Reticulum is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for a small net, or reticle —a net of crosshairs at the focus of a telescope eyepiece that is used to measure star positions.
What is the meaning of the word reticulum?
re·tic·u·lum. (rĭ-tĭk′yə-ləm) n. pl. re·tic·u·la (-lə) 1. A netlike formation or structure; a network. 2. Zoology The second compartment of the stomach of ruminant mammals, lined with a membrane having honeycombed ridges. 3. Reticulum A constellation in the Southern Hemisphere near Dorado and Horologium.
Is reticulum singular or plural?
reticulum, plural: reticulums, reticula n. noun: Refers to person, place, thing, quality, etc. (part of a ruminant's digestive system) retículo nm. nombre masculino: Sustantivo de género exclusivamente masculino, que lleva los artículos el o un en singular, y los o unos en plural. Exemplos: el televisor, un piso.
What does reticulum mean in Latin?
Reticulum is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for a small net, or reticle—a net of crosshairs at the focus of a telescope eyepiece that is used to measure star positions. The constellation is best viewed between October and December, but cannot be seen from middle to northern latitudes.
What is the common name for the reticulum?
What is the common name of the reticulum? Honeycomb. What does the inner lining of the reticulum look like? intersecting ridges, like a honeycomb. Where is the reticulum located? directly behind the diaphragm. Which compartment of the ruminant stomach can get involved in hardware disease?
What is the reticulum also known as?
The reticulum is colloquially referred to as the honeycomb, bonnet', or kings-hood. When cleaned and used for food, it is called "tripe".
Does reticular mean?
net; netlikereticular in American English 1. having the form of a net; netlike. 2. intricate or entangled.
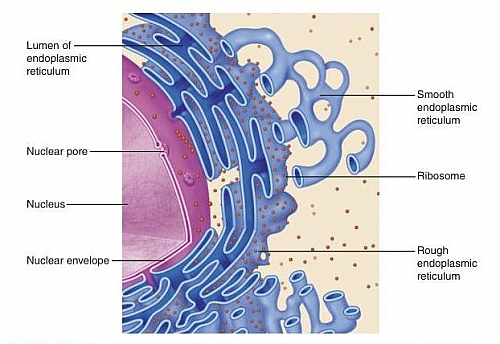
What is the short Definition of endoplasmic reticulum?
Endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes inside a cell through which proteins and other molecules move. Proteins are assembled at organelles called ribosomes.
What is the meaning of nuclear reticulum?
Medical Definition of nuclear reticulum : the diffuse intermeshed granular threads that represent the chromosomes in the resting nucleus. — called also nuclear network.
What does reticular mean in biology?
This word is often used in biology for parts of organisms that are net-like. Parts of our nervous system are often described as reticular, because the nerves resemble a net and also form a network. Definitions of reticular. adjective. resembling or forming a network.
What does reticular mean in anatomy?
reticular fibre, in anatomy, fine fibrous connective tissue occurring in networks to make up the supporting tissue of many organs. The reticular fibres are composed of randomly oriented collagenous fibrils lying in an amorphous matrix substance.
What are the functions of reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The diverse functions of the ER are performed by distinct domains; consisting of tubules, sheets and the nuclear envelope.
What is endoplasmic reticulum example?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. All eukaryotic cells contain an ER. In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell.
What is another word for endoplasmic reticulum?
What is another word for endoplasmic reticulum?endoplasmatic reticulumergastoplasmrough ERsarcoplasmic reticulumsmooth ER
What are the 5 functions of endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum performs the following functions: It is responsible for the production and secretion of steroid hormones. It is also responsible for the synthesis of essential lipids such as phospholipids and cholesterol. It is responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Where is endoplasmic reticulum located?
cytoplasmThe endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membrane-enclosed tubules and sacs (cisternae) that extends from the nuclear membrane throughout the cytoplasm (Figure 9.1). The entire endoplasmic reticulum is enclosed by a continuous membrane and is the largest organelle of most eukaryotic cells.
Does reticulum mean network?
noun, plural re·tic·u·la [ri-tik-yuh-luh] for 1-3. a network; any reticulated system or structure.
What does reticular mean in medicine?
(reh-TIH-kyoo-ler DER-mis) The thick bottom layer of the dermis (the inner layer of the skin). The reticular dermis has blood vessels and connective tissue that supports the skin.
What is reticular function?
The major functions that the reticular formation influences are arousal, consciousness, circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycles, coordination of somatic motor movements, cardiovascular and respiratory control, pain modulation, and habituation.
What is reticular tissue?
Reticular tissue, a type of loose connective tissue in which reticular fibers are the most prominent fibrous component, forms the supporting framework of the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils), bone marrow and liver.
