distributions are also widespread in real life.
What does positively skewed Meann meaning?
What does positively skewed mean in statistics? In statistics, a positively skewed (or right-skewed) distribution is a type of distribution in which most values are clustered around the left tail of the distribution while the right tail of the distribution is longer. Click to see full answer.
What is skewed distribution?
The skewed distribution is a type of distribution whose mean value does not directly coincide with its peak value. Skewness is the measure of the asymmetricity of a distribution. Symmetric distribution is the one whose two halves are mirror images of each other.
What is positive and negative skewness?
The rule of thumb seems to be:
- If the skewness is between -0.5 and 0.5, the data are fairly symmetrical.
- If the skewness is between -1 and -0.5 (negatively skewed) or between 0.5 and 1 (positively skewed), the data are moderately skewed.
- If the skewness is less than -1 (negatively skewed) or greater than 1 (positively skewed), the data are highly skewed.

What does a positively skewed distribution tell us?
In a positively skewed distribution, most values on the graph are on the left side, and the curve is longer towards the right trail. In this distribution, the mean is greater than the median. In finance, it is the chance for more profits than the loss.
What does it mean if a distribution is a positively skewed distribution?
What is a Positively Skewed Distribution? In statistics, a positively skewed (or right-skewed) distribution is a type of distribution in which most values are clustered around the left tail of the distribution while the right tail of the distribution is longer.
Is positively skewed a good thing?
A positive skew could be good or bad, depending on the mean. A positive mean with a positive skew is good, while a negative mean with a positive skew is not good.
What causes a positively skewed distribution?
These distributions tend to occur when there is a lower limit, and most values are relatively close to the lower bound. Values can't be less than this bound but can fall far from the peak on the high end, causing them to skew positively.
How do you interpret skewed data?
Interpreting. If skewness is positive, the data are positively skewed or skewed right, meaning that the right tail of the distribution is longer than the left. If skewness is negative, the data are negatively skewed or skewed left, meaning that the left tail is longer.
What does it mean if the data is skewed in statistics?
Skewed data is data that creates an asymmetrical, skewed curve on a graph. In statistics, the graph of a data set with normal distribution is symmetrical and shaped like a bell. However, skewed data has a "tail" on either side of the graph.
Is a positively skewed distribution normal?
A skewed distribution is neither symmetric nor normal because the data values trail off more sharply on one side than on the other. In business, you often find skewness in data sets that represent sizes using positive numbers (eg, sales or assets).
How do you deal with positively skewed data?
Dealing with skew data:log transformation: transform skewed distribution to a normal distribution. ... Remove outliers.Normalize (min-max)Cube root: when values are too large. ... Square root: applied only to positive values.Reciprocal.Square: apply on left skew.More items...
What does positively skewed histogram mean?
In other words, some histograms are skewed to the right or left. With right-skewed distribution (also known as "positively skewed" distribution), most data falls to the right, or positive side, of the graph's peak. Thus, the histogram skews in such a way that its right side (or "tail") is longer than its left side.
What does it mean if a distribution is skewed positively or negatively?
A distribution is skewed if one of its tails is longer than the other. The first distribution shown has a positive skew. This means that it has a long tail in the positive direction. The distribution below it has a negative skew since it has a long tail in the negative direction.
When the distribution is positively skewed mean median mode?
In case of a positively skewed frequency distribution, the mean is always greater than median and the median is always greater than the mode.
What is a CFI?
CFI is the official provider of the Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst ( FMVA)™ Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)®CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today! certification program, designed to transform anyone into a world-class financial analyst.
What does positive skewness mean?
The positive skewness of a distribution indicates that an investor may expect frequent small losses and a few large gains from the investment. The positively skewed distributions of investment returns are generally more desirable by investors since there is some probability to gain huge profits that can cover all the frequent small losses.
Why is skewness not desirable?
Since a high level of the skewness can generate misleading results from statistical tests, the extreme positive skewness is not desirable for a distribution. In order to overcome such a problem, data transformation tools may be employed to make the skewed data closer to a normal distribution.
