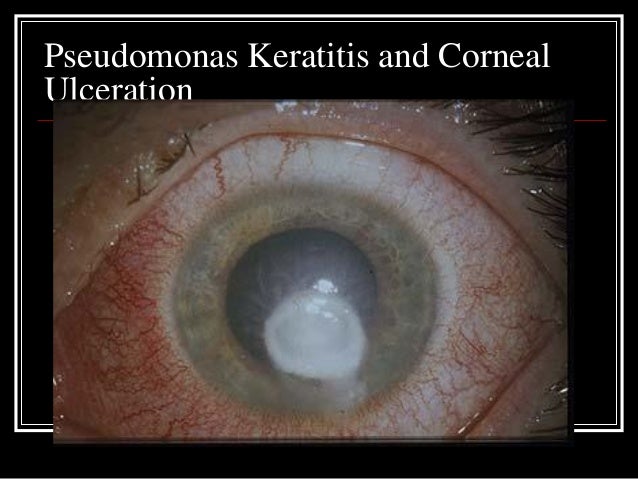
What does a Pseudomonas infection look like?
Pseudomonal cellulitis presents with a dusky red–to–bluish green skin discoloration and purulent discharge. The typical fruity or mouselike odor has been linked to pseudomonal infection. Vesicles and pustules may occur as satellite lesions. The eruption may spread to cover wide areas and cause systemic manifestations.
How do you identify Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Conventional Pseudomonas aeruginosa detection methods are based on the biological characteristics of the bacterium under certain culture conditions, such as Gram-negative or Gram-positive status, or the activities of bacterial molecules such as oxidase, acetamidase, arginine dihydrolase, and pyocyanin.
What color is Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa has a characteristic sweet, fruity odour due to its production of trimethylamine. This organism also produces the greenish-blue pigment pyocyanin, which diffuses into the undersurface of the nail plate, accounting for the green discoloration characteristic of this condition.
How do you identify Pseudomonas?
Selective agar containing inhibitors such as cetrimide can also be used for isolation and presumptive identification. Pseudomonas colonies may be nearly colourless, but white, off-white, cream, and yellow colony pigmentation is common. Fluorescent colonies can be readily observed under ultraviolet light.
Where is Pseudomonas aeruginosa commonly found?
Pseudomonas is a type of bacteria (germ) that is found commonly in the environment, like in soil and in water.
What kills Pseudomonas naturally?
Medical grade manuka honeys are well known to be efficacious against Pseudomonas aeruginosa being bactericidal and inhibiting the development of biofilms; moreover manuka honey effectively kills P. aeruginosa embedded within an established biofilm.
What does Pseudomonas do to humans?
Milder Pseudomonas infections can occur in otherwise healthy people. These include ear infections and skin rashes, especially after exposure to water. Pseudomonas bacteria cause well-known conditions such as hot tub rash, a red and itchy skin rash resulting from contaminated water, and swimmer's ear.
Can Pseudomonas spread from person to person?
Yes. Pseudomonas is contagious. Transmission is possible through contact with contaminated surfaces or equipment, and also the consumption of contaminated water or fruit and vegetables. It can also pass from person to person via contact with hands and skin.
Where do the most serious Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections occur?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common disease-causing form of this bacteria, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Serious infections from P. aeruginosa primarily occur in healthcare settings, but people can also develop infections from hot tubs and swimming pools.
What diseases does Pseudomonas aeruginosa cause?
The most serious infections include malignant external otitis, endophthalmitis, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, and septicemia. The likelihood of recovery from pseudomonas infection is related to the severity of the patient's underlying disease process.
What are the three Pseudomonas infection stages?
Pseudomonas species are both invasive and toxigenic. The 3 stages, according to Pollack (2000), are (1) bacterial attachment and colonization, (2) local infection, and (3) bloodstream dissemination and systemic disease.
How do you treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Pseudomonas infection can be treated with a combination of an antipseudomonal beta-lactam (eg, penicillin or cephalosporin) and an aminoglycoside. Carbapenems (eg, imipenem, meropenem) with antipseudomonal quinolones may be used in conjunction with an aminoglycoside.
