
Symptoms include:
- Blunted upper incisor teeth known as Hutchinson's teeth
- Deafness from auditory nerve disease
- Frontal bossing (prominence of the brow ridge)
- Hard palate defect
- Inflammation of the cornea known as interstitial keratitis
- Protruding mandible
- Saber shins
- Saddle nose (collapse of the bony part of nose)
- Short maxillae
- Swollen knees
What are syphilis sores and what causes them?
When your sex partner has syphilis, the bacteria that cause the disease create open sores. These sores may appear on the genitals, where you might see them. The sores can also develop inside the mouth, anus, or vagina. These sores tend to be painless, so many people don’t know they have syphilis sores.
What are the signs of syphilis in teeth?
Hutchinson teeth is a sign of congenital syphilis, which occurs when a pregnant mother transmits syphilis to her child in utero or at birth. The condition is noticeable when a child’s permanent teeth come in. The incisors and molars take on a triangular or peglike appearance. They’re widely spaced and may have weakened enamel.
How does syphilis affect the body?
At any stage, syphilis can spread and, among other damage, cause damage to the brain and nervous system (neurosyphilis) and the eye (ocular syphilis). Babies born to women who have syphilis can become infected through the placenta or during birth.
What is oral syphilis?
When syphilis is spread during oral sex, bacteria enter a cut or opening in the lining of the lips or mouth. The resulting infection is called oral syphilis. Lesions from the infection typically appear where the bacteria entered your body.
.jpg)
Can STD affect your teeth?
STDs including HIV and AIDs can result in mouth sores, tooth pain and other oral health issues.
Can a dentist identify syphilis?
The dentist also can play an important role in the control of syphilis by identification of the signs and symptoms of syphilis, patient education, and referral. The incidence of syphilis and the impact of control measures are presented with the emphasis on the past 5 years.
How do you know if you have syphilis in your mouth?
During the first stage of infection, syphilis may appear as sores, known as chancres, on your lips, the tip of your tongue, your gums or at the back of your mouth near your tonsils. They start as small red patches and grow into larger, open sores that can be red, yellow or gray in color.
How does syphilis affect the oral cavity?
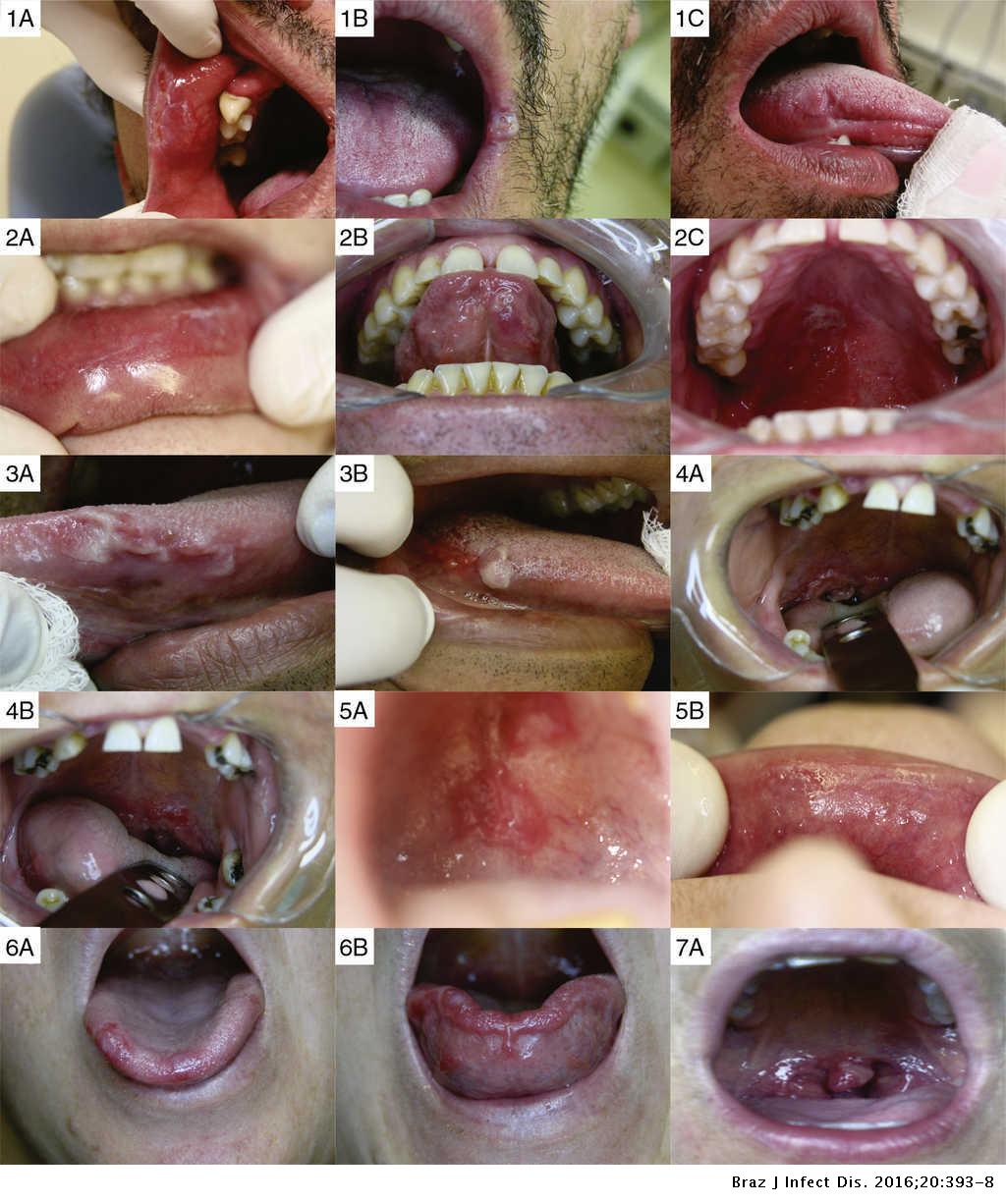
