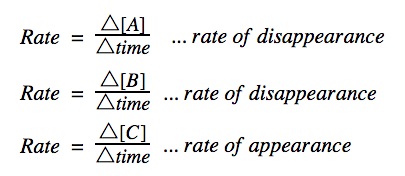
The rate of reaction refers to the speed at which the products are formed from the reactants in a chemical reaction. It gives some insight into the time frame under which a reaction can be completed. For example, the reaction rate of the combustion of cellulose in fire is very high and the reaction is completed in less than a second.
Full Answer
How can you determine the rate of reaction?
- An experiment is carried out to measure the volume of gas collected at regular time intervals.
- A graph of the volume of gas collected against time is plotted.
- The graph plotted has the shape as shown in Figure.
- The graph can be used to determine the average rate of reaction and rate of reaction at a given time.
What factors can increase the rate of reaction?
Factors that affect rate of reaction There are 4 distinct factors that each affect the rate of reaction: → Temperature: increasing the temperature, increases the rate of reactions because: Particles collide more often Particles collide with more energy → Concentration: Increasing the concentration of reactants in solutions increases the frequency of collisions between particles and so increases the rate of reaction → Pressure: Increasing the pressure of reacting gases also increases ...
How to calculate the rate of reaction?
Key Points
- Reaction rate is calculated using the formula rate = Δ [C]/Δt, where Δ [C] is the change in product concentration during time period Δt.
- The rate of reaction can be observed by watching the disappearance of a reactant or the appearance of a product over time.
- If a reaction produces a gas such as oxygen or carbon dioxide, there are two ways to measure the reaction rate: using a gas syringe to measure the gas produced, ...
- If the reaction produces a precipitate, the amount formed can be used to determine reaction rate by measuring how long it takes for the forming precipitate to obscure the visibility ...
What determines how fast the rate of reaction will happen?
There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction: The concentration of the reactants. The more concentrated the faster the rate. Temperature.
What is meant by the rate of a reaction?
The rate of a chemical reaction is defined as the rate of change in concentration of a reactant or product divided by its coefficient from the balanced equation.
What is rate of reaction and why is it important?
The rate of a reaction is a powerful diagnostic tool. By finding out how fast products are made and what causes reactions to slow down we can develop methods to improve production. This information is essential for the large scale manufacture of many chemicals including fertilisers, drugs and household cleaning items.
What factors affect rate of reaction?
Reactant concentration, the physical state of the reactants, and surface area, temperature, and the presence of a catalyst are the four main factors that affect reaction rate.
How do you determine the rate of reaction?
To measure reaction rates, chemists initiate the reaction, measure the concentration of the reactant or product at different times as the reaction progresses, perhaps plot the concentration as a function of time on a graph, and then calculate the change in the concentration per unit time.
Question: What Does "Rate of Reaction" Mean?
Ans: In chemistry, reaction rate refers to the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. It is often expressed in terms of the concentration (amoun...
Question: What is the Average Rate of Reaction?
Ans: The ratio of the change in the concentration of the reactants or products of a chemical reaction to the time interval is known as the average...
Question: What is a Pseudo-first-order Reaction?
Ans: Pseudo-first-order reactions are second-order or bimolecular reactions that are manipulated to behave like first-order reactions. When one rea...
What is reaction rate?
The reaction rate is defined as the rate at which the reactants of a chemical reaction form the products . Reaction rates are expressed as concentration per unit time.
How does concentration affect the rate of a chemical reaction?
Concentration: Increasing the concentration of the reactants increases the rate of a chemical reaction. Pressure: Increasing the pressure increases the rate of reaction.
Why does increasing the temperature increase the rate of a reaction?
In more cases, raising the temperature increases the rate of a reaction because higher kinetic energy leads to more collisions between reactant particles. This increases the chance that some of the colliding particles will have sufficient activation energy to react with each other. The Arrhenius equation is used to quantify the effect ...
What is the role of the nature of a chemical reaction?
The Chemical Reaction: The nature of the chemical reaction plays a large role in determining the reaction rate. In particular, the complexity of the reaction and the state of matter of the reactants are important. For example, reacting a powder in a solution typically proceeds faster than reacting a large chunk of a solid.
What is the Arrhenius equation?
The Arrhenius equation is used to quantify the effect of temperature on the reaction rate. It is important to note that some reaction rates are negatively affected by temperature while a few are independent of temperature. The Chemical Reaction: The nature of the chemical reaction plays a large role in determining the reaction rate.
What is the role of catalyst in a reaction?
Catalyst: A catalyst lowers activation energy and increases reaction rate in both forward and reverse directions.
Does light affect the rate of a reaction?
Light: Light or other electromagnetic radiation often speeds up the reaction rate . In some cases, the energy causes more particle collisions. In others, light acts to form intermediate products that affect the reaction.
What is the rate of a reaction?
The rate of a reaction is a measure of how quickly a reactant is used up, or a product is formed.
What is the rate of a chemical reaction measured in?