How do you test for Pseudomonas aeruginosa in water?
The Pseudalert Test detects the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in water samples. The test is based on a bacterial enzyme detection technology that signals the presence of P. aeruginosa through the hydrolysis of a substrate in the Pseudalert reagent.
What is the morphology of Pseudomonas?
28.4 MORPHOLOGY Pseudomonas is rod shaped, slender (0.5 to 0.8 µm by 1.5 to 3.0 µm) Gram negative organism, motile by polar flagella, sometimes more than two flagella may be present.
What is the colony morphology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
aeruginosa is a variation of the colony morphology. P. aeruginosa iso- lates usually form large and smooth colonies on an agar medium, while atypical colonies such as mucoid or small colony variants (SCVs) have been reported (10, 36).
What does Pseudomonas smell like?
Grown in the laboratory on agar plates P. aeruginosa has a distinctive smell, some say like corn tortilla, grapes, or the traditional English sweet, Pear Drops.
Can P. aeruginosa grow at 42°C?
It is able to grow at 42°C. The combination of pyocyanin production and the ability to grow at 42°C is sufficient to distinguish P.aeruginosa from other Pseudomonas spp. (e.g., P.fluorescens, P.putida, P.stutzeri, P.putrefaciens ). Certain strains of P.aeruginosa may not produce pyocyanin.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa a pathogen?
It is commonly found free living in moist environments but is also a pathogen of plants, animals, and humans. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is often preliminarily identified by its typical odor in vitro . The smell is described as grape-like, tortilla-like or " Philadelphus coronarius -like" (production of aminoacetophenone ).
How Is Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Diagnosed?
aeruginosa, your doctor will perform a physical examination and ask about your symptoms and medical history. Then they’ll send a sample of your blood or other bodily fluid to a lab to test for the bacteria.
What is pseudoma aeruginosa?
What Is Pseudomonas Aeruginosa? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention. Pseudomonas is a group of bacteria that can cause various types of infections. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common disease-causing form of this bacteria, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
How many people died from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in 2017?
Research and Statistics: Who Has Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Being in a healthcare setting puts you at the highest risk of P. aeruginosa. In 2017, P. aeruginosa caused approximately 32,600 infections among patients in hospitals and 2,700 deaths in the United States, according to the CDC.
What happens if you get a pseudomonas infection in your foot?
Pseudomonal infections that enter the bloodstream can also lead to respiratory failure, shock, and death. More on Antibiotics.
Why is it so difficult to treat P. aeruginosa?
aeruginosa infections is becoming more difficult, however, because some bacterial strains show resistance to nearly all classes of powerful antibiotics. Treating these drug-resistant infections requires sending samples to a laboratory to test the bacteria against different antibiotics in hope of finding drugs that are effective against it.
What is the mortality rate for P. aeruginosa?
The mortality rates for P. aeruginosa infections are estimated to range from 18 to 61 percent; more ill patients, such as those with bloodstream infections or cancers of the blood, are at higher risk of dying, per past research.
How is P. aeruginosa spread?
In healthcare settings, P. aeruginosa is spread through improper hygiene, such as from the unclean hands of healthcare workers, or via contaminated medical equipment that wasn't fully sterilized.
What are the risks of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
We have seen many vulnerable people seriously affected by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, those at greater risk include: 1 Burns victims 2 People with cancer 3 People suffering from one or more chronic diseases 4 Premature babies looked after in neonatal hospital units
What about other possible Pseudomonas infections?
Anyone suffering from an infection of any kind – including one caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa – is likely to feel feverish… lethargy is common as well.
How does the outcome of a bacterium infection depend on the body?
The outcome can depend on how quickly the infection is identified as being caused by this bacterium. It also depends on which part of the body is affected and how the bacterium entered the body. As we discovered, if it enters the bloodstream, the situation becomes far more urgent.
Can Legionella cause pneumonia?