Oral manifestations of secondary syphilis include multiple, scattered lesions on the oral mucosa and oropharynx, though the tongue, lips, and jugal mucosa are the most commonly affected sites. Aphthous ulcers similar to gray plaques or ulcers with irregular, whitish edges that are painful at times are also observed.
Does syphilis affect your gums?
Oral symptoms of syphilis include sores on your lips, tongue, gums or elsewhere in the mouth and throat. They could start as small red patches and develop into larger, open sores if left untreated.
Does syphilis cause tooth pain?
Causes of Hutchinson teeth The cause of Hutchinson teeth is exposure to syphilis (a bacterial infection) before or during birth. Syphilis is considered a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It often begins as a sore on the skin of the genitals, rectum, or mouth.
What are the 4 stages of syphilis?
There are four stages of syphilis (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary).
Is oral syphilis rare?
Syphilis is a rare but increasing disease. Due to changing sexual habits, presentation of oral manifestations may rise. Since syphilis may mimic other oral manifestations, diagnoses can be difficult. Clinicians need to be aware that ambiguous oral manifestations may in fact be caused by oral syphilis.
What are the signs of syphilis in a man?
A person with primary syphilis generally has a sore or sores at the original site of infection. These sores usually occur on or around the genitals, around the anus or in the rectum, or in or around the mouth. These sores are usually (but not always) firm, round, and painless.
How common is syphilis in mouth?
While primary syphilis typically involves genitalia, oral manifestations are observed in approximately 4–12% of patients, reflecting sexual practices [2].
What are signs of STDs in your mouth?
Symptoms of Oral STDsSores in the mouth, which may be painless.Lesions similar to cold sores and fever blisters around the mouth.Sore throat and difficulty swallowing.Redness with white spots resembling strep throat.Swollen tonsils and/or lymph nodes.
How long does it take oral syphilis to show up?
It can take 3 weeks or more for the symptoms of syphilis to appear after you're infected. Sometimes the symptoms can improve or go away completely, but if you have not been treated the infection is still in your body. This means you can still pass it on and you're at risk of getting serious problems later on.
Can dentists detect STDs?
