
When to worry about premature atrial contractions?
Premature Atrial Contractions or SVE / APCs are generally harmless. Even VPCs are often harmless – ‘benign’. If they are frequent - more than 5 per hour, 2 or more beats coming consecutively – they are investigated further. ECHOcardiogram is done to see the heart valves ( Mitral Valve Prolapse) / heart muscle ( Cardiomyopathy) and heart ...
What are the causes of premature atrial contractions?
- Stress
- Stimulants Caffeine Tobacco Alcohol
- Underlying Heart Disease Hypertension Valve disorder Previous myocardial infarct
- Abnormal blood levels of magnesium and/or potassium
- Digitalis toxicity
What causes PACs and PVCs?
What causes pacs and pvcs? Author Master Reading 7 min Views 37. Low blood oxygen. It can occur if you have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pneumonia. Several drugs, including decongestants. Elevated adrenaline levels that can be caused by caffeine, exercise, and anxiety. High blood pressure.
What is Pac on EKG?
ECG Library Homepage. A premature atrial complex (PAC) is a premature beat arising from ectopic pacemaking tissue within the atria. There is an abnormal P wave, usually followed by a normal QRS complex. AKA: Atrial ectopics, atrial extrasystoles, atrial premature beats, atrial premature depolarisations.
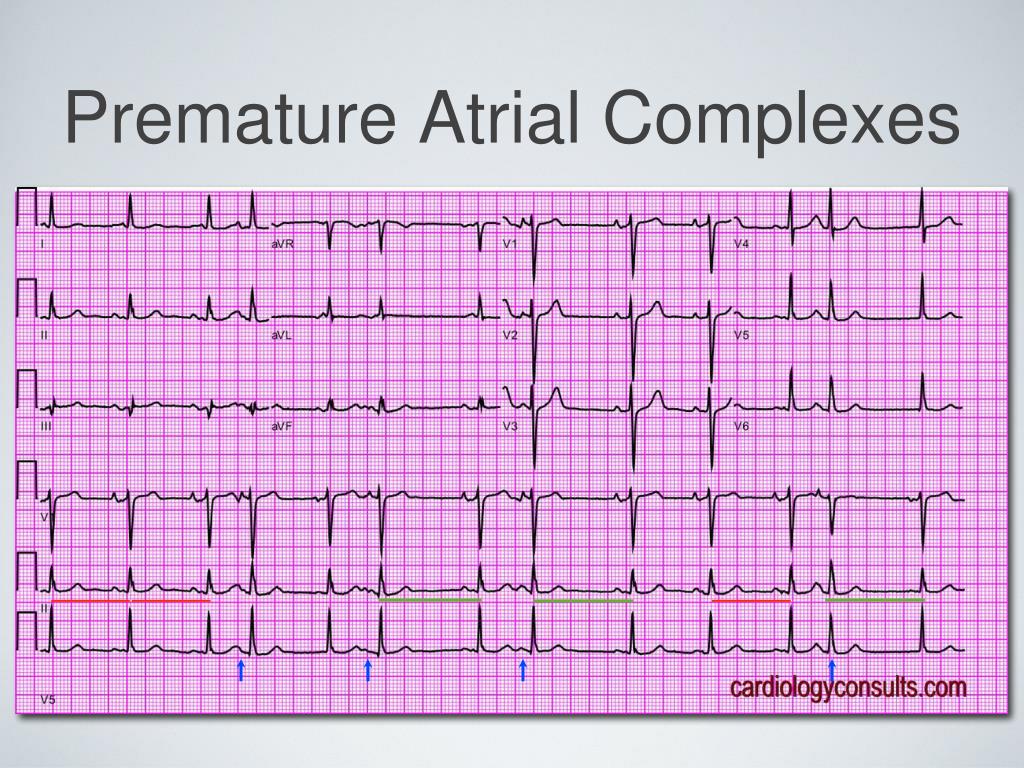
How do they fix premature atrial complexes?
Your provider may treat your premature atrial contractions with:Medication (such as beta blockers).Catheter ablation (rare).
What can cause premature atrial complexes?
Causes of Premature Atrial ContractionsHigh blood pressure.Long history of cigarette smoking and/or drug abuse.Excessive amounts of alcohol consumption over the years.Excessive amount of caffeine or other stimulants.Little to no physical activity.Extreme levels of anxiety.
When should I worry about premature atrial contractions?
Usually, premature atrial contractions have no clear cause and no health risks. In most cases, premature atrial contractions aren't a sign of heart disease and just happen naturally. But some people who have PACs turn out to have related heart conditions, such as: Cardiomyopathy (a weakened heart muscle)
What is premature atrial complex on ECG?
