How to pronounce reticular?
Here are 4 tips that should help you perfect your pronunciation of 'reticular':
- Break 'reticular' down into sounds : [RI] + [TIK] + [YUH] + [LUH] - say it out loud and exaggerate the sounds until you can consistently produce them.
- Record yourself saying 'reticular' in full sentences, then watch yourself and listen. ...
- Look up tutorials on Youtube on how to pronounce 'reticular'.
What does reticular mean?
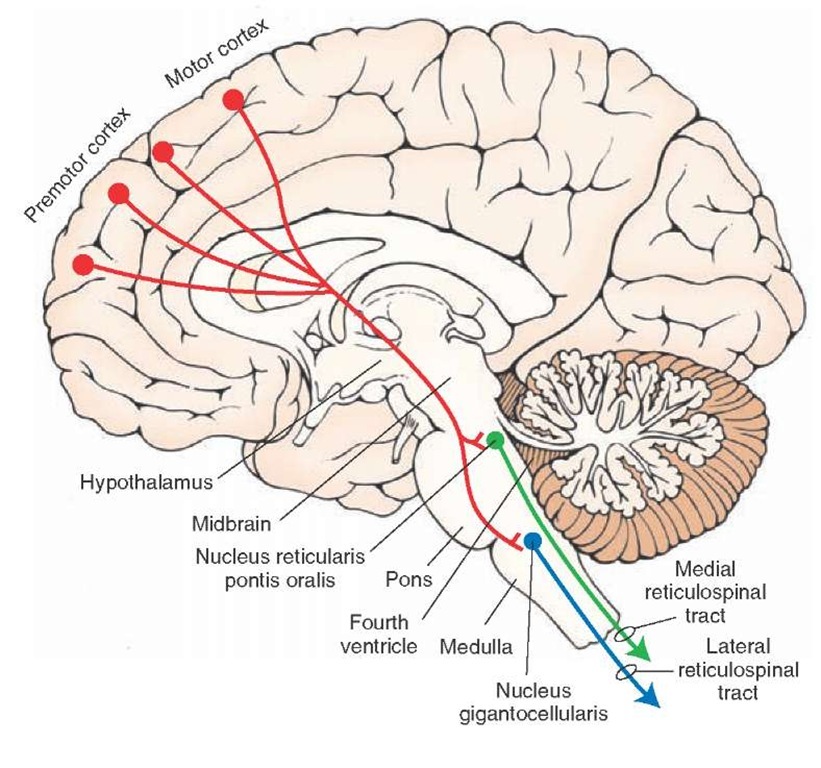
The reticular formation is a portion of the brain that is located in the central core of the brain stem. It passes through the medulla, pons, and stops in the midbrain. Its functions can be classified into 4 categories: motor control, sensory control, visceral control, and control of consciousness.
What is reticular theory?
Reticular theoryis an obsolete scientific theory in neurobiologythat stated that everything in the nervous system, such as brain, is a single continuous network. The concept was postulated by a German anatomist Joseph von Gerlach in 1871, and was most popularised by the Nobel laureate Italian physician Camillo Golgi.
What does reticular formation mean?
The reticular formation is a region in the brainstem that is involved in multiple tasks such as regulating the sleep-wake cycle and filtering incoming stimuli to discriminate irrelevant background stimuli. It is essential for governing some of the basic functions of higher organisms, and is one of the phylogenetically oldest portions of the brain.

Examples of reticular in a Sentence
Recent Examples on the Web Your mindset stems from a collection of neurons at the top of your brain stem called the reticular activating system (RAS) that acts as the search engine of your brain.
Medical Definition of reticular
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
What is reticular tissue?
Reticular tissue is a special subtype of connective tissue that is indistinguishable during routine histological staining. Its subunits, the reticular fibers, are predominant structures in the human body, but they are mainly scattered and mixed with other types of fibers.
What are the cellular structures of reticular tissue?
Some highly cellular locations containing reticular tissue include the endocrine glands, liver, bone marrow, and lymphoid organs . If you think about the structure of those tissues and organs, they all consist of heavily branching septa and internal channels. Reticular tissue also resembles a branched mesh that coincides with the path taken by those septa and channels, almost fitting them “like a glove”. Therefore, the role of the reticular scaffold is to support the cells and the small channels which travel through the respective tissues and organs. For example, in the liver, reticular tissue supports the hepatocytes and the sinusoids.
What is reticulum connective tissue?
Characteristics. Reticular tissue is a special type of connective tissue that predominates in various locations that have a high cellular content. It has a branched and mesh-like pattern, often called reticulum, due to the arrangement of reticular fibers (reticulin). These fibers are actually type III collagen fibrils.
What is the role of reticular fibers in wound healing?
Reticular fibers support the early synthesized extracellular matrix during wound healing, scar tissue formation, and general development. As maturity or repair continues, the majority of them are replaced by the stronger type I collagen.
Why do reticular fibers need special staining?
For visualization purposes, reticular fibers require special staining procedures because they stain poorly with hematoxylin-eosin (H&E). Some of these include: Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) reaction, which takes advantage of the high polysaccharide content of reticular fibers.
What is the role of reticular scaffold?
Therefore, the role of the reticular scaffold is to support the cells and the small channels which travel through the respective tissues and organs. For example, in the liver, reticular tissue supports the hepatocytes and the sinusoids.