First, your dentist can diagnose HIV/AIDS and STDs during a regular dental checkup. For HIV, the most common visible oral signs include oral warts, fever blisters, hairy leukoplakia, or oral thrush.
What oral health professionals need to know about syphilis?
Oral manifestations of secondary syphilis include multiple, scattered lesions on the oral mucosa and oropharynx, though the tongue, lips, and jugal mucosa are the most commonly affected sites. Aphthous ulcers similar to gray plaques or ulcers with irregular, whitish edges that are painful at times are also observed.
What causes Mulberry molars?
The cause of mulberry teeth stems from congenital syphilis. When pregnant women with syphilis transmit the disease to their child, it can result in mulberry molars. While syphilis is a noticeable STD from a bacterial infection, notes the Mayo Clinic, congenital syphilis usually doesn't show signs with newborns.
Why is it important to alert your dentist about syphilis?
Dentists are an important factor in controlling the spread of syphilis because they can diagnose it, they are in a position to act educationally and refer patients for further treatment.
What is syphilis caused by?
Syphilis (lat. Lues) is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum of the genus Spirochetes.
How long does it take for syphilis to show symptoms?
About 25 percent of people with untreated primary stage will develop symptoms of secondary stage within 4 to 6 weeks of the appearance of the primary lesion.
How is congenital syphilis transmitted?
Congenital syphilis of the mouth (lat. Lues connata tarda) is transmitted from untreated infected mother to a child in the womb. In children with congenital syphilis changes occur on the head and in mouth and can manifest as: Hutchinson Triassic (barrel-shaped incisors and first molars, keratitis and inflammation of the middle ear), saddle nose and perioral irregular circular cracks in the transition from skin and the lining of the lips. In survived children there are also certain signs of congenital form visible after a few years.
What is the color of syphilis?
The lesions have red, purple or brown base and irregular, raised edges. Primary syphilis is usually a result of orogenital or oroanal contact with infectious lesions. Transmission of infection by kissing is possible, but very rare. Oral signs in children may indicate sexual abuse.
Where are syphilitic gummas most often located?
Luetic gummas are most often located on the hard palate or tongue , and very rarely can occur on the soft palate, lower jaw and parotid gland.
How long does it take for latent syphilis to become contagious?
In the early stage of latent syphilis (when there are no visual manifestations of the disease), usually within 12 months after the secondary stage, patients are contagious. In the late stage of latent syphilis risk of infection decreases.
What are the symptoms of syphilis?
Syphilis can cause a number of problems with your nervous system, including: 1 Headache 2 Stroke 3 Meningitis 4 Hearing loss 5 Visual problems, including blindness 6 Dementia 7 Loss of pain and temperature sensations 8 Sexual dysfunction in men (impotence) 9 Bladder incontinence
What happens if you don't get syphilis?
About 15% to 30% of people infected with syphilis who don't get treatment will develop complications known as late (tertiary) syphilis. In the late stage, the disease may damage your brain, nerves, eyes, heart, blood vessels, liver, bones and joints. These problems may occur many years after the original, untreated infection.
What is the first sign of syphilis?
Primary syphilis. The first sign of syphilis is a small sore, called a chancre (SHANG-kur). The sore appears at the spot where the bacteria entered your body. While most people infected with syphilis develop only one chancre, some people develop several of them.
How does syphilis spread?
The disease starts as a painless sore — typically on your genitals, rectum or mouth. Syphilis spreads from person to person via skin or mucous membrane contact with these sores.
What is the cause of syphilis?
Causes. The cause of syphilis is a bacterium called Treponema pallidum. The most common route of transmission is through contact with an infected person's sore during sexual activity. The bacteria enter your body through minor cuts or abrasions in your skin or mucous membranes.
How long does syphilis last?
The latent stage can last for years. Signs and symptoms may never return, or the disease may progress to the third (tertiary) stage.
Why is it important to notify your partner of syphilis?
Official, confidential partner notification can help limit the spread of syphilis. The practice also steers those at risk toward counseling and the right treatment. And since you can contract syphilis more than once, partner notification reduces your risk of getting reinfected.
