
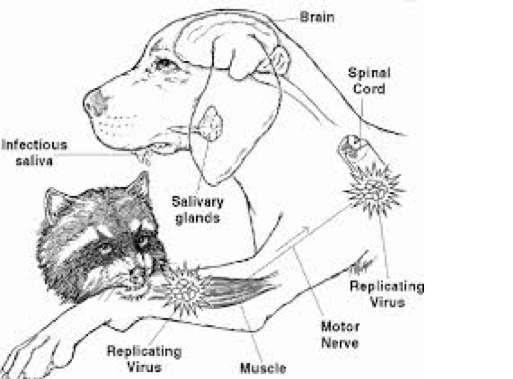
When there´s a bite from an animal with rabies, the virus attaches to a healthy nerve cell. Then the virus multiplies, making a lot more viruses like itself. Those viruses move on and attach to other nerve cells until eventually they get to the brain.
What parts of the body are affected by rabies?
The rabies virus after attacking the brain and central nervous system, affects the salivary glands, gonads, heart, kidneys, the digestive system, lungs and pancreas. Scientists are still not clear about how the virus moves in the body and what mechanism it adopts to bring about damage to the brain.
Can rabies kill you?
Rabies is fatal: Yes, rabies is extremely dangerous, although fortunately very rare. If in doubt, it's best to seek professional treatment right away. Rabies is transmitted by mammals only - so not birds or reptiles.
Can you cure rabies?
There is no cure for rabies. Your healthcare provider will take immediate steps to protect you against developing rabies, including providing post-exposure prophylaxis and, if needed, a course of additional shots of the rabies vaccine. Was this page helpful? 11 Sources
Will there ever be an effective rabies treatment?
Your doctor will likely recommend treatment as soon as possible to prevent the rabies virus from infecting your body if there's a chance you may have been exposed to the rabies virus. Once a rabies infection is established, there's no effective treatment. Though a small number of people have survived rabies, the disease usually causes death.
How does rabies affect the host cell?
The rabies virus, for example, is transmitted when an infected animal bites into a host's muscle. It then spreads into the end terminals of motor neurons innervating the muscle and travels along the neurons' long axon fibers to the neuronal cell bodies.
Does rabies destroy nerve cells?
Despite the dramatic clinical expression in rabies patients, pathological changes are usually mild with little neuronal destruction (15, 18), which has led to the hypothesis that neuronal dysfunction rather than structural damage may be responsible for the development of rabies (24).
How does the rabies affect the organism?
Rabies is caused by the rabies virus. Infected animals have the virus in their saliva. The virus enters the body through broken skin or the eyes, nose, or mouth, and travels through nerves to the brain. There it multiplies and causes inflammation and damage.
How does rabies infect the nervous system?
Rabies virus (RABV) is a pathogen well-adapted to the nervous system, where it infects neurons. RABV is transmitted by the bite of an infected animal. It enters the nervous system via a motor neuron through the neuromuscular junction, or via a sensory nerve through nerve spindles.
Does rabies Eat your brain?
Rabies causes acute inflammation of the brain, producing psychosis and violent aggression. The virus, which paralyzes the body's internal organs, is always deadly for those unable to obtain vaccines in time. Some 55,000 people die from rabies every year.
How does rabies trick the immune system?
In adaptive immunity/inflammation of the CNS, RABV has a clear capacity to suppress host responses, with two mechanisms suggested in in vivo models, specifically blockage of immune effector infiltration via maintenance of BBB integrity, and induction of T-cell apoptosis (Fig. 3).
Why can't we cure rabies?
So why is rabies so difficult to treat? Viral infections can usually be treated using anti-viral drugs, which inhibit virus development. Rabies virus uses a myriad of strategies to avoid the immune system and hide from antiviral drugs, even using the blood brain barrier to protect itself once it has entered the brain.
Does rabies virus enter brain cells?
Rabies virus from the infected saliva enters the wound. Rabies virus travels through the nerves to the spinal cord and brain.
Will rabies ever be cured?
