How do you know if sphericity is assumed?
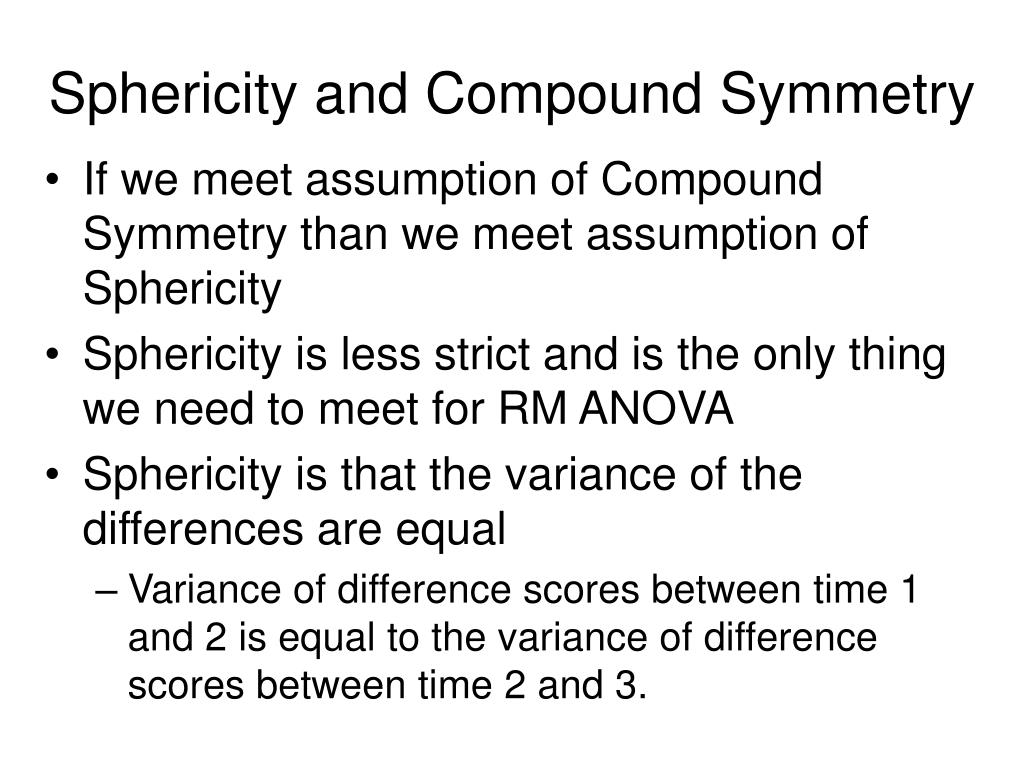
The sphericity assumption is satisfied when the variance of the difference between scores for any two levels of a repeated measures factor is constant. The sphericity assumption is violated when the variance of the difference between scores for any two levels of a repeated measures factor is not constant.
What does Mauchly's test of sphericity tell you?
Mauchly's test of sphericity is used to test whether or not the assumption of sphericity is met in a repeated measures ANOVA. Sphericity refers to the condition where the variances of the differences between all combinations of related groups are equal.
What does sphericity mean in statistics?
Sphericity is an assumed characteristic of data analyzed in repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). Sphericity refers to the equality of variances of the differences between treatment conditions.
What is sphericity assumption in ANOVA?
Repeated measures ANOVA make the assumption that the variances of differences between all combinations of related conditions (or group levels) are equal. This is known as the assumption of sphericity.
How do you know if Mauchly's test is significant?
→ If Mauchly's test statistic is significant (i.e. has a probability value less than . 05) we conclude that there are significant differences between the variance of differences: the condition of sphericity has not been met. → If, Mauchly's test statistic is nonsignificant (i.e. p > .
How do you know if Mauchly's test is violated?