What does it mean when your teeth are a Hutchinson?
See Pictures, Learn Causes, Treatment, and More. Hutchinson teeth is a sign of congenital syphilis , which occurs when a pregnant mother transmits syphilis to her child in utero or at birth. The condition is noticeable when a child’s permanent teeth come in. The incisors and molars take on a triangular or peglike appearance.
What does it mean when a child has a Hutchinson tooth?
Hutchinson teeth is a sign of congenital syphilis, which occurs when a pregnant mother transmits syphilis to her child in utero or at birth. The condition is noticeable when a child’s permanent teeth come in. The incisors and molars take on a triangular or peglike appearance. They’re widely spaced and may have weakened enamel.
Why do I have a hutchinson tooth?
Causes of Hutchinson teeth. The cause of Hutchinson teeth is exposure to syphilis (a bacterial infection) before or during birth. Syphilis is considered a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It often begins as a sore on the skin of the genitals, rectum, or mouth.
When do babies develop Hutchinson teeth?
Babies have the greatest risk for developing Hutchinson teeth and other symptoms if the mother has had syphilis for less than two years. Specifically, the risk increases if the infection hasn’t been treated before week 18 in pregnancy.
How to treat Hutchinson's teeth?
To treat Hutchinson teeth, first visit your pediatrician for a diagnosis and medication, if needed. A blood test or sometimes lumbar puncture can confirm syphilis. Treatment options include a shot of penicillin. If the disease has been present longer than a year, your child may need additional doses.
What is a dental filling?
Fillings. Dental fillings are a common way to fill cavities or holes caused by weakened enamel and other issues. They can be made of composite material (tooth color), dental amalgam (silver), or gold.
What is a crown in dentistry?
Crowns. These are caps that dentists place on teeth to make them more normal in size, shape, and overall function.
What is syphilis?
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause serious health problems if it is not treated. Syphilis is divided into stages (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). There are different signs and symptoms associated with each stage.
How is syphilis spread?
Syphilis can spread from an infected mother to her unborn baby.
How will I or my doctor know if I have syphilis?
Most of the time, a blood test is used to test for syphilis. Some health care providers will diagnose syphilis by testing fluid from a syphilis sore.
How long does a syphilis sore last?
Sores are usually (but not always) firm, round, and painless. Because the sore is painless, it can easily go unnoticed. The sore usually lasts 3 to 6 weeks and heals regardless of whether or not you receive treatment. Even after the sore goes away, you must still receive treatment. This will stop your infection from moving to the secondary stage.
How to prevent syphilis?
If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting syphilis: 1 Being in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested for syphilis and does not have syphilis; 2 Using latex condoms the right way every time you have sex. Condoms prevent transmission of syphilis by preventing contact with a sore. Sometimes sores occur in areas not covered by a condom. Contact with these sores can still transmit syphilis.
What are the symptoms of secondary syphilis?
Symptoms of secondary syphilis include skin rash, swollen lymph nodes, and fever. The signs and symptoms of primary and secondary syphilis can be mild, and they might not be noticed. During the latent stage, there are no signs or symptoms. Tertiary syphilis is associated with severe medical problems.
What is tertiary syphilis?
Tertiary syphilis is associated with severe medical problems. A doctor can usually diagnose tertiary syphilis with the help of multiple tests. It can affect the heart, brain, and other organs of the body.
What is syphilis?
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Syphilis can cause serious health sequelae if not adequately treated.
How do people get syphilis?
Syphilis is transmitted from person to person by direct contact with a syphilitic sore, known as a chancre. Chancres can occur on or around the external genitals, in the vagina, around the anus , or in the rectum, or in or around the mouth. Transmission of syphilis can occur during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. In addition, pregnant women with syphilis can transmit the infection to their unborn child.
How quickly do symptoms appear after infection?
The average time between acquisition of syphilis and the start of the first symptom is 21 days, but can range from 10 to 90 days.
How does syphilis affect a pregnant woman and her baby?
