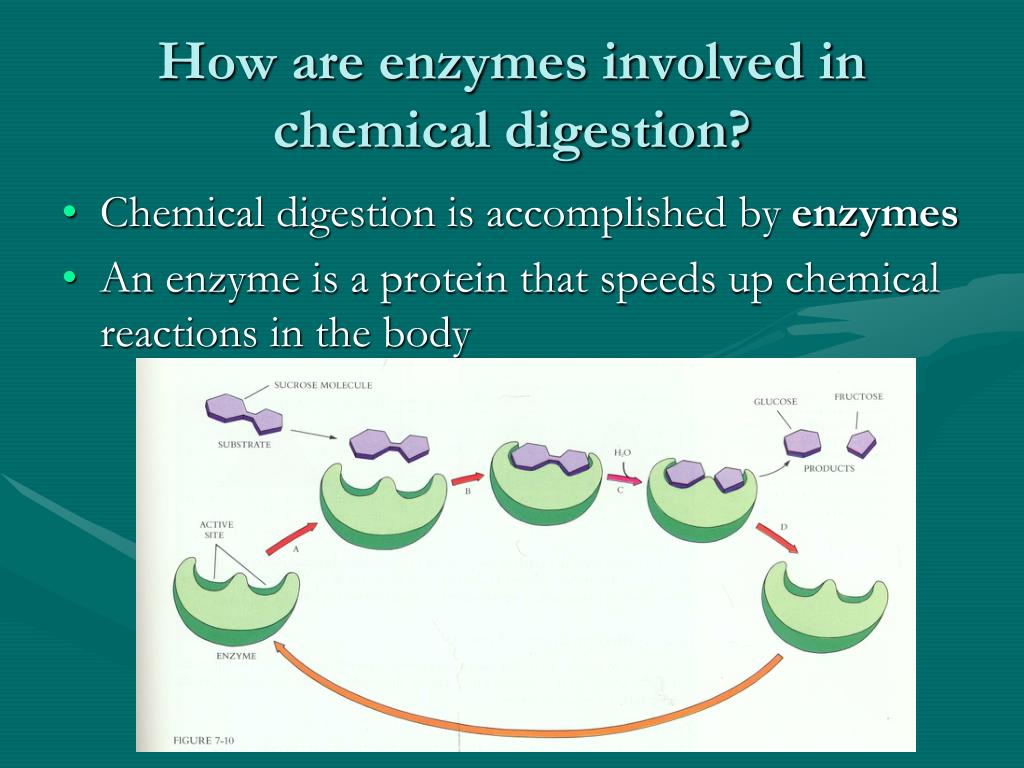
What starches are eventually broken down to?
Starch breaks down to shorter glucose chains. This process starts in the mouth with salivary amylase. The process slows in the stomach and then goes into overdrive in the small intestines. The short glucose chains are broken down to maltose and then to glucose. Can starch break down without amylase?
What does too much starch does to the body?
Too much starch can affect your blood sugar levels and lead to weight gain. The key to a healthy diet is to eat a wide variety of foods, but the truth is that most people have favorite foods — and it's easy, especially if you're a picky eater or always pressed for time, to get stuck in a rut.
Which substance helps break down starch during digestion?
The enzyme that breaks down starch is amylase. Starch is a type of complex carbohydrate made by plants and consists of glucose subunits. Amylase breaks starch into constituent sugar molecules. Depending on the type of amylase, the starch can be broken down into either compound sugars, such as maltose, or simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose.
What helps to break down starch into smaller molecules?
– Amylase is a digestive enzyme that breaks starch down into smaller molecules of carbohydrate. … – First of all, we use salivary glands in our mouth that start the digestive process by breaking off the starch through the secretion of salivary amylase, turning it into maltose, a smaller carbohydrate, when we chew it.