The rate of a chemical reaction can also be measured in Mol s-1.
How to find rate of reaction?
The rate of reaction can be analysed by plotting a graph of mass or volume of product formed against time. The graph shows this for two reactions.
What is the unit of rate?
The units for rate are usually g/s or g/min.
What is the greater the frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles?
The greater the frequency of successful collisions between reactant particles, the greater the reaction rate.
What is reaction rate?
Ans: In chemistry, reaction rate refers to the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. It is often expressed in terms of the concentration (amount per unit volume) of a substance produced in a unit of time or the concentration (amount per unit volume) of a reactant consumed in a unit of time.
What is the ratio of the change in the concentration of the reactants or products of a chemical reaction to the time?
Ans: The ratio of the change in the concentration of the reactants or products of a chemical reaction to the time interval is known as the average rate of reaction.
What is pseudo first order reaction?
Ans: Pseudo-first-order reactions are second-order or bimolecular reactions that are manipulated to behave like first-order reactions. When one reacting material is present in large amounts or is held at a constant concentration in comparison to the other, this reaction occurs.
How does the concentration of gases affect the rate of reaction?
The concentration of gases increases as pressure rises, resulting in a faster rate of reaction. The reaction rate increases as the number of gaseous molecules decreases and decreases as the number of gaseous molecules increases.
How is the average kinetic energy of the reactants measured?
The average kinetic energy of the reactants is measured by temperature. The kinetic energy of the reactants increases as the temperature rises. In other words, the particles are moving faster. Since the reactants are moving faster, further collisions will occur at a faster pace, raising the chances of reactants forming into products and therefore increasing the rate of reaction. A ten-degree increase in temperature causes the reaction rate to double. The temperature dependence of each reaction rate coefficient k is typically given by the Arrhenius equation:
How does electromagnetic radiation speed up a reaction?
As a consequence, electromagnetic radiation can speed up or even make a reaction spontaneous by adding more energy to the reactant particles. This energy is stored in the reacting particles in one way or another, resulting in intermediate species that are easy to react. The particles gain more energy as the strength of light increases, and thus the rate of reaction increases.
What is diffusion in chemistry?
Diffusion is a limiting factor in certain reactions. The reaction rate coefficient takes into account all variables that influence a reaction rate, excluding concentration and reaction order (the coefficient in the rate equation of the reaction).
What is the rate of a reaction?
Hence, the rate of a reaction is defined in terms of the average rate of reaction during the time interval. The change in concentration of any of the reactants or any of the product per unit time over a specified interval of time is called the average rate of reaction.
What is the rate of a chemical reaction?
The rate of a chemical reaction means the speed with which the reactants change into products. The rate of reaction is the change in the concentration of any one of the reactants or products per unit time. It can be expressed in terms of a decrease in the concentration of any of the reactants per unit time or an increase in the concentration ...
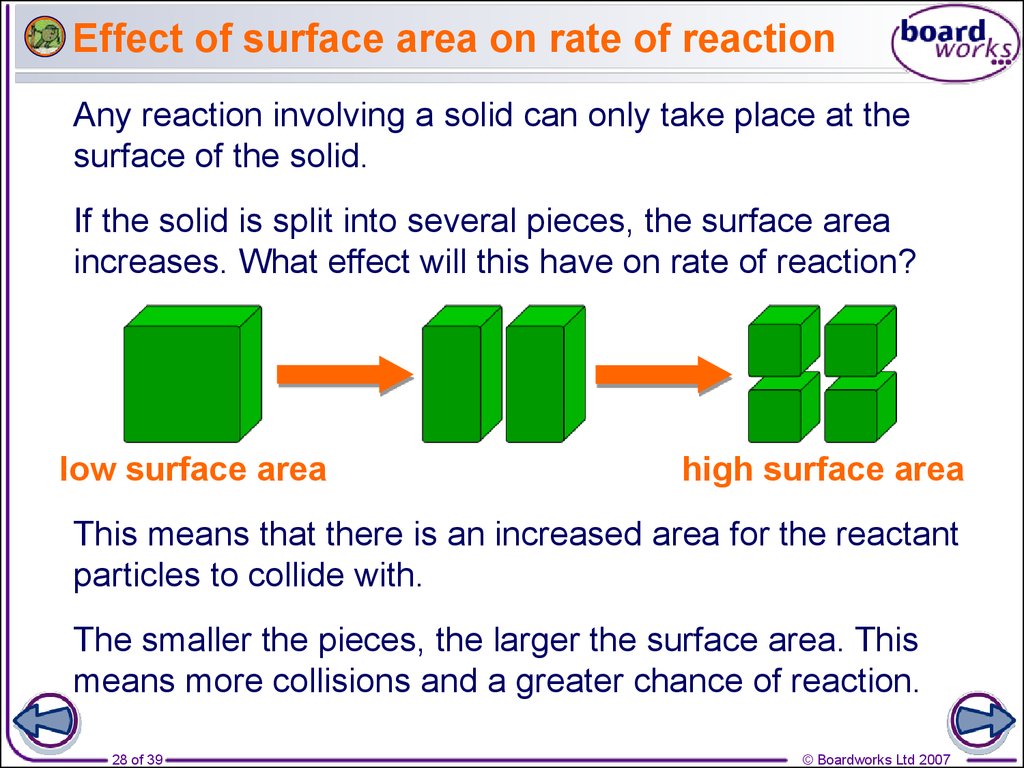
What is the surface area of a reaction?