ECG Library Homepage. A premature atrial complex (PAC) is a premature beat arising from ectopic pacemaking tissue within the atria. There is an abnormal P wave, usually followed by a normal QRS complex. AKA: Atrial ectopics, atrial extrasystoles, atrial premature beats, atrial premature depolarisations.
Can PACs cause stroke?
ISCHEMIC STROKE Larsen et al reported a nearly 2-fold increased risk of stroke in patients with frequent PACs, independent of AF, a finding confirmed in a subsequent meta-analysis. 1,10 This association is also noted for PACs and cryptogenic stroke.
Is premature atrial contractions life threatening?
APCs could mean you have extra connections in your heart's electrical system. These extra connections may cause your heart to occasionally beat irregularly. Although this may be frightening or annoying, it's usually not dangerous unless you experience premature beats often or they impact the quality of your life.
What medications treat PACs?
PAC patients may also experience dizziness or chest pain. Treatment for symptomatic patients includes medications such as beta blockers or calcium blockers.
Can anxiety cause PACs?
Anxiety often causes ectopic beats, and they will usually go away by themselves. There are two types of ectopic heartbeat: Premature atrial contractions (PAC), which originate in the upper chambers, or atria. Premature ventricular contractions (PVC), which originate in the lower chambers, or ventricles.
Do PACs lead to AFIB?
Aims: Premature atrial contractions (PACs) are a common cardiac phenomenon, traditionally considered to be of little clinical significance. Recent studies, however, suggest that PACs are associated with atrial fibrillation (AF), as well as ischaemic stroke, transient ischaemic attack, and mortality.
Can stress cause PVC and PAC?
Heart disease or scarring that interferes with the heart's normal electrical impulses can cause PVCs. Certain medications, alcohol, stress, exercise, caffeine or low blood oxygen, which is caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pneumonia, can also trigger them.
Are PACs benign?
PAC's in general are very common and for the most part benign. They can, however, be a harbinger of more serious arrhythmias, specifically atrial fibrillation. That being said, if the PAC's are causing significant symptoms therapy (typically using anti-arrhythmic drugs or ablation) may be warranted.
The Normal Heart Rhythm
The normal heart rhythm is controlled by a tiny structure called the sinus node, which is located near the top of the heart's right atrium. The sinus node generates the electrical signal that initiates the heartbeat and controls the heart rate.
PAC Symptoms
Fortunately, in the large majority of people, PACs do not cause any symptoms at all.
Causes
PACs are early (that is, premature) electrical impulses that are generated within the cardiac atria, but not from the sinus node. PACs momentarily interrupt the normal sinus rhythm by inserting an extra heartbeat.
How Significant Are PACs?
PACs generally have very little medical significance and are appropriately viewed by most healthcare providers as a variation of "normal."
Treatment
Unless a person's PACs are thought to be triggering episodes of atrial fibrillation, it is almost never necessary to treat them. However, occasionally a person will experience intolerable palpitations from their PACs and treatment will become desirable.
A Word From Verywell
PACs are very common and are almost always benign. Unless there is a good reason to treat them, the best course of action is to leave them alone.
What is a temporary heart monitor?
Temporary heart monitor: A device you wear to check your heart rhythm over extended periods of time.
Where do ventricular contractions start?
They start in different parts of your heart. Premature atrial contractions start in your atria. Premature ventricular contractions start in your ventricles.
Do you need to treat premature atrial contractions?
Premature atrial contractions usually don’t need treatment. They start in your heart’s upper chambers and can give you the feeling of an extra or skipped heartbeat. You should contact your provider if your premature atrial contractions start happening more often.
Is a heart rhythm disturbance more serious than an irregular heartbeat?
No. Atrial fibrillation is a more serious heart rhythm disturbance with an irregular heartbeat.
Is catheter ablation a risk?
Like any invasive procedure, catheter ablation carries risks, but providers generally consider it a low-risk procedure.
Do premature atrial contractions go away?
Usually, premature atrial contractions will go away by themselves. Pay attention to whether the number of premature atrial contractions you’re having goes up.
What is a premature atrial complex?
Premature atrial complexes or PACs consist of extra heartbeats that interrupt the sinus rhythm. They may occur anytime within a day in healthy individuals.
What is the best way to diagnose a premature atrial complex?
Premature atrial complexes are usually diagnosed with a Holter monitor, an electrocardiogram (EKG), or a cardiac event monitor.
What happens if PACs arrive early in the cardiac cycle?