What is a right skewed distribution?
In statistics, a positively skewed (or right-skewed) distribution is a type of distribution in which most values are clustered around the left tail of the distribution while the right tail of the distribution is longer. The positively skewed distribution is a direct opposite of the negatively skewed distribution.
Where is the mean in a positively skewed distribution?
In contrast to a negatively skewed distribution, in which the mean is located on the left from the peak of distribution, in a positively skewed distribution, the mean can be found on the right from the distribution’s peak.
What is a histogram?
Histogram A histogram is used to summarize discrete or continuous data. In other words, a histogram provides a visual interpretation of numerical data by showing the number of data points that fall within a specified range of values (called “bins”). A histogram is similar to a vertical bar graph. However, a histogram,
What is frequency polygon?
Frequency Polygon Frequency PolygonA frequency polygon is a visual representation of a distribution. The visualization tool is used to understand the shape of a distribution. Essentially, the
What is a skew-normal distribution?
A skew-normal distribution is a normal distribution with an extra parameter that skews its shape to either the left or the right. Given the fact that the only thing that changes is the skew of the normal distribution, it shares many characteristics with the normal distribution, such as:
What does it mean when a chart skews left?
Left-skewed distribution, also called negatively skewed distribution, refers to the situation when the chart has a longer tail in the negative direction of its number line. Judging a chart's distribution is not usually done based on the position of the peak value. The elements that constitute a negatively skewed distribution are:
What is a right skewed graph?
A right-skewed distribution, also called a positive skew distribution, is when the chart's tail is longer on its right side and its peak veers to the left. Although there are exceptions, most right-skewed distributions have the mean to the right of the median. Given the fact that a right-skewed graph has no clear center point, it is usually difficult to assign it a typical value, as opposed to a normal distribution with its mean, median and mode equally distributed around the center of the data set.
What is the average human life span?
The average human life span chart is skewed left. If the chart shows values from 1 to 100, representing years of life, the data would show that most people live to around 75 to 80 years old. This means that the chart's tail is longer on its left side, as the values around 75 and 80 are closer to 100 than to 1. It also means that the chart's peak, meaning the average human life span, is closer to the right of the chart.
What happens if the skew value is zero?
The skew value is different from zero. If the value is zero, the skew-normal distribution becomes a normal distribution
How can skewed distribution help you?
Learning about skewed distribution can help you improve your knowledge of statistics. Regardless of how you use statistics in your line of work, knowing what skewed distribution is and how to interpret it can have a direct impact on your job success. Being familiar with skewed distribution is a valuable skill, but it requires research and practice. In this article, we discuss what skewed distribution is, explain the meaning of the distribution skewing left or right and provide examples of skewed distribution.
Why is the chart skew right?
One of the main reasons for the occurrence of a right-skewed distribution is that the chart's lower limits are considerably lower than the rest of the chart's data, causing the entire chart to skew right.
What Does Skewness Tell You?
Investors note skewness when judging a return distribution because it, like kurtosis, considers the extremes of the data set rather than focusing solely on the average. Short- and medium-term investors in particular need to look at extremes because they are less likely to hold a position long enough to be confident that the average will work itself out.
What is negatively skewed distribution?
Negatively-skewed distributions are also known as left-skewed distributions. Skewness is used along with kurtosis to better judge the likelihood of events falling in the tails of a probability distribution.
What is the difference between a negative skew and a positive skew?
Negative skew refers to a longer or fatter tail on the left side of the distribution, while positive skew refers to a longer or fatter tail on the right. The mean of positively skewed data will be greater than the median. In a distribution that is negatively skewed, the exact opposite is the case: the mean of negatively skewed data will be less ...
How does Pearson's second coefficient of skewness work?
Pearson’s second coefficient of skewness, or Pearson median skewness, subtracts the median from the mean, multiplies the difference by three, and divides the product by the standard deviation.
