What are science terms that start with Q?
Quantum Mechanics: The physical science used to calculate and analyse the energies and spatial distributions of small particles confined to very small regions of space. quantum theory: The general theory which describes the allowed energies of atoms and molecules. A quaternary amine is an amine with four carbon atoms bonded to the amine nitrogen.
What is a scientific word that starts with Q?
What science word that starts with letter q?
- Quark: A sub atomic particle.
- Quenching: The process rapid cooling to obtain certian material properities. (For instance, low crystallinity and thereby higher toughness.)
- Quinoline: A famous heterocyclic aromatic organic compound whose derivatives has a wide range of applications.
What does the Q in Coulombs law stand for?
where Q1 represents the quantity of charge on object 1 (in Coulombs), Q2 represents the quantity of charge on object 2 (in Coulombs), and d represents the distance of separation between the two objects (in meters). The symbol k is a proportionality constant known as the Coulomb's law constant.
What does the Q in qtips stand for?
“Q-tips” are officially called “Quality Tips.” The “Q,” then, stands for “Quality.” Q-Tips were conceived by Leo Gerstenzang, whose wife inspired him by poking toothpicks into cotton swabs and using them to clean hard to read places. In 1923 he founded the Leo Gerstenzang Novelty Co to manufacture ready-to-use cotton swabs.
What is Q unit in physics?
The coulomb is defined as the quantity of charge that passes through the cross section of an electrical conductor carrying one ampere for one second. This unit was proposed in 1946 and ratified in 1948. The lowercase symbol q is often used to denote a quantity of electric charge.
What is the value for Q in physics?
In nuclear physics and chemistry, the Q value for a reaction is the amount of energy absorbed or released during the nuclear reaction. The value relates to the enthalpy of a chemical reaction or the energy of radioactive decay products. It can be determined from the masses of reactants and products.
What does Q mean in physics heat?
Q = m•C•ΔT where Q is the quantity of heat transferred to or from the object, m is the mass of the object, C is the specific heat capacity of the material the object is composed of, and ΔT is the resulting temperature change of the object.
What is Q in physics electric field?
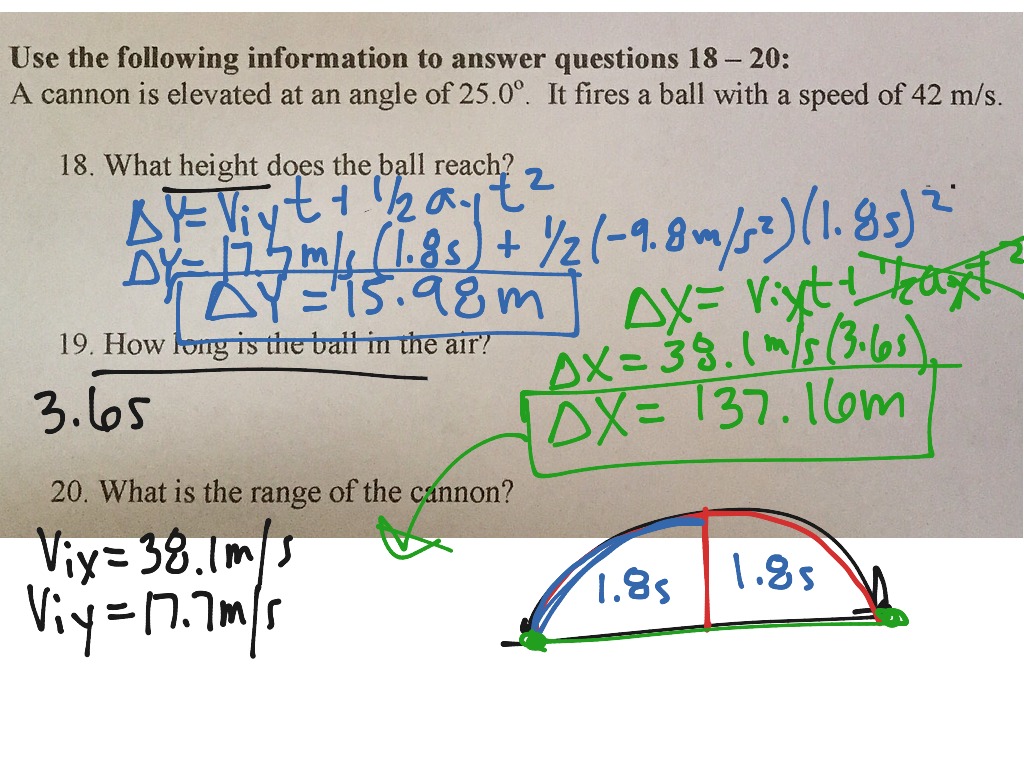
The symbol q in the equation is the quantity of charge on the test charge (not the source charge). Recall that the electric field strength is defined in terms of how it is measured or tested; thus, the test charge finds its way into the equation. Electric field is the force per quantity of charge on the test charge.