See more
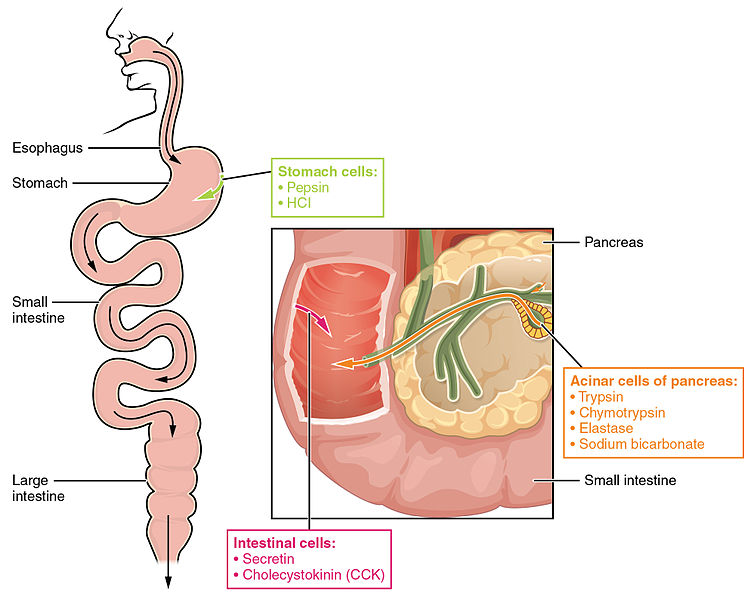
What do you get when you break down starch?
When all is said and done, starches have been broken down into their smallest, usable components: primarily the monosaccharide glucose, as well as some fructose and galactose. These simple sugars are known as the "end products" of starch digestion. Your body can now distribute them for use as energy or store them.
Where does starch break down?
Most carbohydrate digestion occurs in the small intestine, thanks to a suite of enzymes. Pancreatic amylase is secreted from the pancreas into the small intestine, and like salivary amylase, it breaks starch down to small oligosaccharides (containing 3 to 10 glucose molecules) and maltose.
What is starch broken down into by amylase?
Amylases digest starch into smaller molecules, ultimately yielding maltose, which in turn is cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase.
How is starch broken down into glucose?
When you eat starchy foods, the starches are broken down into sugars, including glucose, maltotriose and maltose, by an enzyme called amylase found in your saliva and small intestine. These compound sugars are further broken down into simple sugars by other enzymes, including maltase, lactase, sucrase and isomaltase.
How is starch digested into glucose?
Starch digestion involves the breakdown by α-amylase to small linear and branched malto-oligosaccharides, which are in turn hydrolyzed to glucose by the mucosal α-glucosidases, maltase-glucoamylase (MGAM) and sucrase-isomaltase (SI).
Why is starch broken down into maltose?
During digestion, starch is partially transformed into maltose by the pancreatic or salivary enzymes called amylases; maltase secreted by the intestine then converts maltose into glucose. The glucose so produced is either utilized by the body or stored in the liver as glycogen (animal starch).
Is starch digested in the stomach?
The starch starts to digest itself in the mouth region and breaks down to form the particles of the maltose sugar. The maltose then reaches the stomach where the salivary amylase activity is prevented due to the gastric juices present in it. Then the maltose reaches the small intestine where it is digested.
How is starch metabolized in the body?
The body digests starch by metabolizing it into glucose, which passes into the bloodstream and circulates the body. Glucose fuels virtually every cell, tissue, and organ in the body. If there is excess glucose, the liver stores it as glycogen. Glucose is essential for brain function.
Where does starch digestion begin quizlet?
Starch digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase.
Where do starches come from?
Starches are most commonly found in grains and breads and are an abundant source of energy for the body. The process of breaking down starches in the body begins in the mouth. Saliva, along with chewing, literally breaks the food down into small pieces that are able to be processed easily by the stomach. Saliva also contains enzymes that begin breaking down starches on a cellular level, converting them into maltose.
What is maltose in food?
Maltose is a carbohydrate that is more easily processed by the body. Once the food is swallowed and passed into the stomach, various acids and enzymes go to work on deconstructing the maltose and converting it into glucose.