What does reticular formation mean in psychology?
an extensive network of nerve cell bodies and fibers within the brainstem, extending from the medulla oblongata to the upper part of the midbrain, that is widely connected to the spinal cord, cerebellum, thalamus, and cerebral cortex.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.All e...
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The ER can be classified in two functionally distinct forms: smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The morpholo...
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves important functions particularly in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins. Differen...
When was the endoplasmic reticulum discovered?
The ER was first noted in the late 19th century, when studies of stained cells indicated the presence of some type of extensive cytoplasmic structu...
What is the granular reticulum?
sarcoplasmic reticulum a form of agranular reticulum in the sarcoplasm of striated muscle, comprising a system of smooth-surfaced tubules surrounding each myofibril.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
endoplasmic reticulum an ultramicroscopic organelle of nearly all higher plant and animal cells, consisting of a system of membrane-bound cavities in the cytoplasm, occurring in two types: granular or rough-surfaced, bearing large numbers of ribosomes on its outer surface, and agranular or smooth-surfaced.
What is a netlike structure?
1. A netlike formation or structure; a network. 2. Zoology The second compartment of the stomach of ruminant mammals, lined with a membrane having honeycombed ridges. The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company.
What is the reticulum?
reticulum. for 4. a network; any reticulated system or structure. Anatomy. a network of intercellular fibers in certain tissues. a network of structures in the endoplasm or nucleus of certain cells. Zoology. the second stomach of ruminating animals, between the rumen and the omasum.
Where is the yolk in the reticulum?
The yolk is contained in the meshes of this reticulum in the manner already described for other ova.
What is a network in biology?
for 4. a network; any reticulated system or structure. Anatomy. a network of intercellular fibers in certain tissues. a network of structures in the endoplasm or nucleus of certain cells. Zoology. the second stomach of ruminating animals, between the rumen and the omasum.
Is the entire body a reticulum?
It is even held that these fibres penetrate the cell walls and connect adjoining cells, so that the entire body is a reticulum.
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a membrane that runs along the filaments of the muscle and provides a source of calcium for the activation of muscles ( MacIntosh, Gardiner, & McComas, 2006 ). The sarcoplasmic reticulum has a regular repeating pattern just like the repeating structure of the sarcomere. Hill (1949) showed that a substance released at the surface of the membrane would take too long to reach the middle and initiate muscle activation. However, the diffusion distance for calcium to get into the muscle fibers is quite small due to the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ridgway and Gordon (1975) showed the rise and fall of calcium concentration in the sarcoplasm by using a protein isolated from jellyfish which gives off light when it binds to calcium ions. They measured this in barnacle fibers and found similar results to those previously found in frog muscle fibers ( Rudel & Taylor, 1973 ). Baylor, Chandler, and Marshall (1983) found that after an initial rapid release of calcium, there is a longer maintained period of calcium intake. Calcium is released into the muscle by the sarcoplasmic reticulum where it diffuses to the thin filaments and binds to regulatory sites on troponin to activate muscle contraction ( Baylor & Hollingworth, 2011 ). The sarcoplasmic reticulum provides the muscle with the source of calcium needed to contract.
What is the SER in a cell?
The SER in most cells is relatively sparse. However, in cells that synthesize steroid hormones (e.g., the adrenal cortex or gonads) or that catabolize lipid-soluble molecules (e.g., liver cells make certain drugs more water-soluble so that they may be excreted), the SER may be particularly conspicuous. The SER is also responsible for sequestering intracellular Ca++; release of Ca++ from the SER is a mechanism by which cells can rapidly respond to extracellular signals. Finally, in muscle cells, specialized SER called sarcoplasmic reticulum regulates the successive cycles of myofiber contraction (Ca++ released into the cytosol) and relaxation (Ca++ pumped back into the SER).
What is the SR membrane?
The SR is a specialized type of the smooth ER that regulates the Ca 2 + concentration in the cytoplasm inside muscle cells. The SR membrane is rich in phospholipids, which amount to more than 78% of the total lipid content [141]. Among the phospholipids, the main component is PC (37%–70%), followed by PE (19%–33%), and the lowest amount was observed for negatively charged PS and sphingomyelin that account for 4%–13% and 3%–12%, respectively. In addition, cholesterol is present, but in a very low concentration (less than 2%) [141,142]. The typical feature of the SR membrane is a lipid asymmetry that likely contributes to the curvature stress in membranes. For example, PE molecules reside more in the outer (cytosolic) leaflet, whereas PS molecules are localized in the inner leaflet of the SR membrane [143]. Considering the fatty acid pattern of phospholipids in the SR membrane, the dominant components are polyunsaturated species that account for approximately 55% of the total content, from which the fatty acids C18:2, C20:4, and C22:6 are the three major components. Saturated fatty acids with prevalent C16:0 and C18:0 chains represent 34% of the total content. On the other hand, monounsaturated fatty acids are found in a very small amount (approximately 9%), the major representative of which is the C18:1 acyl chain [141,144].