You may know that Legionella bacteria can cause a form of pneumonia when inhaled via mist or fine water droplets, such as spray. However, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is more adept at causing illness in several ways. Here, we look at the different types of infection it can trigger.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa an opportunist?
It is understandable, then, that Pseudomonas aeruginosa is viewed as an opportunist. Whenever it invades the immune system of someone who cannot easily fight off infection, it can threaten that individual’s life.
Is Legionella a disease?
Legionella & Pseudomonas. Legionnaires’ disease has become far better known in recent years hitting the headlines as cases crop up around the world. The disease can be potentially fatal and is caused by the Legionella bacteria.
Does Pseudomonas aeruginosa present a major challenge for hospitals?
Those responsible for handling infection control in hospitals do priorit ise Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
What color is Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
After 24, Pseudomonas aeruginosa appear as blue-green colonies. If other Pseudomonas or non-fermenting bacteria are present, they are not blue-green in color. It's worth noting that the pigments (water-soluble pigments) produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa may vary depending on the medium or strain of bacteria.
How big are Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonies?
In MacConkey agar, Pseudomonas aeruginosa forms flat and smooth colonies that are between 2 and 3mm in diameter. Generally, these colonies have regular margins and have an alligator skin-like appearance when viewed from above. See more on Cell Culture.
Why is Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to antibiotics?
This is due to a number of virulence factors associated with the organism. For this reason, Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing is an important test to determine the most effective treatment to treat infections caused by the bacterium.
How many polar flagella are there in Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
For some of the strains, studies have revealed the presence of two to three polar flagella used for movement. In addition to the flagella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa also possess pili on their surface which are used for adhesion and a form of motility known as twitching motility.
What is a nosocomial infection?
Essentially, nosocomial infections are hospital-acquired infections and thus occur post-admission. Some of these infections include: Burn wound infections - In addition to Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyrogens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the leading causes of invasive infections among burn patients.
What temperature does Pseudomonas aeruginosa grow?
While the bacterium grows well at 37 degrees C, it can also survive at the temperature range between 4 and 42 degrees C. To study various characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, some of the media used include Pseudomonas isolation agar, LB Broth, King A, and MOPS ( [3- (N-morpholino) propane-sulfonic acid]).
Which structure is used for swimming in moist environments?
Flagellum - As mentioned, Pseudomonas aeruginosa contains a single polar flagellum used for swimming in moist environments. In addition to motility, this structure has also been shown to play an important role in attachment to the epithelium, invasion as well as biofilm formation.
Where is Pseudomonas aeruginosa found?
Like other members of the genus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a free-living bacterium, commonly found in soil and water. However, it occurs regularly on the surfaces of plants and occasionally on the surfaces of animals.
What does it mean if your Pseudomonas aeruginosa result is too high?
High levels of Pseudomonas aeruginosa may indicate increased intestinal inflammatory activity and may cause abdominal cramping and loose stools. Some strains of P. aeroginosa may produce toxins that can damage cells.
What is the most common gram negative bacteria?
Pseudomonas species are gram-negative bacteria found widely in the environment. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common species causing infection and can affect every portion of the intestine.
What is the simplest medium for growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
In the laboratory, the simplest medium for growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa consists of acetate as a source of carbon and ammonium sulfate as a source of nitrogen.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa Gram negative?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative rod measuring 0.5 to 0.8 µm by 1.5 to 3.0 µm. Almost all strains are motile by means of a single polar flagellum. The bacterium is ubiquitous in soil and water, and on surfaces in contact with soil or water.
Is Pseudomonas a bacterium?
The typical Pseudomonas bacterium in nature might be found in a biofilm, attached to some surface or substrate, or in a planktonic form, as a unicellular organism, actively swimming by means of its flagellum. Pseudomonas is one of the most vigorous, fast-swimming bacteria seen in hay infusions and pond water samples.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to salts?
It is resistant to high concentrations of salts and dyes, weak antiseptics, and many commonly used antibiotics. - Pseudomonas aeruginosa has a predilection for growth in moist environments, which is probably a reflection of its natural existence in soil and water.