Once a rabies infection is established, there's no effective treatment. Though a small number of people have survived rabies, the disease usually causes death. For that reason, if you think you've been exposed to rabies, you must get a series of shots to prevent the infection from taking hold.
Why does rabies make you afraid of water?
People used to call rabies hydrophobia because it appears to cause a fear of water. The reason is that the infection causes intense spasms in the throat when a person tries to swallow. Even the thought of swallowing water can cause spasms, making it appear that the individual is afraid of water.
What part of the brain is affected by rabies?
Once rabies attacks the central nervous system, it causes encephalitis (brain swelling). Inflammation surrounding brain blood vessels is often seen. Areas of the brain frequently targeted by the rabies virus are the hippocampus, limbic areas, medulla and cerebellum.
What are the 3 stages of rabies?
There are three clinical phases of the disease:Prodromal phase - the onset of clinical rabies in man includes 2-4 days of prodromal. ... Excitation phase - the excitation phase begins gradually and may persist to death. ... Paralytic phase - hydrophobia, if present, disappears and swallowing becomes possible,
How fast does rabies travel through nerves?
Rabies virus binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction and travels toward the spinal cord within axons of peripheral nerves by retrograde fast axonal transport at a rate of approximately 50–100 mm per day.
How rabies virus moves through nerve cells and how it might be stopped?
Summary: Researchers found that the rabies virus travels through neurons differently than other neuron-invading viruses, and that its journey can be stopped by a drug commonly used to treat amoebic dysentery.
What part of the brain is affected by rabies?
Once rabies attacks the central nervous system, it causes encephalitis (brain swelling). Inflammation surrounding brain blood vessels is often seen. Areas of the brain frequently targeted by the rabies virus are the hippocampus, limbic areas, medulla and cerebellum.
What virus attacks nervous system?
Dengue-virus (DENV), Zika virus (ZIKV), Chikungunya-virus, Japanese Encephalitis, tick-borne encephalitis, West-Nile-virus and St. Louis Encephalitis are among the most common flaviviral infections in which the CNS is involved.
What is rabies in mammals?
What is Rabies? Rabies is a preventable viral disease most often transmitted through the bite of a rabid animal. The rabies virus infects the central nervous system of mammals, ultimately causing disease in the brain and death. The vast majority of rabies cases reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ...
What is the process of fusion of the rabies virus envelope to the host cell membrane?
The fusion of the rabies virus envelope to the host cell membrane (adsorption) initiates the infection process. The interaction of the G protein and specific cell surface receptors may be involved.
What is the M protein in rabies?
The glycoprotein forms approximately 400 trimeric spikes which are tightly arranged on the surface of the virus. The M protein is associated both with the envelope and the RNP and may be the central protein of rhabdovirus assembly. The basic structure and composition of rabies virus is depicted in the longitudinal diagram below.
How many proteins are in the rabies genome?
Rhabdoviruses are approximately 180 nm long and 75 nm wide. The rabies genome encodes five proteins: nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), matrix protein (M), glycoprotein (G) and polymerase (L). All rhabdoviruses have two major structural components: a helical ribonucleoprotein core (RNP) and a surrounding envelope. In the RNP, genomic RNA is tightly encased by the nucleoprotein. Two other viral proteins, the phospoprotein and the large protein (L-protein or polymerase) are associated with the RNP.
What is the rabid virus?
Rabies virus belongs to the order Mononegavirales, viruses with a nonsegmented, negative-stranded RNA genomes. Within this group, viruses with a distinct “bullet” shape are classified in the Rhabdoviridae family, which includes at least three genera of animal viruses, Lyssavirus, Ephemerovirus, and Vesiculovirus. The genus Lyssavirus includes rabies virus, Lagos bat, Mokola virus, Duvenhage virus, European bat virus 1 & 2 and Australian bat virus.
Where does the virus come from in the salivary gland?
Conversely, virus in the salivary glands buds primarily from the cell membrane into the acinar lumen.
How does rabies affect the brain?