When a pregnant woman has syphilis, the infection can be transmitted to her unborn baby. All pregnant women should be tested for syphilis at the first prenatal visit. Some women need to be tested again during the third trimester (28 weeks gestation) and at delivery. This includes women who live in areas of high syphilis morbidity, are previously untested, had a positive screening test in the first trimester, or are at higher risk for syphilis (i.e., multiple sex partners, drug use, transactional sex, late entry into prenatal care or no prenatal care, meth or heroin use, incarceration themselves or of sex partners, unstable housing, or homelessness). 3 There should also be a discussion about ongoing risk behavior and treatment of sex partners to assess the risk for reinfection. Any woman who delivers a stillborn infant after 20 week’s gestation should also be tested for syphilis.
What is the link between syphilis and HIV?
In the United States, approximately half of men who have sex with men (MSM) with primary and secondary (P&S) syphilis were also living with HIV. 2 In addition, MSM who are HIV-negative and diagnosed with P&S syphilis are more likely to be infected with HIV in the future. 6 Genital sores caused by syphilis make it easier to transmit and acquire HIV infection sexually. There is an estimated 2- to 5-fold increased risk of acquiring HIV if exposed to that infection when syphilis is present. 7 Furthermore, syphilis and certain other STDs might be indicators of ongoing behaviors and exposures that place a person at greater risk for acquiring HIV.
What is the treatment for syphilis?
For detailed treatment recommendations, please refer to the 2021 CDC STI Treatment Guidelines. The recommended treatment for adults and adolescents with primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis is Benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units administered intramuscularly in a single dose. The recommended treatment for adults and adolescents with late latent syphilis or latent syphilis of unknown duration is Benzathine penicillin G 7.2 million units total, administered as 3 doses of 2.4 million units administered intramuscularly each at weekly intervals. The recommended treatment for neurosyphilis, ocular syphilis, or otosyphilis is Aqueous crystalline penicillin G 18-24 million units per day, administered as 3-4 million units intravenously every 4 hours or continuous infusion, for 10-14 days. Treatment will prevent disease progression, but it might not repair damage already done.
Will syphilis recur?
After appropriate treatment, clinical and serologic response to treatment will be followed. However, even following successful treatment, reinfection can occur. Persons with signs or symptoms that persist or recur or who have a sustained fourfold increase in nontreponemal test titer likely were reinfected or experienced treatment failure. For further details on the management of persistent syphilis or reinfection, refer to the 2021 STI Treatment Guidelines
How long does it take for syphilis to start?
When it begins: The primary stage of syphilis begins 10 to 90 days after you become infected. Most people develop symptoms about 3 weeks after having sex with someone who has syphilis. What you may notice: During this stage, you may have: One or more open sores called chancres, which often feel firm and painless.
What is the name of the sores that feel firm and painless?
One or more open sores called chancres, which often feel firm and painless
How do you know if you have neurosyphilis?
Neurosyphilis requires special treatment to cure it. You may need tests like an eye exam or other tests to tell if you have neurosyphilis. Syphilis can also affect your eyes at any stage. Signs that this has happened include having red, irritated eyes and problems seeing clearly. Some people go blind.
How long does it take for a sore to heal from syphilis?
These open sores usually heal and go away within 3 to 6 weeks. While the sores heal on their own, you still need treatment. Without treatment, syphilis can move to the next stage.
When does the latent stage of syphilis begin?
When it begins: The latent stage of syphilis begins after the rash and other signs and symptoms clear.
How do you know if you have a sore?
Some people enter this stage immediately after (or as) their sores clear. What you may notice: As the disease spreads throughout your body, many signs and symptoms can develop. The most common are: Rash (can appear on the skin in many ways and begin before the sores in first stage heal)
What is the disease that attacks the heart and blood vessels?
A condition called cardiovascular syphilis, which attacks your heart and blood vessels. A condition called neurosyphilis, which attacks your nerves, spinal cord, and brain. In this stage, syphilis becomes so destructive that it can cause death. Even in this stage, treatment can stop the syphilis from getting worse.
What causes syphilis?
This disease is caused by bacteria . To survive, these bacteria need to live on or inside the human body. They cannot survive on a toilet seat, towel, or bedding.