What is the role of ER in pathogenesis?
ER plays an important role in the pathogenesis: Aβ is formed by γ-secretase complex presenilin 1 (PS-1) and PS-2 , which is located at the interface between mitochondria and ER.
Is the Nebenkern part of the cytoplasm?
The Nebenkern, because of its high concentration of E.R. membranes, might be considered as a possible region in the cytoplasm where this material is being formed . The Nebenkern is made up of a dense aggregation of concentric rings, and one could, perhaps, consider the possibility of the membranes peeling off from such a germ center. The same sort of appearance has also been noted in association with the nuclear membrane and has led to the suggestion that the endoplasmic reticulum is formed in this region and that the layers are, in fact, peeling off the nuclear membrane. However it may quite easily be interpreted the opposite way, i.e., the close apposition of the existing ergastoplasm around the nuclear membrane may be a part of the complex canalicular system that permits an almost direct passage through the nuclear membrane direct into the cisternae of the reticulum. Again, there are a number of authors who think the endoplasmic reticulum is associated with mitochondria. There is no doubt that many pictures of mitochondria, closely surrounded by concentric layers of endoplasmic reticulum have been obtained, and we, ourselves, have found this particularly well demonstrated around the mitochondria of the liver cells of scorbutic guinea pigs. In some cases, Sheridan has found a tremendous concentration of many layers of reticulum around the mitochondria, as though, in fact, the reticulum is being formed on the surface of the mitochondrial membrane and is being split off. Rouiller and his colleagues have demonstrated that, in animals which have been poisoned, the endoplasmic reticulum, destroyed or badly damaged by the treatment, always reappears in association with mitochondria. The membranes of the reticulum may not undergo direct physical formation in the sense that the membranes are produced on the surface of the mitochondrial membrane and split off; it may be that the mitochondria supply the energy necessary for the production of these membranes. Furthermore the close relationship between the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitochondria may simply be physiological, that is they are cooperating in some metabolic process such as the synthesis of protein. However, the origin of the endoplasmic reticulum is a problem that is far from solved, and we must await further evidence before drawing a conclusion.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. All eukaryotic cells contain an ER. In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell. The ER can be classified in two functionally distinct forms: ...
Who introduced the term "endoplasmic reticulum"?
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, Porter and colleagues Helen P. Thompson and Frances Kallman introduced the term endoplasmic reticulum to describe the organelle. Porter later worked with Romanian-born American cell biologist George E. Palade to elucidate key characteristics of the ER. Kara Rogers.
What is the ER in eukaryotic cells?
All eukaryotic cells contain an endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell. Differences in certain physical and functional characteristics distinguish the two types of ER, known as rough ER and smooth ER. Rough ER is named for its rough appearance, ...
What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the liver?
In cells of the liver, it contributes to the detoxification of drugs and harmful chemicals. The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a specialized type of smooth ER that regulates the calcium ion concentration in the cytoplasm of striated muscle cells. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content.
Why is the rough ER called the rough ER?
Rough ER is named for its rough appearance, which is due to the ribosomes attached to its outer (cytoplasmic) surface. Rough ER lies immediately adjacent to the cell nucleus, and its membrane is continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope.
What percentage of the membrane content of an animal cell is ER?
In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell.
Is smooth ER ribosome?
See all videos for this article. Smooth ER, by contrast, is not associated with ribosomes , and its functions differ. The smooth ER is involved in the synthesis of lipids, including cholesterol and phospholipids, which are used in the production of new cellular membrane.
What does "reticulum" mean?
re•tic•u•lum. n., pl. -la (-lə). 1. a network; any reticulated system or structure. 2. a. a network of intercellular fibers in certain tissues. b. a network of structures in the endoplasm or nucleus of certain cells.
What is the reticulum?
reticulum. ( rɪˈtɪkjʊləm) n, pl -la ( -lə) 1. (Anatomy) any fine network, esp one in the body composed of cells, fibres, etc. 2. (Zoology) the second compartment of the stomach of ruminants, situated between the rumen and psalterium. [C17: from Latin: little net, from rēte net]
What is a netlike structure?
1. A netlike formation or structure; a network. 2. Zoology The second compartment of the stomach of ruminant mammals, lined with a membrane having honeycombed ridges. 3. Reticulum A constellation in the Southern Hemisphere near Dorado and Horologium. [Latin rēticulum, diminutive of rēte, net .]