Apr. 25, 2018 — The rabies virus wreaks havoc on the brain, triggering psychosis and death. To get where it needs to go, the virus must first trick the nervous system and cross the blood brain barrier -- a process ...
How does rabies travel?
Researchers found that the rabies virus travels through neurons differently than other neuron-invading viruses, and that its journey can be stopped by a drug commonly used to treat amoebic dysentery. To successfully infect its host, the rabies virus must move from the nerve ending to the nerve cell body where it can replicate. ...
How have viruses influenced evolution?
Feb. 7, 2018 — A virus may have influenced the evolution of multicellular life. Biologist have found a virus family that has a similar set of genes as eukaryotes, placing giant viruses in the evolutionary journey ...
How many people died from rabies in 2015?
Though rabies infections in humans are rare in the United States, the virus killed over 17,000 people worldwide in 2015. Alpha herpesviruses, such as herpes simplex viruses, also enter peripheral nerve terminals and move along axons to the neuronal cell body, where they can lie dormant for the life of the host.
How does alpha herpes virus affect the neuronal transport system?
Enquist and colleagues previously found that alpha herpesviruses engage the neuronal transport machinery by stimulating protein synthesis at infected nerve terminals. Viral transport to the cell body can therefore be blocked by drugs that inhibit protein synthesis, as well as by cellular antiviral proteins called interferons. advertisement. ...
Where does the rabies virus move?
FULL STORY. To successfully infect its host, the rabies virus must move from the nerve ending to the nerve cell body where it can replicate. advertisement. In a study published July 20 in the journal PLoS Pathogens, researchers from Princeton University reveal that the rabies virus moves differently compared to other neuron-invading viruses ...
Where does the virus spread?
From there, the virus can spread throughout the central nervous system and into the salivary glands, where it can be readily transmitted to other hosts.
How does rabies affect humans?
Rabies affects mammals and is generally transmitted via the bite or scratch of an animal carrying the virus.
How does rabies get into the brain?
During a typical bite, the virus gets introduced into the muscle, where it will reproduce and then enter the nerves, eventually leading to the brain, Rodney Rohde, Ph.D., professor of clinical laboratory science at Texas State University and author of a forthcoming book on rabies, tells SELF. This is part of the reason the time between rabies exposure and the development of symptoms is so variable: A bite in the ankle could take months to travel to the brain, while a bite on the arm or shoulder has a much shorter journey. Eventually the virus also ends up in the saliva, through which it can be transmitted to others.
How many people die from rabies each year?
And that’s fair, given that rabies deaths are not common in the U.S. Globally, rabies causes about 59,000 deaths each year, according to the CDC, most of them due to bites from rabid dogs. In the U.S., there have been 23 rabies deaths accounted for between 2008 and 2017, per the CDC—and eight of those deaths were due to bites that occurred in other countries.
How long does it take for rabies to get to the brain?
This is part of the reason the time between rabies exposure and the development of symptoms is so variable: A bite in the ankle could take months to travel to the brain, while a bite on the arm or shoulder has a much shorter journey.
Who should be offered rabies shots?
People who are at a high risk of rabies exposure (think: veterinarians, animal lab workers or handlers, or people traveling to parts of the world where rabies is more prevalent , who may be around animals) may be offered rabies vaccines as a preventive measure. If they work with animals regularly, they will have to stay up to date on their vaccinations with guidance from a doctor.
Can you test for rabies in animals?
Unfortunately, there are no good tests for rabies in animals, other than observing them for a period to see if they exhibit classically rabid behavior (which you can’t do if the animal is wild and can’t be tracked). Diagnosis is done after death, by testing the brain.
Can dogs get rabies from being outside?
Also, keep an eye on your pets if they go outdoors. Dogs or cats that spend any time outdoors could be in contact with sick wildlife, and if the owner isn’t watching them, even a quick exposure could spread rabies. “If they’re out there and they run across a skunk and fight through a fence, or get bitten by a skunk or a fox, or pick up a bat—cats love to play with sick bats—then suddenly they’ve been exposed and you don’t know,” Rohde explains.
