What is suprapatellar joint effusion?
What is Suprapatellar Joint Effusion? Suprapatellar joint effusion is painful and usually affects knee joint movement. Knee effusion is also commonly termed as water on the knee.
What is suprapatellar bursa?
suprapatellar bursa. su·pra·pa·tel·lar bur·sa. a large bursa between the inferior part of the femur and the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle. It usually communicates with the cavity of the knee joint and is pathologically distended with blood or synovial fluid in suprapatellar bursitis ("water on the knee").
What is the best treatment for suprapatellar effusion?
Physical Therapy. Physical therapy is an important part of treatment of suprapatellar joint effusion, however, it must be done, as advised by the treating physician. Physical therapy includes the use of treatment modalities to provide relief from knee pain, swelling and aims at improving joint function and mobility.
What does moderate suprapatella swelling mean?
The use of the word “moderate” is, in the opinion of the radiologist the fluid, swelling is not huge, but less than huge does not mean insignificant. Suprapatella means above the patella, closer to your head than your foot swelling.

What is the Suprapatellar?
Suprapatellar bursa is located between the distal femur (leg bone) and the quadriceps tendon. It permits free movement of the quadriceps tendon over the distal femur. It allows for full flexion (bending) and extension (straightening) of the knee. It can be irritated by a direct blow or from repeated stress or motions.
Where is the Suprapatellar region?
Suprapatellar bursa is located between the quadriceps tendon and femur, and it develops before the birth as a separate synovial compartment proximal to the knee joint.
How is Suprapatellar effusion treated?
Treatment of suprapatellar bursitis can include: resting and avoiding activities that could irritate the area, such as kneeling, jumping, or running. taking over-the-counter (OTC) pain medication such as ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) and acetaminophen (Tylenol) to help relieve pain and swelling.
What is Suprapatellar pouch effusion?
Suprapatellar pouch effusion-synovitis is associated with cartilage defects in knee OA patients with high systemic inflammation.
How long does it take to recover from knee effusion?
Recovery. Generally, it takes about 6 weeks to recover from a knee injury. If you need surgery, recovery time can range between 8 weeks to 12 months.
How long does a joint effusion take to heal?
How long does joint effusion take to heal? How long joint effusion takes to heal depends on what caused it. If one of the bones that makes up the joint breaks, you might have joint effusion for weeks or months. If you have joint effusion because of osteoarthritis, you might deal with swollen joints for your lifetime.
Is walking good for fluid on knee?
If you have mild to moderate pain in your knees due to osteoarthritis, walking and other exercise helps mobilize your joint fluid and lubricate the joints. You should walk and do other exercises that move your knee joints.
What happens if knee effusion is left untreated?
Left untreated, fluid on the knee can limit joint movement and cause supporting muscles to weaken and atrophy. See your doctor if you notice knee swelling that isn't improving within a day or two, despite home treatment. Seek immediate medical care if you have an injury involving the knee.
What is the fastest way to get rid of fluid on the knee?
Lifestyle and home remediesRest. Avoid weight-bearing activities as much as possible.Ice and elevation. To control pain and swelling, apply ice to your knee for 15 to 20 minutes every 2 to 4 hours. ... Compression. Wrapping your knee with an elastic bandage can help control the swelling.Pain relievers.
What causes fluid on the knee without injury?
Common causes include arthritis and injury to the ligaments or meniscus, which is cartilage in the knee. A small amount of fluid exists in normal joints. In some cases, however — for example, with rheumatoid arthritis — excess fluid can build up, and the knee becomes puffy and swollen.
Why does fluid build up in the knee?
Injuries that can cause fluid buildup in and around the knee joint include: Torn ligament, particularly the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Cartilage (meniscus) tear. Irritation from overuse.
Is a knee effusion painful?
Knee effusion, commonly known as “water on the knee”, occurs when excess fluid accumulates in and around your knee joint. This can cause a tremendous amount of pain and discomfort.
What causes Suprapatellar bursitis?
This condition is caused due to many reasons, some of which are as follows: A direct hit or injury to the specific bursa. Regular and repeated pressure on the knee due to prolonged kneeling or jumping. Bacteriological infection in your knee.
What is Suprapatellar fat pad impingement?
Fat pad impingement occurs when the infrapatellar fat pad can become impinged (pinched) between the patella (kneecap) and the femoral condyle (large bony prominence at the end of the long bone of the thigh). Impingement causes microtrauma within the fat pad, resulting in pain, swelling and inflammation.