What temperature does P. aeruginosa grow?
P. aeruginosagrows well at 37°C, and can also survive at a wide range of temperatures from 4°C to 42°C. When selecting temperatures for growth, consider that temperature can affect virulence, and that below 30°C some virulence pathways are not active. Bacteria on plates can be stored at 4°C for future use with a recommended limit of one week. Cultures grow best with aeration, regardless of media, but P. aeruginosais capable of growing anaerobically on some carbon sources when supplied with nitrate as the terminal electron acceptor. We typically grow P. aeruginosain 18mm glass tubes with 3 ml of media on a roller drum and generally note exponential doubling times for PAO1 of 1 to 1.5 hours in minimal media (such as MOPS Glucose, see Reagents and Solutions) and 25 to 35 minutes in a rich broth such as LB (see Appendix 4A).
How long to inoculate P. aeruginosa?
Inoculate P. aeruginosainto LB broth with appropriate antibiotics and grow culture of P. aeruginosafor 16–24 hours at 37°C.
What is the best medium for P. aeruginosa growth?
To study growth on these sole nutrient sources, various defined minimal media are used to grow P. aeruginosasuch as MOPS (3-(N-Morpholino) Propane-Sulfonic Acid) medium, M9, or M63. Defined medium formulations can be modified to study the role of various carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur sources on P. aeruginosagrowth and virulence. We have found the most robust growth for a variety of carbon sources on MOPS medium. Other media that are used for P. aeruginosainclude Pseudomonas isolation agar (PIA, Difco) that is used to select against E. coliafter conjugations, and King A which stimulates pyocyanin production.
Can P. aeruginosa be frozen?
P. aeruginosacan be preserved in frozen stocks of either 20% glycerol or 10% skim milk (Cody et al., 2008) that can be stored at −80°C. Growing bacteria on fresh plates from frozen stocks is important when starting experiments to ensure consistent results, particularly for clinical isolates from CF samples, as they can have very high mutation rates. When starting a strain from a frozen stock it is recommended that the bacteria be streaked out onto an LB agar plate, and a subsequent liquid culture started the next day from the fresh plate. Isolates can grow poorly when placed directly into liquid, particularly with antibiotics present. Recovery of strains directly onto MOPS agar plates is not recommended.
Is P. aeruginosa a BSL-2 pathogen?
CAUTION: P. aeruginosais a Biosafety Level 2 (BSL-2) pathogen. Follow your institutional guidelines for handling and safety while working with BSL-2 organisms. For general biosafety information, see Unit 1A.1.
Is P. aeruginosa hardy?
P. aeruginosais a hardy bacterium that can be grown easily in a wide variety of conditions and temperatures. This unit describes the basic techniques to maintain and grow P. aeruginosain the laboratory.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa a Gram-negative bacterium?
Pseudomonas aerugi nosais a common, free-living, Gram-negative bacterium that can cause significant disease as an opportunistic pathogen. Rapid growth, facile genetics, and a large suite of virulence-related phenotypes make P. aeruginosaa common model organism to study Gram-nega tive opportunistic pathogens and basic microbiology. This unit describes the basic laboratory growth and maintenance of P. aeruginosa.
How to test for pseudomonas?
They may take a sample of pus, blood, or tissue, and send it to a laboratory. The laboratory will then test the sample for the presence of pseudomonas.
Where are pseudomonas found?
The bacteria are found widely in the environment, such as in soil, water, and plants. They usually do not cause infections in healthy people. If an infection does occur in a healthy person, it is generally mild. More severe infections occur in people who are ...
What is the most common species of pseudomonas?
Only a few of the many species cause disease. The most common species that causes infection is called Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Trusted Source.
What is the name of the infection caused by pseudomonas?
Blood. A bacterial infection of the blood is called bacteremia. A blood infection is one of the most severe infections caused by pseudomonas. Symptoms may include: fever. chills. fatigue. muscle and joint pain.
What is it called when a bacterium infects the skin?