Surface Area. For a reaction involving a solid reactant or a catalyst, the smaller is the particle size, i.e., the greater is the surface area, the faster is the reaction. Finely divided solid reactants possess a large surface area as compared to massive reactants and react much faster.
What is the effect of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction?
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of reaction and remains unchanged in amount and chemical composition at the end of a reaction. The catalyst forms an activated complex with the reactants at lower potential energy. Hence the activation energy of the reaction decreases, and the rate of reaction increases.
What is the rate of change of concentration of any one of the reactants or products at a particular instant of time?
The rate of reaction at any instant of time during the reaction is defined in terms of the instantane ous rate of reaction. The rate of change of concentration of any one of the reactants or products at a particular instant of time is called the instantaneous rate of reaction.
How does the rate of a reaction increase?
In general, the rate of a reaction increases by increasing the concentration of the reactants and vice versa. When the concentration of a reactant is increased, the possibility of molecular collisions increases. Therefore, the rate of reaction increases.
Why are ionic reactions so fast?
The reactions involving ionic or polar substances are very fast because of the electrostatic force existing between the molecules and are easily broken in an aqueous solution. A chemical reaction involving covalent reactants involves the breaking of old bonds and the formation of new bonds. Hence, its reaction rate depends upon the ease with which the specific bonds are broken and formed.
What increases the rate of a chemical reaction?
Several factors can increase the rate of a chemical reaction. In general, anything that increases the number of collisions between particles will increase the reaction rate, and anything that decreases the number of collisions between particles will decrease the chemical reaction rate.
What is activation energy?
Activation energy is a fixed amount for a reaction - a constant which is derived from the bonds in the reactants which need to be broken so that the products can be formed.
Is the rate always positive?
Note that the rate is always expressed as a positive number (that’s the reason for the negative sign in front of the Δ [A]).
Is the rate of reaction kinetic or kinetic?
The rate of reaction, however, is of kinetic importance. That is a question of how quickly the bonds break, not how easily the reaction proceeds.
How to find the rate of a reaction?
The rate of these reactions can be obtained either from the concentration of one reactant squared or from the concentration of two separate reactants.
How to write rate expression of reaction?
First, the rate expression of the reaction is written (r = k [A] x [B] y ..)
How to find partial order of a reaction?
The partial order corresponding to each reactant is now calculated by conducting the reaction with varying concentrations of the reactant in question and the concentration of the other reactants kept constant.
Why is the concentration of one reactant constant?
The concentration of the reactant may be constant because it is present in excess when compared to the concentration of other reactants, or because it is a catalyst.
What is the molecularity of a reaction?
The molecularity of a reaction refers to the number of atoms, molecules, or ions which must undergo a collision with each other in a short time interval for the chemical reaction to proceed. The key differences between molecularity and reaction order are tabulated below. It can be a whole number or a fraction.
What is the order of a reaction?
The Order of reaction refers to the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of the species taking part in it. In order to obtain the reaction order, the rate expression (or the rate equation) of the reaction in question must be obtained. Once the rate equation is obtained, the entire composition of the mixture ...
What happens when you get the rate equation?
Once the rate equation is obtained, the entire composition of the mixture of all the species in the reaction can be understood.

Average Rate of Reaction
Units of Rate of Reaction
Factors Affecting Rate of Chemical Reactions
Nature of Reactant
Concentration of Reactants
- Concentrations of reactants and products are usually expressed in moles per liter, and time is usually expressed in seconds or minutes. Therefore, the units of the rate of reactions are \({\rm{mol}}\,{{\rm{L}}^{ – 1}}{{\rm{S}}^{ – 1}}\) or \({\rm{mol}}\,{{\rm{L}}^{ – 1}}{\min ^{ – 1}}.\) When the reactants and products are in the gaseous state, their concentrations are expressed i…
Solved Numerical
- The rate of a chemical reaction depends upon several factors like the nature of the reactant, the concentration of the reactants, temperature, presence of a catalyst, the surface area of the reactant, radiation, etc.
Summary
- The rate of a chemical reaction depends upon the amount of energy required to break different bonds, and different amounts of energy are released in the formation of different bonds. The reactions involving ionic or polar substances are very fast because of the electrostatic force between the molecules and are easily broken in an aqueous solution. Example: The oxidation of …
FAQs
- In general, the rate of a reaction increases by increasing the concentration of the reactants and vice versa. When the concentration of a reactant is increased, the possibility of molecular collisions increases. Therefore, the rate of reaction increases.