PACs that arrive very early in the cardiac cycle may not trigger the ventricles so an abnormal P wave is not followed by a QRS complex , but is followed by a compensatory pause before the next beat.
What is the P wave in an ECG?
The P wave represents the electrical signals from the atria. It is normally followed by a short delay, represented by a straight line, before it proceeds to the ventricles. Depolarization of the ventricles results in the largest part of the ECG signal, known as the QRS complex.Repolarization of the heart muscle (myocardium) is represented by the ST segment, an isoelectric line, and the T wave, which is seen as an upright deflection.
How to know if you have a heart attack?
Other associated symptoms that must prompt you to seek medical consultation include: 1 lightheadedness orfainting 2 becoming sweaty or pale 3 difficulty breathing 4 chest pain 5 more than six episodes, with abnormal heartbeats coming in threes or more 6 having more than 100 beats per minute at rest
Which wave is produced by a PACS that arises close to the atrioventricular node?
PACS that arise close to the atrioventricular node produce an inverted P wave.
Can premature atrial complexes cause heartbeats?
Premature atrial complexes usually do not cause symptoms, although you may sometimes feel skipped beats, stronger heartbeats or a fluttering sensation in the chest.
What is PVC in heart?
A similar condition -- premature ventricular contraction (PVC) -- starts in the lower chambers, called “ventricles,” of your heart. Any time your heart shifts out of its usual rhythm, doctors call it an “ arrhythmia .”. There are lots of different kinds, including PACs.
What are the conditions that can cause PACs?
But some people who have PACs turn out to have related heart conditions, such as: Cardiomyopathy (a weakened heart muscle) Coronary heart disease (fatty deposits in your blood vessels) If your doctor finds that you have a condition related to the premature heartbeats, you’ll work together to make a treatment plan.
What is the clinical significance of PACs?
Clinical significance of PACs. PACs are a normal electrophysiological phenomenon not usually requiring investigation or treatment. Frequent PACs may cause palpitations and a sense of the heart “skipping a beat”.
Can PVCs be conducted to ventricles?
Similiarly, PVCs arriving very early in the cycle may not be conducted to the ventricles at all. In this case, you will see an abnormal P wave that is not followed by a QRS complex (“blocked PAC”). It is usually followed by a compensatory pause as the sinus node resets. The P wave typically has a different morphology and axis to the sinus P waves.
What is a premature heart beat?
A premature atrial beat is followed by a pause. The subsequent heart beat is longer and stronger than normal as it needs to pump the accumulated blood out of the heart chamber. The incidence of premature atrial beats increases at slower basic sinus bradycardia rates. Premature complexes can occur occasionally, in a regular pattern or several may occur at one time. Most people have such premature beats at some time or the other in their lives.
How to diagnose premature heartbeat?
A thorough physical exam and an evaluation of the patient’s medical history will enable the doctor to confirm the diagnosis. Diagnostic tests such as an ECG, or electrocardiogram, can help the medical practitioner determine whether or not the patient is suffering from premature atrial beats. An ECG shows a heart beat in a 3 wave form. The first wave is known as P, the second as QRS and the third as T. When a premature atrial complex or premature heartbeat occurs, the P wave is observed to occur closer than expected to the preceding T wave on the ECG. Treatment is only prescribed if the patient complains of discomfort caused by the frequent occurrence of such heartbeats. Medications such as beta-adrenergic antagonists or calcium channel antagonists are found to be effective.
Can premature heart beats go unnoticed?
Generally, such premature heart beats go unnoticed as they are symptomless. Sometimes, the affected person experiences mild palpitations. Others feel as though their heart has skipped a beat and this feeling is followed by a thumping in the chest that’s caused by the subsequent stronger heart beat.
Can premature atrial complexes cause tachycardia?
Although premature atrial complexes are harmless, they can lead to atrial tachycardia or episodes of very rapid and regular heartbeats . This is because they cause excitation of ventricles at the atrioventricular nodal system. They can also lead to a decrease in cardiac output or the amount of blood being pumped out by the heart in a specified amount of time.
What is premature atrial contraction?
Premature atrial contractions can be conducted to the ventricles normally, blocked at the AV node, or conduct aberrantly (i.e., abnormal QRS morphology). Click to see full answer.
What is abnormal intraventricular conduction?
Aberrant Ventricular Conduction: defined as the intermittent abnormal intraventricular conduction of a supraventricular impulse. The phenomenon comes about because of unequal refractoriness of the bundle branches and critical prematurity of a supraventricular impulse (see diagram of Three Fates of PACs).