What is a mutated rabies virus?
Mutant rabies virus. Rabies virus that has been mutated from the original wild-type sequence. Pseudotyped rabies virus. Rabies virus in which the envelope gene has been replaced with the envelope gene from another virus. Pseudorabies virus.
How long does rabies take to incubate?
Incubation period of 1-3 months is typical, although incubation more than 1 year has been reported in humans. Administration of rabies POST-exposure prophylaxis is a medical urgency, not a medical emergency, but decisions must not be delayed.
What is a pseudotype of rabies?
Pseudotyped rabies virus: Rabies virus in which the rabies envelope gene is deleted can be pseudotypes with a number of different envelope genes, including EnvA, VSV-g, avian sarcoma leucosis virus glycoprotein, or HIV env. This pseudotyping alters the cell tropism of the virus and can be useful for specific experimental purposes.
How to treat rabies post exposure?
There is no established treatment for rabies once symptoms have begun, but supportive therapy may include intubation, sedation, mechanical ventilation, fluid and electrolyte management, nutrition, and management of intercurrent illnesses and complications. Incubation period of 1-3 months is typical, although incubation more than 1 year has been reported in humans. Administration of rabies POST-exposure prophylaxis is a medical urgency, not a medical emergency, but decisions must not be delayed. Prophylaxis is occasionally complicated by adverse reactions, but these reactions are rarely severe. Therefore, when a documented or likely exposure has occurred, POST-exposure prophylaxis should be administered regardless of the length of the delay, provided that compatible clinical signs of rabies are not present in the exposed person. Rabies virus is inactivated by desiccation, ultraviolet irradiation, and other factors and does not persist in the environment. In general, if the suspect material is dry, the virus can be considered noninfectious. Non-bite exposures other than organ or tissue transplants have almost never been proven to cause rabies, and post-exposure prophylaxis is not indicated unless the non-bite exposure met the definition of saliva or other potentially infectious material being introduced into fresh, open cuts in skin or onto mucous membranes.
How many cases of rabies have been attributed to aerosol exposures in laboratories?
Two cases of rabies have been attributed to probable aerosol exposures in laboratories, and two cases of rabies have been attributed to possible airborne exposures in caves containing millions of free-tailed bats (Tadarida brasiliensis) in the Southwest. However, alternative infection routes cannot be discounted.
What is the family of rhabdoviridae?
Family Rhabdoviridae, genus Lyssavirus; bullet-shaped, enveloped virus; approximately 75nm in diameter by 180 nm in length; single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome. Recombinant rabies virus vectors: Replication-deficient rabies vectors can be useful tools for investigation into neuronal trafficking or targeted expression in neurons.
Is rabies a negative strand virus?
Therefore, there is essentially no risk to generate replication competent rabies virus.
How does rabies travel?
The Virus Travels through the Body. From numerous studies conducted on rabid dogs, cats, and ferrets, we know that when the rabies virus isintroduced into a muscle through a bite from another animal, it travels from the site of the bite to the brain by moving within nerves. The animal does not appear ill during this time.
Where does rabies go after it has reached the brain?
Late in the disease, after the virus has reached the brain and multiplied there to cause an inflammation of the brain, it moves from the brain to the salivary glands and saliva. Also at this time, after the virus has multiplied in the brain, almost all animals begin to show the first signs of rabies.
What happens when a virus hits the brain?
When it reaches the brain, the virus multiplies rapidly and passes to the salivary glands. The animal begins to show signs of the disease.
What virus enters the wound?
Rabies virus from the infected saliva enters the wound.
How long does rabies last after a bite?
The time between the bite and the appearance of symptoms is called the incubation period and it may last for weeks to months. A bite by the animal during the incubation period does not carry a risk of rabies because the virus has not yet made it to the saliva.
How long does it take for rabies to show?
Most of these signs are obvious to even an untrained observer, but within a short period of time, usually within 3 to 5 days, the virus has caused enough damage to the brain that the animal begins to show unmistakable signs of rabies.