How do you find the charge q?
Charge is measured in coulombs, C. The charge of an electron is 1.6 x 10 -19 C. In other words, it takes 6,250,000,000,000,000,000 electrons to make up 1 coulomb of charge....The relationship between current I and quantity of charge Q.I =I = Q ÷ tQ = ItQ = I x tt =t = Q ÷ I
Why does Q stand for energy?
An uppercase letter Q was first used to symbolize “the absolute quantity of heat” by the French engineer, Benoit-Paul-Émile Clapeyron (1799−1864), in his famous memoir of 1834 in which he first quantified what it is now known as the Carnot cycle (1).
Why is heat energy Q?
The symbol Q for the total amount of energy transferred as heat was used by Rudolf Clausius in 1850: "Let the amount of heat which must be imparted during the transition of the gas in a definite manner from any given state to another, in which its volume is v and its temperature t, be called Q" .
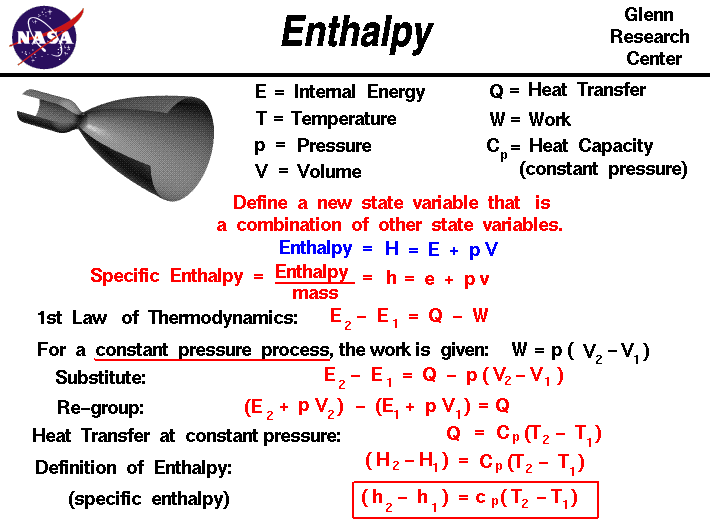
Is Q the same as Delta H?
Q is the energy transfer due to thermal reactions such as heating water, cooking, etc. anywhere where there is a heat transfer. You can say that Q (Heat) is energy in transit. Enthalpy (Delta H), on the other hand, is the state of the system, the total heat content.
What is the Q of Proton?
Protons and electrons have an another intrinsic property called charge. qproton = 1.602*10-19 C, qelectron = -1.602*10-19 C. The charge of a fundamental particle may be positive or negative, but its magnitude is always an integer multiple of the fundamental quantity qe = 1.6*10-19 C. Unlike mass, charge is quantized.
What is Q MC △ T?
The amount of heat gained or lost by a sample (q) can be calculated using the equation q = mcΔT, where m is the mass of the sample, c is the specific heat, and ΔT is the temperature change.
What is Q in specific heat formula?
Heat capacity formula Q is the amount of supplied or subtracted heat (in joules), m is the mass of the sample, and ΔT is the difference between the initial and final temperatures. Heat capacity is measured in J/(kg·K).
What is Q heat transfer?
The transfer of heat energy is defined as heat flux, Q. By definition, this is the flow of heat energy through a defined area over a defined time. So, the units for Q are Joules (energy) divided by area (square meters) and time (seconds).
What does Q stand for in thermodynamics?
Q is the net heat transferred into the system—that is, Q is the sum of all heat transfer into and out of the system. W is the net work done on the system.
How many Q&A communities are there on Stack Exchange?
Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
What is the meaning of "back up"?
Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience.
What are the symbols used in physics?
Look at radiation with the greek alphabet, alpha, beta, gamma . Then elementary particles kaon, lamda, mu, nu, xi , sigma , tau , phi,chi psi, omega. They were skipping the ones common to both alphabets, or used already generally, as pi. J/psi shows egos coming in :) .
Who is the father of modern chemistry?
Antoine Lavoisier. He is widely considered in popular literature as the "father of modern chemistry". 3 [4] ... His first memoirs on this topic were read to the Academy of Sciences in 1777, but his most significant contribution to this field was made in the winter of 1782/1783 in association with Laplace.