When this bacterium infects the skin, it most often affects the hair follicles. This is called folliculitis. Symptoms may include:
Is a pseudomonade a pathogen?
More severe infections occur in people who are already hospitalized with another illness or condition, or people who have a weak immune system. Pseudomonades are fairly common pathogens involved in infections acquired in a hospital setting. ...
Is pseudomonas an opportunistic infection?
Pseudomonas infections are considered opportunistic infections. This means that the organism only causes disease when a person’s immune system is already impaired. Conditions that may increase the risk of infection include: Infections can be severe in people whose immune systems are already compromised.
Why did the biofilm protect Pseudomonas?
Also, it probably was the biofilm that protected the Pseudomonas from being completely eradicated because of the glycocalyx that has the potential to shield the organisms from the effects of antibiotics.
Is nasal mucosa erythematous?
On physical exam, the nasal mucosa was found to be erythematous and swollen with purulent secretions visible. The rest of the physical exam was non-contributory. Based on these findings, my initial concern was allergic fungal sinusitis and a DNA analysis was performed.
Does DNA analysis help with sinusitis?
Not only does DNA analysis help in identifying the true pathogens, but allows for more precise antibiotic regimens to treat the infection. This will allow for better antibiotic stewardship by lessening the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics in chronic infections, which will reduce the rate of resistance by targeting the actual offending agents and not what grows the best on regular media, leading to multiple courses of antibiotics that are missing the mark.
Is there fungus in the biofilm of Pseudomonas?
To my surprise, no fungus was detected, but there were some interesting findings nonetheless from the DNA analysis. Pseudomonas was a minor player in the biofilm of this patient in particular. It turned out that a majority of organisms of the biofilm were anaerobes and the true pathogens for the patient’s persistent infection.

Culture Characteristics
Gram Stain
Requirements For Gram Stain Include
- Sample - Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in culture can be used. 1. Glass slides 2. Gram stain reagents 3. Wire loop 4. Water 5. Burner
Procedure
- · If the sample is obtained from a culture plate, then it's necessary to add a drop of water onto the glass slidebefore aseptically adding a small amount of the bacteria. This can be achieved by using a sterile wire loop to place the sample on to the drop of water · Using the wire loop or glass stir stick/rod, make a good smear of the sample at the middle of the glass slide · Allow the slide …
Observation
- When viewed under the microscope, Pseudomonas aeruginosa will appear as reddish/pink rods. This indicates that they are Gram-negative bacteria given that they are unable to retain the primary stain (crystal violet). Under high magnification, studies have shown Pseudomonas aeruginosa to range from 0.5 to 0.8um in diameter and 1.5 to 3.0um in length ...
Infection
- As mentioned, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is responsible for various hospital-acquired infections. According to a report that was published by the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control in 2012, about 9 percent of all health-care-associated infections are caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa making it the fourth most common pathogen responsible for infectio…
Nosocomial Infections
- Essentially, nosocomial infections are hospital-acquired infections and thus occur post-admission. Some of these infections include: Burn wound infections - In addition to Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyrogens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the leading causes of invasive infections among burn patients. Here, the site of injury (from the burn…
Urinary Tract Infection
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa has been shown to be particularly effective at forming surface-associated biofilms. For patients who use catheters, the bacterium has been shown to form biofilm on the surface of these catheters (indwelling catheters) and ultimately cause an infection as they proliferate.
Pathogenesis and Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is made possible by several virulence factors that include: Lipopolysaccharide- Lipopolysaccharide is one of the main components of the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In addition to Lipid A, a hydrophobic domain, this component of the outer membrane also consists of O-antigen (distal polysaccharide) which not …
Antibiotic Resistance
- Following an infection, Pseudomonas aeruginosa has been shown to be resistant to a variety of antimicrobials. There are several modes of resistance which include: Intrinsic resistance to antibiotics- Essentially, intrinsic antibiotic resistance refers to the innate ability of bacteria to evade the impacts of antibiotics. This may be achieved through various structural and functiona…