Mauchly's Test is used in SPSS to assess the statistical assumption of sphericity when using repeated-measures ANOVA. If Mauchly's Test yields a p-value LESS THAN . 05, then the assumption has been violated. The Greenhouse-Geisser correction is used to correct for this prevalent violation.
When the assumption of sphericity is violated what action is needed?
Answer: 8. When the assumption of sphericity is violated, what action is needed? Correct the model degrees of freedom and correct the error degrees of freedom.
What is sphericity used to find?
Sphericity is a measure of the degree to which a particle approximates the shape of a sphere, and is independent of its size. Roundness is the measure of the sharpness of a particle's edges and corners.
How do I test sphericity in SPSS?
Sphericity. This means that the population variances of all possible difference scores (com_1 - com_2, com_1 - com_3 and so on) are equal. Sphericity is tested with Mauchly's test which is always included in SPSS' repeated measures ANOVA output so we'll get to that later.
How do you interpret ANOVA results?
Interpret the key results for One-Way ANOVAStep 1: Determine whether the differences between group means are statistically significant.Step 2: Examine the group means.Step 3: Compare the group means.Step 4: Determine how well the model fits your data.More items...
How do you know if sphericity is violated in SPSS?
If the p-value is LESS THAN . 05, then researchers have violated the assumption of sphericity. If the p-value is MORE THAN . 05, then researchers have not violated the assumption of sphericity.
How do I report Mauchly's?
We could report Mauchly's test for these data as: → Mauchly's test indicated that the assumption of sphericity had been violated, χ2(5) = 11.41, p = . 047. Output 3 shows the results of the ANOVA for the within-subjects variable.
Does Mauchly's test of sphericity have to be significant or nonsignificant?
→ Mauchly's test should be nonsignificant if we are to assume that the condition of sphericity has been met. → Sometimes when you look at the significance, all you see is a dot. There is no significance value. The reason that this happens is that you need at least three conditions for sphericity to be an issue.
What is sphericity used to find?
Sphericity is a measure of the degree to which a particle approximates the shape of a sphere, and is independent of its size. Roundness is the measure of the sharpness of a particle's edges and corners.
When the assumption of sphericity is violated what action is needed?
Answer: 8. When the assumption of sphericity is violated, what action is needed? Correct the model degrees of freedom and correct the error degrees of freedom.
What does greenhouse Geisser do?
The Greenhouse-Geisser is used to assess the change in a continuous outcome with three or more observations across time or within-subjects. In most cases, the assumption of sphericity is violated for this type of within-subjects analysis and the Greenhouse-Geisser correction is robust to the violation.
What is the assumption of sphericity?
The assumption of sphericity refers to the equality of variances of the differences between treatment levels. In Repeated Measures ANOVA it is a measure of the homogeneity of the variances of the differences between levels so it is quite similar to homogeneity of variance in between-groups in the univariate ANOVA.
What is sphericity in ANOVA?
Sphericity applies to repeated measures ANOVA and MANOVA. While technically not an assumption of Factor Analysis, “Bartlett’s test of sphericity” is applied to test the hypothesis that variables are uncorrelated with each other – so they only correlate with themselves (referred to as an “identity matrix”). Here we want the test of sphericity ...
What happens if you violate sphericity in ANOVA?
The violation of sphericity may cause our ANOVA or MANOVA significance test to become too “liberal” which increases the likelihood of a Type I error (incorrectly rejecting a true null hypothesis).
What is the definition of sphericity?
Hakon Wadell defined sphericity as the surface area of a sphere of the same volume as the particle divided by the actual surface area of the particle.
What is sphericity in science?
Sphericity is a specific example of a compactness measure of a shape. Defined by Wadell in 1935, the sphericity, is the surface area of the particle. The sphericity of a sphere is unity by definition and, by the isoperimetric inequality, any particle which is not a sphere will have sphericity less than 1.
What is the analogue of sphericity?
Sphericity applies in three dimensions; its analogue in two dimensions, such as the cross sectional circles along a cylindrical object such as a shaft, is called roundness .