Why is there so much variation in the time between exposure and the onset of the disease?
The reason there is so much variation in the time between exposure and the onset of the disease is that many factors come into play , including the site of the exposure, the type of rabies virus, and any immunity in the animal or person exposed.
How does rabies get into the brain?
A new article sheds light on how the virus hijacks the transport system in nerve cells to reach the brain with maximal speed and efficiency. Rabies (and rabies virus, its causative agent) is usually transmitted through the bite of an infected animal into muscle tissue of the new host. From there, the virus travels all the way to ...
How is rabies transmitted?
Rabies is usually transmitted through the bite of an infected animal into muscle tissue of the new host. From there, the virus travels all the way to the brain where it multiplies and causes the usually fatal disease. A new article sheds light on how the virus hijacks the transport system in nerve cells to reach the brain with maximal speed ...
What virus hijacks the communication systems in the host cells?
May 8, 2017 — An international study has shone light on the way the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) hijacks the communication systems in the host cells it infects, uncovering potential new therapeutic targets for the ...
How many people die from rabies in 2017?
Oct. 11, 2017 — Scientists may finally understand how the rabies virus can drastically change its host's behavior to help spread the disease, which kills about 59,000 people annually. A new study shows how a small ...
How fast does rabies move?
When the researchers measured the speed of transport, they found that when rabies virus is transported with p75NTR, it moves at about 8 centimeters (a bit more than 3 inches) per day. Surprisingly, this is considerably faster (by about 40%) than the transport speed for NGF, the regular partner of p75NTR.
Where does the virus travel?
From there, the virus travels all the way to the brain where it multiplies and causes the usually fatal disease. An article published on August 28th in PLOS Pathogens sheds light on how the virus hijacks the transport system in nerve cells to reach the brain with maximal speed and efficiency. advertisement. Pathogens that travel in the blood can ...
Where are nerve cells located?
Nerve cells (or neurons) in the periphery, i.e. the outskirts of the body, as opposed to the central nervous system or CNS), are highly asymmetric: they have a cell body from which a long protrusion called an axon extends to another nerve cell or a target organ like muscle, along a specific transmission route.
How does rabies attack the brain?
How rabies 'hijacks' neurons to attack brain. For the first time, scientists have discovered the exact mechanism the killer rabies virus uses to efficiently enter the central nervous system, where it erupts in a toxic explosion of symptoms. An improved understanding of how this mechanism works could lead to new treatments for disorders such as ...
What diseases can rabies cause?
Rabies causes acute inflammation of the brain, producing psychosis and violent aggression.
How did the researchers track the rabies virus?
To track the rabies virus in the nervous system, the researchers grew mouse sensory neurons in an observation chamber and used live cell imaging to track the path taken by the virus particles. The researchers "saw" the virus hijack the "train" transporting cell components along a neuron and drove it straight into the spinal cord. Once in the spinal cord, the virus caught the first available train to the brain, where it wrought havoc before speeding through the rest of the body, shutting it down organ by organ.
What diseases can disrupt the neuron train?
Disruptions of the neuron train system also contribute to neurodegenerative diseases, like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). According to Dr. Perlson, "An improved understanding of how the neuron train works could lead to new treatments for these disorders as well.".
How many people die from rabies every year?
The virus, which paralyzes the body's internal organs, is always deadly for those unable to obtain vaccines in time. Some 55,000 people die from rabies every year. For the first time, Tel Aviv University scientists have discovered ...
Where did the virus go?
Once in the spinal cord, the virus caught the first available train to the brain, where it wrought havoc before speeding through the rest of the body, shutting it down organ by organ. Nerve cells, or neurons, outside the central nervous system are highly asymmetric.
What is the role of axons in neuronal survival?
In addition to rapid transmission of electric impulses, axons also transport molecular materials over these distances. "Axonal transport is a delicate and crucial process for neuronal survival, and when disrupted it can lead to neurodegenerative diseases," said Dr. Perlson.