What is the reticulum?
For other uses, see Reticulum (disambiguation). The reticulum is the second chamber in the alimentary canal of a ruminant animal. Anatomically it is considered the smaller portion of the reticulorumen along with the rumen.
What is the reticulum called?
The reticulum is colloquially referred to as the honeycomb. It is also known as the bonnet and as the kings-hood. When cleaned and used for food, it is called " tripe ". Heavy or dense feed and foreign objects will settle here.
What happens in the first contraction of the reticulum?
In the first contraction there is sending large particles back into the rumen while the reticulo-omasal orifice allows the passage of finer particles. In the second contraction the reticulum contracts completely so the empty reticulum can refill with contents from the rumen.
Where is the rumen located in the stomach?
Together these two compartments make up 84% of the volume of the total stomach. The rumen is located at the base of the esophagus. The reticulum is colloquially referred to as the honeycomb.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum serves many general functions, including the folding of protein molecules in sacs called cisternae and the transport of these synthesized proteins to the Golgi Apparatus, which further processes them for transport to their final destinations: lysosomes, the plasma membrane or for secretion.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum? What is its function?
The endoplasmic reticulum, found in eukaryotic cells, is a network of tubes or flat sacs — kind of like a labyrinth of membranes — that serves as the factory of the cell, manufacturing and packaging up proteins and lipids to send around the cell, and even outside of it. About half of the total membrane surface area in an animal cell is found in the endoplasmic reticulum. Which molecules the endoplasmic reticulum makes depends a lot on what kind of cell it is — for instance, the endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells store a lot of calcium ions because muscle cells need these to make muscles contract, and organs in the digestive system tend to have cells with an endoplasmic reticulum that manufactures a variety of different kinds of cholesterol.
Why does the liver have smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Liver cells contain lots of smooth endoplasmic reticulum because the liver plays a big role in detoxification. So, if you've had a few too many glasses of wine, it's the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in your liver that's helping move things along the next morning.
Which two types of eukaryotic cells do not contain an endoplasmic reticulum?
Two types of eukaryotic cells that do not contain an endoplasmic reticulum are red blood cells and sperm.
Is the endoplasmic reticulum the same as the smooth?
Advertisement. There are two different regions to the endoplasmic reticulum — rough and smooth — and both are found in both plant and animal cells, and although they appear to be separate when you look at them under the microscope, they're really just different compartments of the same organelle.
Why is the rough endoplasmic reticulum important?
D is correct. The rough endoplasmic reticulum plays an important role in synthesizing proteins destined for secretion from the cell. Therefore, it is studded with ribosomes and polysomes, which are translating mRNA containing the code for these proteins. This process is particularly important during lactation since milk contains a number of proteins that sustain a baby during the initial months.
What is the role of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
It also plays an important role in modulating the response of cell to stress and in quality control for correct protein folding. When the number of unfolded proteins increases, cells alter their tubules:sheets ratio. This could arise from the greater area available within the sheets of the rough ER to rescue unfolded protein, or could reflect the need for the distinct proteome of the rough ER.
What changes occur when ribosomes detach from sheets of rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Changes to the pattern of microtubule polymerization are also reflected in changes to ER morphology. Additionally, when ribosomes detach from sheets of rough endoplasmic reticulum, these structures can disperse and form tubular cisternae. The edges of ER sheets have a high-curvature that needs to be stabilized.
Why are proteins removed from the ER?
In spite of these mechanisms to ensure that proteins are folded correctly, some need to be removed from the system, either due to errors in translation or due to genetic mutations leading to the production of defective proteins. This is accomplished by the quality control systems within the ER that ‘proof read’ newly synthesized proteins. When the polypeptide has not folded into its native state, molecular chaperones bind to the polypeptide again and make another attempt at folding the protein into its correct shape. When repeated attempts fail, misfolded proteins can be exported to the cytosol, and removed through the proteasome using ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation.
What is the role of the rough ER in apoptosis?
The rough ER is also involved in the response of the cell to unfolded proteins and plays a role in the induction of apoptosis, due to its close interaction with mitochondria. The rough ER is characterized by the presence of membrane-bound ribosomes that give it a distinctive appearance under the microscope.
Why are two classes of proteins redundant?
These two classes of proteins are redundant, since the overexpression of one protein appears to compensate for the lack of the other protein.
Which cells secrete rough ER?
Therefore, rough ER is prominent in liver cells that secrete serum albumin, cells of the digestive system that secrete enzymes, endocrine cells that synthesize and secrete protein hormones (such as insulin) and in cells that create the proteins of the extracellular matrix.