What is the measure of sphericity?
Sphericity is a measure of how spherical an object is. Proposed by Waddell in 1935, the sphericity of a particle is defined as the ratio of the surface area of an equal-volume sphere to the actual surface area of the particle:
Who discovered working sphericity?
The concept of working sphericity was introduced by Aschenbrenner (1956) as another method for approximating sphericity of volcanic particles based on form dimensions. Working sphericity is the sphericity of a tetrakaidekahedron derived from its flatness and elongation ratios, which is modified to equal the average sphericity between a tetrakaidekahedron and sphere when f = e = 1 ( Aschenbrenner, 1956 ). When rewritten as flatness, f, and elongation, e, ratios, working sphericity can be defined as ( Alfano et al., 2011a; Bonadonna and Costa, 2013; Bonadonna et al., 2013; Bagheri et al., 2015 ):
What is the maximum sphericity of a particle?
Sphericity has a maximum value of 1 , which corresponds to a particle with a perfectly spherical shape. Sphericity depends on both form and roundness of the particle ( Blott and Pye, 2007 ). The sphericity of irregular particles is a function of particle surface area. Direct measurements of sphericity of the same particles referenced above, which used 3-D laser scanning and SEM micro-CT sphericity of lapilli-size particles, yields values of 0.53–0.81 (average 0.69), while for coarse ash was between 0.44 and 0.86 ( Bagheri et al., 2015 ).
What is the best correlation between sphericity and stability field?
Sphericity showed the best correlation with stability field rating. Taking a stabilit y field rating of 2 as the maximum permissible, the sphericity should not be less than 0.55.
What is the difference between spherical and nonspherical molecules?
The difference between spherical molecules and nonspherical molecules was investigated by Pitzer (1955). The greater the deviation from sphericity, the more difficult for two molecules to approach each other. As a result, the potential minimum of nonspherical molecules is narrower than that of spherical molecules.
How many terms does each subdomain take for a power series?
From a process of inverse differential transformation, it can be shown that the solutions of each subdomain takes n + 1 term for the power series, i.e.,
What is the best r-squared value for sphericity?
The best r-squared value was 0.53 for sphericity.
What is the purpose of Mauchly's test of sphericity?
Mauchly’s test of sphericity is used to test whether or not the assumption of sphericity is met in a repeated measures ANOVA.
What software is used to test for sphericity?
To determine if these differences are statistically significant, we can perform Mauchly’s test of sphericity using some statistical software like R, SPSS, Python, etc.
What happens if the p-value of the test is less than some significance level?
α = .05) then we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the variances of the differences are not equal.
Why is sphericity only evaluated for variables with more than two levels?
Sphericity is evaluated only for variables with more than two levels because sphericity necessarily holds for conditions with only two levels. The violation of sphericity assumption may distort the variance calculations resulting to a more liberal repeated measures ANOVA test (i.e., an increase in the Type I error rate).
Why is a significant p-value 0.05?
Thus, a significant p-value (p <= 0.05) indicates that the variances of group differences are not equal.
What does epsilon mean?
Note that, the epsilon provides a measure of the degree to which sphericity has been violated. A value of 1 indicates no departure from sphericity (all variances of group differences are equal). A violation of sphericity results in an epsilon value below 1. The further epsilon is from 1, the worse the violation.
Is the variance of t2 t3 greater than the variance of t1 t2 t?
From the results above, the variance of “t2-t3” appear to be much greater than the variances of “t1-t2” and “t1-t3”, suggesting that the data may violate the assumption of sphericity.
Is Mauchly's test of sphericity significant?
In our example, the Mauchly’s test of sphericity is not significant ( p > 0.05); this indicates that, the variances of the differences between the levels of the within-subjects factor are equal. So, we can assume the sphericity of the covariance matrix and interpret the standard output available in the ANOVA table.