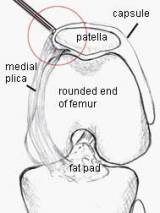
What is the Suprapatellar fat pad?
The suprapatellar fat pad (solid straight arrow) is triangular in shape, located superior to the patella, posterior to the quadriceps tendon and anterior to the suprapatellar recess. The prefemoral fat pad (empty arrow) is anterior to the distal shaft of the femur and posterior to the suprapatellar recess.
What is mild joint effusion in the knee?
A swollen knee occurs when excess fluid collects in or around your knee joint. Health care providers might refer to this condition as an effusion (uh-FU-zhun) in your knee joint. A swollen knee may be the result of trauma, overuse injuries, or an underlying disease or condition.
Where does the suprapatellarbursa originate?
It originates from the anterior surface of the distal aspect of the femur and inserts into the proximal and posterior aspects of the suprapatellarbursa.
What does "above the patella" mean?
Above the patella, denoting especially a bursa.
Is popliteal fat present in suprapatellar regions?
Popliteal fat was totally absent, but infrapatellar fat was very well preserved, and some adipose tissue was also evident in suprapatellarregions (Fig.
How do you know if you have suprapatellar bursitis?
If you’ve developed suprapatellar bursitis, you may experience the following symptoms just above your knee joint: dull, achy pain or tenderness. swelling or redness. warmth. loss or reduction in motion. You may feel these symptoms when you put pressure on the area through activities such as kneeling, jumping, or running.
What tests are used to diagnose suprapatellar bursitis?
Imaging tests that may be used can include: X-ray. magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ultrasound.
How long does it take to recover from suprapatellar bursitis?
Typically, you’ll be able to return to your normal activities in two to six weeks. Be sure to carefully follow your doctor’s guidelines as to when you can resume normal activities.
What is the purpose of a bursa?
A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that helps to provide a cushion and to reduce friction between the bones, tendons, and ligaments of your joints. There are many bursae located throughout your body.
Can a blood test be done on a suprapatellar bursa?
Additionally, your doctor may order blood tests to confirm or rule out other conditions that could be affecting your knee, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. If infection of your suprapatellar bursa is suspected , your doctor may use a needle to remove a small amount of fluid from the bursa for testing.
What happens when the joint recesses are communicated with the suprapatellar bursa?
Communication with the joint recesses usually results in fluid accumulation in the suprapatellar bursa directly abutting the SPFP, where as there is little or no communication with areas surrounding the IPFP.
What order is the inferior patella released?
Under the guide of an arthroscope, it was released from the inferior patella with a blunt needle drill in the following order: inner and outer groove, suprapatellar bursa, bilateral retinaculum, patellar joint, intercondylar fossa, bilateral compartment, and adhes- ions between the femur and the quadriceps.
Knee Effusion – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Knee effusion, commonly known as “water on the knee”, occurs when excess fluid accumulates in and around your knee joint. This can cause a tremendous amount of pain and discomfort. If you suffer from knee effusion, it is important to be well-informed so that you can make educated decisions about your health and treatment.
Knee Effusion Causes
A swollen knee may be the result of trauma, overuse, or even an underlying medical condition. Common causes of knee effusion include:
Knee Effusion Treatments
As with most soft tissue injuries, you should try self-treatment measures before seeing a doctor. These include:
Causes and Treatment of Abnormal Joint Swelling
Carol Eustice is a writer covering arthritis and chronic illness, who herself has been diagnosed with both rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Joint Effusion Symptoms
Regardless of what is causing fluid in your joint, the symptoms are similar, though their severity can vary. Classic symptoms of joint effusion include: 1
Causes
Effusion is a sign of joint inflammation, and can be broadly classified as either infectious (septic) or non-infectious (aseptic). Joint effusion caused by infection is called " septic arthritis ." Aseptic joint effusion can be the result of an injury or arthritis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a joint effusion may involve a physical exam, imaging tests, and a lab evaluation of the fluid in your joint. 7 In addition, the healthcare provider will also review your medical history, current health, and other symptoms.
Treatment
The standard first-line treatment for fluid on a joint includes rest, ice application, immobilization, and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) like Advil (ibuprofen) or Aleve (naproxen). 10
Prevention
While joint effusion can’t always be avoided, there are things you can do to significantly lower your risk: 13
Summary
Excess fluid around a joint—called an effusion—affects larger joints, such as the knee. A joint effusion can occur as a result of injury, infection, or different types of arthritis.