How does syphilis spread?
Syphilis can spread from one person to another through: Oral, anal, or vaginal sex. Genital-to-genital contact. An open wound in your skin. Kissing (if syphilis has caused mouth sores) A woman who is pregnant can give syphilis to her unborn baby: Syphilis can spread from mother to baby before (or during) birth.
Where do you see syphilis sores?
These sores may appear on the genitals, where you might see them. The sores can also develop inside the mouth, anus, or vagina. These sores tend to be painless, so many people don’t know they have syphilis sores. When you touch these sores during sex, the bacteria spread from your partner to you.
Can you get tested for syphilis while pregnant?
Most pregnant women in the United States get tested for syphilis during a prenatal checkup. When the disease is caught early, syphilis can be treated before it affects the baby. To find out how doctors find, treat, and cure syphilis, go to: Syphilis: Diagnosis and treatment. Image.
Does ART help with syphilis?
ART helps to slow down HIV. ART cannot reduce your risk of developing other sexually transmitted diseases, such as syphilis.
Can you get syphilis from a toilet seat?
You cannot get syphilis from a toilet seat, towel, or bedding.
Can anyone get syphilis?
Anyone can get syphilis. This disease spreads mainly through sexual contact, so you have a greater risk of getting syphilis if you are sexually active and:
How much more likely is syphilis to get HIV?
Increased HIV risk. If you have syphilis, you’re up to 5 times more likely to get HIV. That’s because syphilis sores can be open, making it easy for HIV to get into your body while you’re having sex.
What are the symptoms of syphilis?
If it’s not treated, syphilis can cause problems with your nervous system. Symptoms include: 1 Severe headache 2 Stroke 3 Loss of muscle coordination 4 Paralysis or inability to move part of your body 5 Numbness 6 A mental disorder called dementia 7 Blindness or changes to vision
What happens if you don't get syphilis?
If you have syphilis and don’t get treated, the infection can lead to a number of serious -- even life-threatening -- conditions. They develop over many years and may include:
Can you pass syphilis to a baby?
If you have syphilis and are pregnant, you can pass it on to your unborn child. You might also have a higher risk of miscarriage, stillbirth (your baby being born dead), or your newborn dying within a few days. Untreated babies who are born with syphilis can also have problems with their bones, blood, liver, spleen, brain, and skin.
Do gums go away?
Gummas. These are small bumps of dead tissue and fiber. They can form throughout your body if you don’t get treated. You can get them in your internal organs and on bones or skin in the late stages. They typically go away with treatment.
Overview
- Syphilis is a bacterial infection usually spread by sexual contact. The disease starts as a painless sore — typically on the genitals, rectum or mouth. Syphilis spreads from person to person via skin or mucous membrane contact with these sores. After the initial infection, the syphilis bacteria can remain inactive in the body for decades before bec...
Symptoms
- Syphilis develops in stages, and symptoms vary with each stage. But the stages may overlap, and symptoms don't always occur in the same order. You may be infected with syphilis without noticing any symptoms for years.
Causes
- The cause of syphilis is a bacterium called Treponema pallidum. The most common way syphilis is spread is through contact with an infected person's sore during sexual activity. The bacteria enter the body through minor cuts or abrasions in the skin or mucous membranes. Syphilis is contagious during its primary and secondary stages, and sometimes in the early latent period. L…
Risk Factors
- You face an increased risk of acquiring syphilis if you: 1. Engage in unprotected sex 2. Have sex with multiple partners 3. Are a man who has sex with men 4. Are infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS
Complications
- Without treatment, syphilis can lead to damage throughout your body. Syphilis also increases the risk of HIVinfection and can cause problems during pregnancy. Treatment can help prevent future damage but can't repair or reverse damage that's already occurred.
Prevention
- There is no vaccine for syphilis. To help prevent the spread of syphilis, follow these suggestions: 1. Abstain or be monogamous.The only certain way to avoid syphilis is to avoid (abstain from) having sex. The next-best option is to have mutually monogamous sex in which both partners have sex only with each other and neither partner is infected. 2. Use a latex condom.Condoms c…