Where does reticular fiber synthesis take place?
The entire process of reticular fiber synthesis is compartmentalized: procollagen (precursor) is synthesized intracellularly within organelles, the collagen monomers (subunit) at the level of the plasma membrane, while the assembly into reticular fibers takes place in the extracellular matrix.
What is the reticular system?
The reticular formation is a neuron network in the brainstem that enables consciousness, sensory and motor function, and endocrine and neurotransmitter regulation. This part of the central nervous system, spread in three main columns from one end of the brainstem to the other, is a core relay point that connects the nerves of the spinal cord with the brain via efferent and afferent neurons. Its full range of functions is not fully known.
Which organs are involved in the reticular formation?
It is thought that the reticular formation transmits the information that controls the release and inhibition of an extensive range of hormones; this theory is supported by the fact that it lies extremely close to important neuroendocrine secretory organs such as the pineal, pituitary, and hypothalamus glands .
How do the reticular activating systems work?
These are the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) that brings sensory messages from the RF to the brain cortex and vice versa , and the descending reticular system (DRS) that brings messages to and from the motor neurons of the spinal cord. You should see both systems as two parts of a single parallel system; they work at the same time, and the brainstem reticular formation modulates how many messages are processed. The two systems (ARAS and DRS) influence each other. That is why, if you are watching a really scary horror film, your muscles become tense – both your emotions and your muscles react. And when the scariest moment is over, you relax. The group term of reticular activating system or RAS is confusingly named, as it not only activates but deactivates associated neurons.
Why is reticular formation fatal?
Greater trauma to the site of the reticular formation is often fatal due to its central role in vital functions such as breathing and consciousness.
Where are reticular veins located?
Location. Reticular veins typically appear on the backs of your knees, on your inner thighs, or near your ankles. Symptoms. Reticular veins can cause pain or other discomforts in your lower legs. While reticular veins don’t always cause symptoms, their appearance can be a cosmetic concern for some people.
Which is smaller, a reticular vein or a varicose vein?
Reticular veins are smaller than varicose veins. Reticular veins also appear flatter and less twisted than varicose veins.
What is the best treatment for enlarged reticular veins?
Sclerotherapy is one of the most effective treatments for enlarged or painful reticular veins, according to a 2015 research review. This treatment involves injecting material that destroys your reticular veins by damaging your veins’ lining. This causes your veins to collapse and become blocked.
Why do my reticular veins leak backwards?
Reticular veins come from a condition called vascular or venous insufficiency. Your veins have small “valves” that keep blood from flowing backward as your blood returns to your heart. However, with vascular insufficiency, your blood leaks backward because of a concern with your valve function.
How big are reticular veins?
The most immediate noticeable difference between reticular veins and spider veins are their sizes. Reticular veins are larger (about 3 millimeters or fewer) than spider veins (usually 1 millimeter or fewer), according to a 2017 research review. Trusted Source. . You can have both reticular veins and spider veins.
Can reticular veins cause discomfort?
While reticular veins are mostly a cosmetic concern, they can cause uncomfortable symptoms. Keep reading to find out why reticular veins form and how doctors treat them.
Is it dangerous to have reticular veins?
Reticular veins can be uncomfortable or painful, but they aren’t usually dangerous. However, they do indicate that blood isn’t flowing through your veins as well as it could be. If you have reticular veins, you may wish to take steps to improve blood flow to your lower legs. These steps include:
What is the reticular activating system?
The reticular activating system is an impressive-sounding name for a fairly small piece of the brain. This lesson describes the structure and function of this piece of the brain, which is important in attention, goal-achievement, and keeping you alive.
How much information does the human eye capture?
And a human eye captures more than 300 megapixels of visual information every second! Despite all of this sensory information, it's estimated that the conscious mind can only handle slightly more than 100 pieces of information every second.
What is the Ras in the brain?
Often, the RAS is compared to a filter or a nightclub bouncer that works for your brain.
What is areolar tissue?
areolar tissueconnective tissue made up largely of interlacing fibers.
What is a sclerous T?
sclerous t's the cartilaginous, fibrous, and osseous tissues. skeletal tissue the bony, ligamentous, fibrous, and cartilaginous tissue forming the skeleton and its attachments. splenic tissue red pulp. subcutaneous tissue the layer of loose connective tissue directly under the skin. tissue typing identification of tissue types for purposes ...
What is the term for the dense fibrous tissue that binds together and is the support of the various structures of?
cicatricial tissue the dense fibrous tissue forming a cicatrix, derived directly from granulation tissue; called also scar tissue. connective tissue the tissue that binds together and is the support of the various structures of the body; see also connective tissue.
What is connective tissue?
a group or layer of similarly specialized cells that together perform certain special functions. adenoid tissue lymphoid tissue. adipose tissue connective tissue made of fat cells in a meshwork of areolar tissue. areolar tissue connective tissue made up largely of interlacing fibers. bony tissue osseous tissue.
Which tissue binds together and is the support of the various structures of the body?
connective tissuethe tissue that binds together and is the support of the various structures of the body; see also connective tissue.
What is subcutaneous tissue?
subcutaneous tissue the layer of loose connective tissue directly under the skin. tissue typing identification of tissue types for purposes of predicting acceptance or rejection of grafts and transplants. The process and purposes of tissue typing are essentially the same as for blood typing. The major difference lies in the kinds ...