Why is skewness used in kurtosis?
Skewness is used along with kurtosis to better judge the likelihood of events falling in the tails of a probability distribution.
What is skewed data?
Skewness refers to a distortion or asymmetry that deviates from the symmetrical bell curve, or normal distribution, in a set of data. If the curve is shifted to the left or to the right, it is said to be skewed. Skewness can be quantified as a representation of the extent to which a given distribution varies from a normal distribution.
What is negative skew?
In the curve of a distribution, the data on the right side of the curve may taper differently from the data on the left side. These taperings are known as "tails.". Negative skew refers to a longer or fatter tail on ...
Why is the right skewed distribution so skewed?
Analysts also refer to them as positively skewed. This condition occurs because probabilities taper off more slowly for higher values. Consequently, you’ll find extreme values far from the peak on the high end more frequently than on the low.
What is a skewed distribution?
A skewed distribution occurs when one tail is longer than the other. Skewness defines the asymmetry of a distribution. Unlike the familiar normal distribution with its bell-shaped curve, these distributions are asymmetric. The two halves of the distribution are not mirror images because the data are not distributed equally on both sides of the distribution’s peak.
What does skewed data mean?
When data are skewed, they do not follow a normal distribution. You might need to use a distribution test to identify the distribution of your data. The following probability distributions are skewed:
Why is the direction of the long tail important?
The crucial point to keep in mind is that the direction of the long tail defines the skew because it indicates where you’ll find the majority of exceptional values.
What is right skewed mean?
Right-skewed: The mean is greater than the median. The mean overestimates the most common values.
Do left skewed distributions exist?
Left-skewed distributions occur less frequently than their right handed counterparts, but they exist. Frequently, they occur when there is an upper limit that values cannot exceed, and most scores are near that limit. Values can’t exceed the cap, but they can extend relatively far from the peak on the lower side, causing a negative skew.
Which direction does the probability of events tapers off?
The normal distribution has a central peak where most observations occur, and the probability of events tapers off equally in both the positive and negative directions on the X-axis. Both halves contain equal numbers of observations. Unusual values are equally likely in both tails.
What Is Normal Distribution?
Before we explain what it means when data is skewed right , let's review the definition of normal distribution.
What Does Skewed Right Mean?
While normal distribution is one of the most common forms of distribution, not all data sets follow this basic curve. In other words, some histograms are skewed to the right or left.
What Causes a Right-Skewed Histogram?
Data skewed to the right is usually a result of a lower boundary in a data set (whereas data skewed to the left is a result of a higher boundary). So if the data set's lower bounds are extremely low relative to the rest of the data, this will cause the data to skew right.
Why is it so hard to assign a typical value on a right skewed graph?
By contrast, with normal distribution, because the mean, median, and mode are all equal and come at the center of the data set, you can easily use this value to more accurately generalize the data.
Why is there a skew in the data?
Another cause of skewness is start-up effects. For example, if a procedure initially has a lot of successes during a long start-up period, this could create a positive skew on the data. (On the opposite hand, a start-up period with several initial failures can negatively skew data.)
What is the difference between mean, median, and mode?
In this case, the mode is the highest point of the histogram, whereas the median and mean fall to the right of it (or, visually, the right of the peak). Note that the mean will always be to the right of the median.

Central Tendency Measures in Positively Skewed Distributions
Positively Skewed Distribution in Finance
- In finance, the concept of skewness is utilized in the analysis of the distribution of the returns of investments. Although many finance theories and models assume that the returns from securitiesfollow a normal distribution, in reality, the returns are usually skewed. The positive skewness of a distribution indicates that an investor may expect fr...
Additional Resources
- CFI is the official provider of the Business Intelligence & Data Analyst (BIDA)®certification program, designed to transform anyone into a world-class financial analyst. To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional CFI resources below: 1. Cumulative Frequency Distribution 2. Frequency Polygon 3. Harmonic Mean …